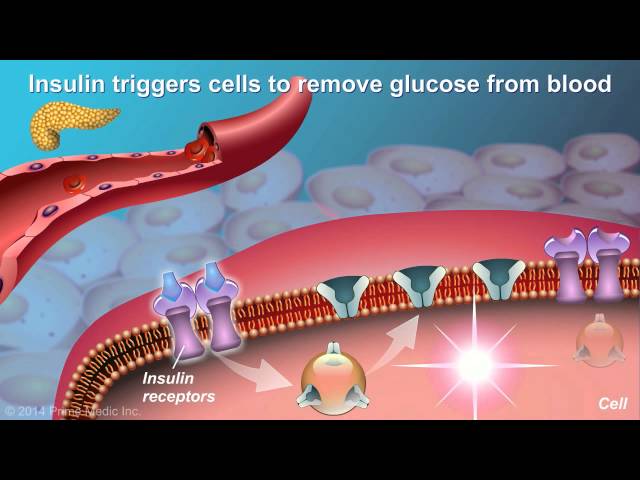
Diabetes type 2 is a chronic condition that affects the way your body uses sugar. With diabetes type 2, your body doesn’t make enough insulin or doesn’t use insulin well. Glucose then builds up in your blood instead of being used for energy. Over time, high blood glucose levels can damage your heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves.
Diabetes type 2 is the most common type of diabetes. It usually develops in adults over the age of 35 who are overweight or obese. However, it can also develop in younger people and people of all weights.
There is no cure for diabetes type 2, but it can be managed with medication, diet, and exercise. Managing diabetes type 2 can help prevent serious health problems.
What is Diabetes Type 2?
Diabetes type 2 is a chronic condition that affects the way your body uses sugar. There are three key aspects of diabetes type 2.
- Insulin resistance: This is when your body doesn’t respond well to insulin, a hormone that helps glucose enter your cells for energy.
- Glucose intolerance: This is when your blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be diagnosed with diabetes.
- Type 2 diabetes: This is when your blood sugar levels are consistently too high.
Diabetes type 2 is a serious condition, but it can be managed with medication, diet, and exercise. Managing diabetes type 2 can help prevent serious health problems, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness.
Insulin resistance
Insulin resistance is a key factor in the development of type 2 diabetes. When your body is insulin resistant, it doesn’t respond well to the insulin that is produced by your pancreas. This means that glucose cannot enter your cells as easily, and your blood sugar levels rise.
Over time, high blood sugar levels can damage your blood vessels and organs. This can lead to serious health problems, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness.
There are a number of things that can contribute to insulin resistance, including obesity, physical inactivity, and a diet high in processed foods and sugary drinks.
If you are overweight or obese, losing even a small amount of weight can help to improve your insulin sensitivity. Regular physical activity can also help to improve insulin sensitivity. Eating a healthy diet that is low in processed foods and sugary drinks can also help to improve insulin sensitivity.
If you have been diagnosed with insulin resistance, it is important to work with your doctor to develop a treatment plan. Treatment may include lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, as well as medication.
Glucose intolerance
Glucose intolerance is a condition in which your blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be diagnosed with diabetes. This can be a precursor to type 2 diabetes, and it is important to be aware of the risks and take steps to prevent its progression.
There are a number of causes of glucose intolerance, including obesity, physical inactivity, and a diet high in processed foods and sugary drinks. When you have glucose intolerance, your body does not respond well to insulin, a hormone that helps glucose enter your cells for energy. This can lead to high blood sugar levels.
Over time, high blood sugar levels can damage your blood vessels and organs. This can lead to serious health problems, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness.
If you have been diagnosed with glucose intolerance, it is important to work with your doctor to develop a treatment plan. Treatment may include lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, as well as medication.
Type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way your body uses sugar. When you have type 2 diabetes, your body does not make enough insulin or does not use insulin well. Glucose then builds up in your blood instead of being used for energy. Over time, high blood glucose levels can damage your heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves.
Type 2 diabetes is the most common type of diabetes. It usually develops in adults over the age of 35 who are overweight or obese. However, it can also develop in younger people and people of all weights.
There is no cure for type 2 diabetes, but it can be managed with medication, diet, and exercise. Managing type 2 diabetes can help prevent serious health problems.
The connection between “Type 2 diabetes: This is when your blood sugar levels are consistently too high.” and “what is diabetes type 2”
Type 2 diabetes is characterized by consistently high blood sugar levels. This is a key component of the definition of diabetes type 2. Without consistently high blood sugar levels, a person would not be diagnosed with diabetes type 2.
High blood sugar levels can cause a number of health problems, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness. Therefore, it is important to manage blood sugar levels to prevent these complications.
Conclusion
Type 2 diabetes is a serious condition that can lead to a number of health problems. However, it can be managed with medication, diet, and exercise. Managing blood sugar levels is key to preventing the complications of diabetes type 2.
FAQs on Diabetes Type 2
Diabetes type 2 is a serious condition, but it can be managed with medication, diet, and exercise. Here are some frequently asked questions about diabetes type 2:
Question 1: What is diabetes type 2?
Diabetes type 2 is a chronic condition that affects the way your body uses sugar. When you have diabetes type 2, your body does not make enough insulin or does not use insulin well. Glucose then builds up in your blood instead of being used for energy. Over time, high blood glucose levels can damage your heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves.
Question 2: What are the symptoms of diabetes type 2?
The symptoms of diabetes type 2 can include: increased thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, increased hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, slow-healing sores, and frequent infections.
Question 3: What causes diabetes type 2?
The exact cause of diabetes type 2 is unknown, but it is thought to be caused by a combination of factors, including genetics, obesity, and physical inactivity.
Question 4: How is diabetes type 2 diagnosed?
Diabetes type 2 is diagnosed with a blood test that measures your blood sugar levels.
Question 5: How is diabetes type 2 treated?
Diabetes type 2 is treated with medication, diet, and exercise. Medication can help to lower your blood sugar levels, and diet and exercise can help you to lose weight and improve your insulin sensitivity.
Question 6: Can diabetes type 2 be prevented?
There is no sure way to prevent diabetes type 2, but you can reduce your risk by maintaining a healthy weight, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise.
Summary
Diabetes type 2 is a serious condition, but it can be managed with medication, diet, and exercise. If you have diabetes type 2, it is important to work with your doctor to develop a treatment plan that is right for you.
Next Article Section:
[Insert link or description of the next article section]
Tips on Managing Diabetes Type 2
Diabetes type 2 is a serious condition, but it can be managed with medication, diet, and exercise. Here are some tips to help you manage your diabetes type 2:
Tip 1: Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly.
This will help you to track your progress and make adjustments to your treatment plan as needed.Tip 2: Take your medication as prescribed.
Medication can help to lower your blood sugar levels and improve your insulin sensitivity.Tip 3: Eat a healthy diet.
A healthy diet for diabetes type 2 includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It is also important to limit your intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and saturated and trans fats.Tip 4: Get regular exercise.
Regular exercise can help to lower your blood sugar levels and improve your insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.Tip 5: Lose weight if you are overweight or obese.
Losing weight can help to improve your insulin sensitivity and lower your blood sugar levels.Tip 6: Quit smoking.
Smoking can damage your blood vessels and make it harder to control your blood sugar levels.Tip 7: Manage stress.
Stress can raise your blood sugar levels. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, yoga, or meditation.Tip 8: Get regular checkups.
Regular checkups will help you to monitor your progress and make adjustments to your treatment plan as needed.SummaryManaging diabetes type 2 can be challenging, but it is important to remember that you are not alone. There are many resources available to help you, including your doctor, diabetes educator, and support groups. By following these tips, you can take control of your diabetes type 2 and live a healthy life.
Next Article Section:
[Insert link or description of the next article section]
Conclusion
Diabetes type 2 is a serious chronic condition that affects the body’s ability to use sugar for energy. It is characterized by consistently high blood sugar levels, which can lead to a number of health problems, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness.
There is no cure for diabetes type 2, but it can be managed with medication, diet, and exercise. Managing blood sugar levels is key to preventing the complications of diabetes type 2.
If you have diabetes type 2, it is important to work with your doctor to develop a treatment plan that is right for you. By following your treatment plan and making healthy lifestyle choices, you can manage your diabetes type 2 and live a long and healthy life.
Youtube Video: