Diabetes encompasses a group of metabolic disorders characterized by elevated blood sugar levels. The term “tipos de diabetes” in Spanish translates to “types of diabetes” and refers to the different categories of this condition. The two primary types of diabetes are type 1 and type 2, with distinct causes and treatment approaches.
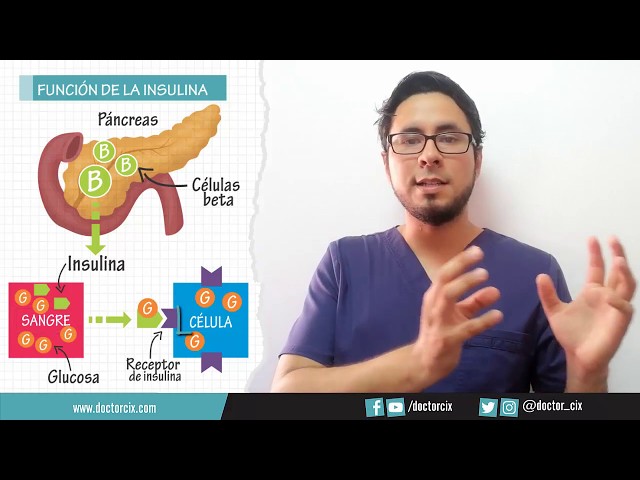
Type 1 diabetes, previously known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes, results from the body’s inability to produce insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. This type typically develops in children and young adults, and individuals with type 1 diabetes require lifelong insulin therapy to manage their condition.
Type 2 diabetes, formerly referred to as adult-onset or non-insulin-dependent diabetes, arises when the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough insulin. This type is more common in adults, particularly those who are overweight or obese, and can often be managed through lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise. However, some individuals with type 2 diabetes may eventually require medication or insulin therapy.
Understanding the different types of diabetes is crucial for proper diagnosis, treatment, and management of this condition. Early detection and appropriate interventions can help prevent or delay the onset of complications associated with diabetes, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and blindness.
Tipos de Diabetes
Understanding the different types of diabetes is crucial for proper diagnosis, treatment, and management of this condition. Here are seven key aspects to consider:
- Type 1: Insulin-dependent, typically develops in children and young adults.
- Type 2: More common in adults, often linked to obesity or overweight.
- Gestational: Develops during pregnancy, usually resolves after childbirth.
- Monogenic: Rare form caused by a single gene mutation.
- Secondary: Caused by another underlying medical condition.
- Prediabetes: Blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not high enough for a diabetes diagnosis.
- Management: Varies depending on the type of diabetes, may include lifestyle changes, medication, or insulin therapy.
These key aspects highlight the diverse nature of diabetes, its causes, and the range of approaches required for effective management. Early detection, proper diagnosis, and appropriate treatment can help prevent or delay the onset of complications associated with diabetes, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and blindness.
Type 1
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. Without insulin, the body cannot properly absorb glucose from the blood, leading to dangerously high blood sugar levels.
Type 1 diabetes is one of the most common types of diabetes among children and young adults, although it can develop at any age. It is considered an insulin-dependent type of diabetes because individuals with Type 1 diabetes require lifelong insulin therapy to manage their blood sugar levels.
Understanding the connection between Type 1 diabetes and the broader category of “tipos de diabetes” is crucial for several reasons. First, it helps healthcare providers make an accurate diagnosis and determine the appropriate treatment plan. Secondly, it enables individuals with Type 1 diabetes to connect with others who have similar experiences and challenges.
Furthermore, recognizing the specific characteristics of Type 1 diabetes is essential for raising awareness and promoting early detection. Early diagnosis and management of Type 1 diabetes can help prevent or delay the onset of serious complications, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and blindness.
In conclusion, Type 1 diabetes is a distinct type of diabetes that requires specialized treatment and management. Understanding its connection to the broader category of “tipos de diabetes” is crucial for accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and improved outcomes for individuals with this condition.
Type 2
Type 2 diabetes is the most common type of diabetes, accounting for over 90% of all cases. It is characterized by insulin resistance, a condition in which the body does not respond properly to insulin, and impaired insulin secretion, where the pancreas does not produce enough insulin.
Obesity and overweight are major risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes. Excess weight can lead to insulin resistance, which makes it harder for the body to use insulin effectively. This can result in high blood sugar levels and eventually lead to type 2 diabetes.
Understanding the connection between type 2 diabetes and obesity/overweight is crucial for several reasons. First, it helps individuals understand their risk of developing type 2 diabetes and take steps to prevent it. Secondly, it enables healthcare providers to make an accurate diagnosis and determine the appropriate treatment plan.
Additionally, recognizing the link between type 2 diabetes and obesity/overweight is essential for public health initiatives aimed at reducing the prevalence of diabetes. By promoting healthy lifestyles and encouraging weight management, we can help prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes and its associated complications.
In conclusion, type 2 diabetes is a major public health concern, and understanding its connection to obesity and overweight is crucial for prevention, diagnosis, and management. By raising awareness and promoting healthy lifestyle choices, we can work towards reducing the burden of type 2 diabetes and improving the overall health of our communities.
Gestational
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It usually goes away after childbirth, but it can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Gestational diabetes is one of the most common types of diabetes during pregnancy, affecting up to 18% of pregnant women.
- Causes: Gestational diabetes is caused by the hormones produced during pregnancy, which can make the body more resistant to insulin. This can lead to high blood sugar levels.
- Symptoms: Most women with gestational diabetes do not have any symptoms. However, some women may experience increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue.
- Treatment: Gestational diabetes is usually treated with diet and exercise. In some cases, medication may also be necessary to control blood sugar levels.
- Risks: Gestational diabetes can increase the risk of developing preeclampsia, a serious condition that can lead to high blood pressure and seizures. It can also increase the risk of having a large baby, which can lead to complications during childbirth.
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with proper care. By following their doctor’s recommendations, women with gestational diabetes can help to reduce their risk of developing complications and having a healthy baby.
Monogenic
Monogenic diabetes is a rare form of diabetes caused by a mutation in a single gene. This type of diabetes is inherited, meaning that it is passed down from parents to children. Monogenic diabetes accounts for about 1-2% of all cases of diabetes.
There are several different types of monogenic diabetes, each caused by a mutation in a different gene. The most common type of monogenic diabetes is neonatal diabetes, which is caused by a mutation in the KCNJ11 gene. Neonatal diabetes is a severe form of diabetes that develops in the first six months of life.
Other types of monogenic diabetes include maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) and Wolfram syndrome. MODY is a milder form of diabetes that develops in children and young adults. Wolfram syndrome is a rare disorder that affects multiple organs, including the pancreas, brain, and eyes.
Understanding the connection between monogenic diabetes and “tipos de diabetes” is important for several reasons. First, it helps healthcare providers make an accurate diagnosis and determine the appropriate treatment plan. Secondly, it enables individuals with monogenic diabetes to connect with others who have similar experiences and challenges.
Additionally, recognizing the specific characteristics of monogenic diabetes is essential for raising awareness and promoting early detection. Early diagnosis and management of monogenic diabetes can help prevent or delay the onset of serious complications, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and blindness.
In conclusion, monogenic diabetes is a rare but important type of diabetes that is caused by a single gene mutation. Understanding the connection between monogenic diabetes and “tipos de diabetes” is crucial for accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and improved outcomes for individuals with this condition.
Secondary
Secondary diabetes is a type of diabetes that is caused by another underlying medical condition, such as pancreatitis, Cushing’s syndrome, or certain medications. It is important to identify and treat the underlying condition in order to effectively manage the diabetes.
- Pancreatitis: Pancreatitis is a condition that causes inflammation of the pancreas. This can damage the pancreas and lead to diabetes by reducing the production of insulin.
- Cushing’s syndrome: Cushing’s syndrome is a condition that causes the body to produce too much cortisol. Cortisol is a hormone that can increase blood sugar levels.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as steroids and beta-blockers, can cause diabetes by increasing blood sugar levels.
Understanding the connection between secondary diabetes and “tipos de diabetes” is important for several reasons. First, it helps healthcare providers make an accurate diagnosis and determine the appropriate treatment plan. Secondly, it enables individuals with secondary diabetes to connect with others who have similar experiences and challenges.
Additionally, recognizing the specific characteristics of secondary diabetes is essential for raising awareness and promoting early detection. Early diagnosis and management of secondary diabetes can help prevent or delay the onset of serious complications, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and blindness.
In conclusion, secondary diabetes is a type of diabetes that is caused by another underlying medical condition. Understanding the connection between secondary diabetes and “tipos de diabetes” is crucial for accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and improved outcomes for individuals with this condition.
Prediabetes
Prediabetes is a condition characterized by blood sugar levels that are higher than normal, but not high enough to be diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. It is an important condition to be aware of, as it can lead to type 2 diabetes and other serious health problems if left untreated.
- Increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes: Prediabetes is a major risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes. In fact, people with prediabetes are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes than people with normal blood sugar levels.
- Increased risk of heart disease and stroke: Prediabetes is also a risk factor for heart disease and stroke. People with prediabetes have a higher risk of developing these conditions than people with normal blood sugar levels.
- Other health problems: Prediabetes can also lead to other health problems, such as fatty liver disease, kidney disease, and eye problems.
Understanding the connection between prediabetes and “tipos de diabetes” is crucial for several reasons. First, it helps healthcare providers make an accurate diagnosis and determine the appropriate treatment plan. Secondly, it enables individuals with prediabetes to take steps to prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes and other serious health problems.
If you have prediabetes, there are things you can do to lower your risk of developing type 2 diabetes and other health problems. These include:
- Losing weight
- Eating a healthy diet
- Getting regular exercise
- Taking medication, if needed
By making these lifestyle changes, you can improve your overall health and reduce your risk of developing serious health problems.
Management
The management and treatment of diabetes vary depending on the type of diabetes, with the primary goal being to control blood sugar levels and prevent complications. Let’s explore the connection between diabetes management and its different types:
-
Type 1 Diabetes: Insulin Dependence
Individuals with type 1 diabetes require lifelong insulin therapy as their bodies cannot produce insulin. Insulin is administered through injections or an insulin pump to regulate blood sugar levels.
-
Type 2 Diabetes: Lifestyle Modifications and Medications
Type 2 diabetes management often involves lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing weight. Oral medications may be prescribed to improve insulin sensitivity or increase insulin production.
-
Gestational Diabetes: Monitoring and Dietary Changes
Gestational diabetes usually resolves after childbirth. Management involves monitoring blood sugar levels and making dietary changes to control blood sugar levels.
-
Other Types of Diabetes: Tailored Treatment
Monogenic and secondary diabetes require individualized treatment plans based on the underlying cause and specific genetic factors.
Understanding the diverse management approaches for different types of diabetes is crucial for effective treatment and prevention of complications. Proper diagnosis and personalized management plans are essential to optimize outcomes for individuals with diabetes.
FAQs on Tipos de Diabetes
Below are commonly asked questions and their respective answers to provide a better understanding of different types of diabetes.
Question 1: What are the main types of diabetes?
There are several types of diabetes, including type 1, type 2, gestational, monogenic, and secondary diabetes.
Question 2: What causes type 1 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
Question 3: What is the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is an insulin-dependent condition, while type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance and impaired insulin production.
Question 4: What are the symptoms of diabetes?
Common symptoms may include increased thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, and blurred vision.
Question 5: How is diabetes treated?
Treatment varies depending on the type of diabetes and may involve lifestyle modifications, medication, or insulin therapy.
Question 6: Can diabetes be prevented?
While some types of diabetes cannot be prevented, maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and following a balanced diet can reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
These FAQs provide general information about different types of diabetes. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis, personalized treatment, and management of your specific condition.
Transitioning to the next article section…
Tips for Managing Tipos de Diabetes
Effectively managing different types of diabetes is crucial for maintaining good health and preventing complications. Here are several essential tips to consider:
Tip 1: Monitor Blood Sugar Regularly
Regular blood sugar monitoring allows you to track your glucose levels and make necessary adjustments to your diet, medication, or insulin dosage. This helps keep your blood sugar within a healthy range and reduces the risk of complications.
Tip 2: Follow a Healthy Diet
Maintaining a balanced diet is vital for managing diabetes. Focus on consuming fiber-rich fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats to regulate blood sugar levels.
Tip 3: Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Regular exercise improves insulin sensitivity and helps control blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. Consult your healthcare provider before starting an exercise program.
Tip 4: Take Medications as Prescribed
If you are prescribed medications for diabetes, it is essential to take them as directed. These medications help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Skipping orng doses can affect your blood sugar control.
Tip 5: Manage Stress
Stress can raise blood sugar levels. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, meditation, or spending time in nature. Stress management techniques can help improve overall well-being and blood sugar control.
Tip 6: Get Enough Sleep
Adequate sleep is important for overall health and diabetes management. When you don’t get enough sleep, your body produces more stress hormones, which can elevate blood sugar levels.
Tip 7: Quit Smoking
Smoking negatively impacts blood sugar control and increases the risk of diabetes complications. Quitting smoking is one of the most beneficial things you can do for your overall health and diabetes management.
Tip 8: See Your Healthcare Provider Regularly
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential for monitoring your diabetes and making any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan. This includes eye exams, foot exams, and blood tests to assess your overall health and prevent complications.
Following these tips can significantly improve your diabetes management, enhance your overall health, and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
Transitioning to the article’s conclusion…
Tipos de Diabetes
In summary, “tipos de diabetes” encompasses a diverse range of conditions characterized by elevated blood sugar levels. This article explored the different types of diabetes, including type 1, type 2, gestational, monogenic, and secondary diabetes, emphasizing their unique characteristics, causes, and management approaches.
Understanding the nuances of each type of diabetes is crucial for accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and effective disease management. Proper monitoring, lifestyle modifications, medication adherence, and regular healthcare check-ups are essential for maintaining optimal blood sugar control and preventing complications.
By raising awareness about the different types of diabetes and promoting proactive management strategies, we can empower individuals to take control of their health, improve their quality of life, and reduce the long-term impact of this prevalent condition.
Youtube Video: