Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels. Over time, high blood sugar levels can damage various organs and tissues, leading to a range of complications.
Some of the most common type 2 diabetes complications include:
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Kidney disease
- Eye damage, including blindness
- Nerve damage, including numbness and pain
- Foot ulcers and amputations
These complications can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and can even be life-threatening. However, they can often be prevented or delayed with proper diabetes management, including:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Eating a healthy diet
- Getting regular exercise
- Taking medication as prescribed
- Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly
If you have type 2 diabetes, it is essential to work closely with your doctor to manage your condition and reduce your risk of developing complications.
Type 2 Diabetes Complications
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels. Over time, high blood sugar levels can damage various organs and tissues, leading to a range of complications.
- Cardiovascular disease: Type 2 diabetes increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular problems.
- Kidney disease: High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys, leading to kidney failure.
- Eye damage: Diabetes can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to blindness.
- Nerve damage: High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves, leading to numbness, pain, and other problems.
- Foot ulcers: Diabetes can cause foot ulcers, which are difficult to heal and can lead to amputation.
- Amputations: In severe cases, diabetes can lead to amputation of the toes, feet, or legs.
These complications can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and can even be life-threatening. However, they can often be prevented or delayed with proper diabetes management, including maintaining a healthy weight, eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, taking medication as prescribed, and monitoring blood sugar levels regularly.
Cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in people with type 2 diabetes. High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels and heart, leading to a buildup of plaque in the arteries. This plaque can narrow the arteries and make it difficult for blood to flow to the heart and brain, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke.
In addition, diabetes can damage the nerves that control the heart and blood vessels, leading to high blood pressure and other heart problems. People with diabetes are also more likely to have high cholesterol and obesity, which are other risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Preventing and managing cardiovascular disease is essential for people with type 2 diabetes. This includes controlling blood sugar levels, maintaining a healthy weight, eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and taking medication as prescribed. By following these steps, people with diabetes can reduce their risk of developing cardiovascular complications and improve their overall health.
Kidney disease
Kidney disease is a common complication of type 2 diabetes. High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to scarring and a decline in kidney function. Over time, this damage can lead to kidney failure, which is a life-threatening condition.
- Glomerular disease: This is the most common type of kidney damage in people with diabetes. It occurs when the small blood vessels in the kidneys (glomeruli) are damaged, leading to protein and blood leaking into the urine. Glomerular disease can progress to kidney failure if it is not treated.
- Tubular disease: This type of kidney damage occurs when the tubules in the kidneys are damaged. The tubules are responsible for reabsorbing water and nutrients from the urine. Tubular damage can lead to a loss of these nutrients in the urine, as well as an inability to concentrate the urine, leading to frequent urination.
- Interstitial disease: This type of kidney damage occurs when the interstitial tissue in the kidneys is damaged. The interstitial tissue is responsible for supporting the blood vessels and tubules in the kidneys. Interstitial damage can lead to scarring and a decline in kidney function.
- Nephropathy: This is a general term for kidney damage caused by diabetes. Nephropathy can range from mild to severe, and it can eventually lead to kidney failure. People with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing nephropathy if they have poor blood sugar control, high blood pressure, or other risk factors for kidney disease.
Kidney disease is a serious complication of type 2 diabetes, but it can be prevented or delayed with proper diabetes management. This includes controlling blood sugar levels, maintaining a healthy weight, eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and taking medication as prescribed. By following these steps, people with diabetes can reduce their risk of developing kidney disease and improve their overall health.
Eye damage
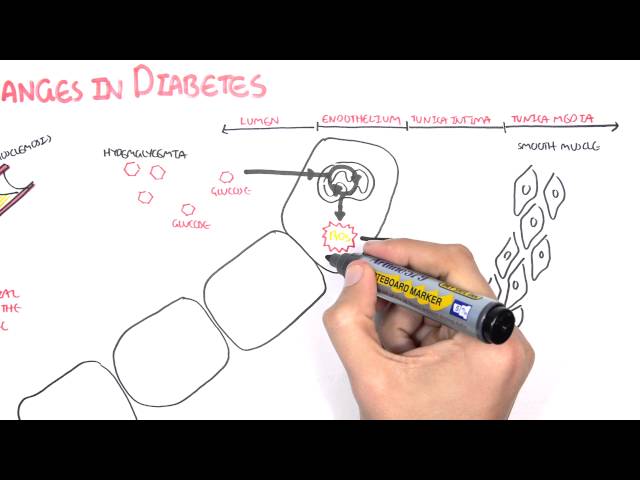
Eye damage is a serious complication of type 2 diabetes. High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to a condition called diabetic retinopathy. Diabetic retinopathy can cause a range of problems, including blurred vision, floaters, and bleeding in the eye. In severe cases, diabetic retinopathy can lead to blindness.
Diabetic retinopathy is one of the most common complications of type 2 diabetes, affecting up to 80% of people with the condition. It is also the leading cause of blindness in people of working age.
There are a number of risk factors for diabetic retinopathy, including:
- Poor blood sugar control
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Obesity
- Smoking
Diabetic retinopathy can be prevented or delayed with proper diabetes management. This includes controlling blood sugar levels, maintaining a healthy weight, eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and taking medication as prescribed.
Regular eye exams are also important for people with diabetes. Eye exams can help to detect diabetic retinopathy early, when it is most treatable. Treatment options for diabetic retinopathy include laser therapy, eye injections, and surgery.
By following these steps, people with diabetes can reduce their risk of developing eye damage and improve their overall health.
Nerve damage
Nerve damage is a common complication of type 2 diabetes. High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves throughout the body, leading to a condition called diabetic neuropathy. Diabetic neuropathy can cause a range of problems, including numbness, pain, tingling, and weakness in the hands, feet, and legs.
Diabetic neuropathy is a serious condition that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. It can make it difficult to walk, work, and perform everyday activities. In severe cases, diabetic neuropathy can lead to amputation.
There are a number of risk factors for diabetic neuropathy, including:
- Poor blood sugar control
- Long duration of diabetes
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Obesity
- Smoking
Diabetic neuropathy can be prevented or delayed with proper diabetes management. This includes controlling blood sugar levels, maintaining a healthy weight, eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and taking medication as prescribed.
There are a number of treatments available for diabetic neuropathy, including medication, physical therapy, and surgery. However, there is no cure for diabetic neuropathy, so it is important to prevent or delay the condition with proper diabetes management.
Foot ulcers
Foot ulcers are a serious complication of diabetes. They are open sores that can develop on the feet of people with diabetes due to poor circulation and nerve damage. Foot ulcers are difficult to heal and can easily become infected. In severe cases, they can lead to amputation of the toe, foot, or leg.
Foot ulcers are a major cause of hospitalization and amputation in people with diabetes. They can also lead to other serious complications, such as sepsis and death.
Preventing foot ulcers is essential for people with diabetes. This includes taking good care of your feet, checking your feet daily for any cuts or sores, and wearing proper footwear. If you do develop a foot ulcer, it is important to see your doctor right away to get treatment.
By following these steps, people with diabetes can reduce their risk of developing foot ulcers and other serious complications.
Amputations
Amputation is a serious complication of type 2 diabetes. It is the most severe form of foot ulcer, and it can lead to significant disability and even death. Amputations are often performed to prevent the spread of infection or to relieve pain.
There are a number of factors that can contribute to the development of amputations in people with diabetes. These include:
- Poor blood sugar control
- Peripheral artery disease
- Neuropathy
- Foot ulcers
Amputations are a devastating complication of diabetes, but they can be prevented. By managing your blood sugar levels, taking care of your feet, and following your doctor’s instructions, you can reduce your risk of developing foot ulcers and amputations.
If you have diabetes, it is important to be aware of the risk of amputations. Talk to your doctor about what you can do to reduce your risk.
FAQs on Type 2 Diabetes Complications
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that can lead to a variety of serious complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, eye damage, nerve damage, foot ulcers, and amputations. These complications can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and can even be life-threatening.
Question 1: What are the most common complications of type 2 diabetes?
Answer: The most common complications of type 2 diabetes include heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, eye damage, nerve damage, foot ulcers, and amputations.
Question 2: How can I prevent the complications of type 2 diabetes?
Answer: The best way to prevent the complications of type 2 diabetes is to manage your blood sugar levels, maintain a healthy weight, eat a healthy diet, get regular exercise, and take medication as prescribed by your doctor.
Question 3: What are the symptoms of diabetic retinopathy?
Answer: The symptoms of diabetic retinopathy can include blurred vision, floaters, and bleeding in the eye. In severe cases, diabetic retinopathy can lead to blindness.
Question 4: What are the symptoms of diabetic neuropathy?
Answer: The symptoms of diabetic neuropathy can include numbness, pain, tingling, and weakness in the hands, feet, and legs.
Question 5: What are the symptoms of a foot ulcer?
Answer: The symptoms of a foot ulcer can include pain, redness, swelling, and drainage. Foot ulcers can be difficult to heal and can easily become infected.
Question 6: What is the best way to treat a foot ulcer?
Answer: The best way to treat a foot ulcer is to see your doctor right away. Your doctor will clean the ulcer and prescribe antibiotics to prevent infection. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the ulcer.
Summary of key takeaways or final thought:
The complications of type 2 diabetes are serious, but they can be prevented or delayed with proper diabetes management. If you have type 2 diabetes, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions and make healthy lifestyle choices to reduce your risk of developing complications.
Transition to the next article section:
If you have any questions or concerns about the complications of type 2 diabetes, please talk to your doctor.
Tips to Prevent Type 2 Diabetes Complications
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that can lead to a variety of serious complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, eye damage, nerve damage, foot ulcers, and amputations. These complications can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and can even be life-threatening.
The good news is that many of these complications can be prevented or delayed with proper diabetes management. Here are five tips to help you prevent type 2 diabetes complications:
Tip 1: Control your blood sugar levels
High blood sugar levels are the main cause of diabetes complications. By controlling your blood sugar levels, you can reduce your risk of developing these complications.
Tip 2: Maintain a healthy weight
Obesity is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes and its complications. Maintaining a healthy weight can help you reduce your risk of developing diabetes and its complications.
Tip 3: Eat a healthy diet
Eating a healthy diet is essential for managing diabetes and preventing complications. A healthy diet for people with diabetes includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It also limits saturated fat, cholesterol, and sodium.
Tip 4: Get regular exercise
Regular exercise is another important part of managing diabetes and preventing complications. Exercise helps to lower blood sugar levels and improve circulation.
Tip 5: Take your medication as prescribed
If you are taking medication for diabetes, it is important to take it as prescribed by your doctor. Medication can help to lower blood sugar levels and reduce your risk of developing complications.
Summary of key takeaways or benefits:
By following these tips, you can help to prevent or delay the complications of type 2 diabetes and improve your overall health.
Transition to the article’s conclusion:
If you have any questions or concerns about the complications of type 2 diabetes, please talk to your doctor.
Conclusion
Type 2 diabetes is a serious chronic condition that can lead to a variety of devastating complications. These complications can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and can even be life-threatening. However, many of these complications can be prevented or delayed with proper diabetes management.
If you have type 2 diabetes, it is important to work closely with your doctor to manage your condition and reduce your risk of developing complications. This includes controlling your blood sugar levels, maintaining a healthy weight, eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and taking medication as prescribed. By following these steps, you can help to improve your overall health and well-being.
Youtube Video: