Sugar level reading for diabetes refers to the process of measuring the concentration of glucose in the blood of individuals with diabetes. Glucose is the primary source of energy for the body and is obtained from the food we eat. In diabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin, or the insulin it produces does not work properly, leading to elevated blood glucose levels. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is crucial for managing diabetes effectively and preventing complications.
Sugar level reading for diabetes provides valuable information about how well diabetes is being managed and helps individuals make informed decisions about their treatment plan. It allows them to identify patterns in their blood glucose levels and adjust their medication, diet, or lifestyle accordingly. This monitoring helps prevent blood glucose levels from becoming too high or too low, reducing the risk of both short-term and long-term complications, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness.
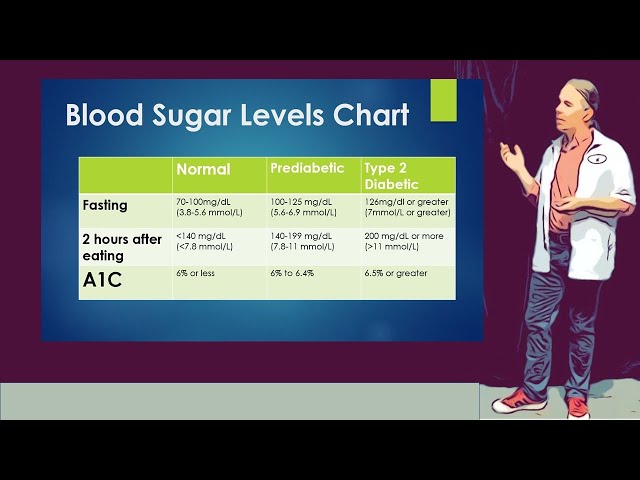
Sugar Level Reading for Diabetes
Regular sugar level reading is essential for managing diabetes effectively. Key aspects to consider include:
- Frequency: How often should blood sugar levels be checked?
- Timing: When should blood sugar levels be checked?
- Method: What methods are available for blood sugar monitoring?
- Accuracy: How accurate are different blood sugar monitoring methods?
- Interpretation: What do blood sugar readings mean?
- Goals: What are the target blood sugar ranges for people with diabetes?
- Action: What actions should be taken based on blood sugar readings?
- Technology: What technological advancements are available for blood sugar monitoring?
These aspects are interconnected and essential for understanding and managing blood sugar levels in diabetes. For example, the frequency and timing of blood sugar checks depend on the individual’s diabetes management plan and lifestyle. The method of monitoring should be accurate and convenient for the individual. Interpretation of blood sugar readings requires an understanding of target ranges and the potential impact of various factors, such as food, exercise, and stress. Based on blood sugar readings, individuals may need to adjust their insulin doses, diet, or activity levels. Technological advancements, such as continuous glucose monitors, provide real-time data and can significantly improve blood sugar management.
Frequency
The frequency of blood sugar checks is a crucial aspect of sugar level reading for diabetes. It is closely tied to effective diabetes management and helps individuals maintain healthy blood glucose levels.
Regular blood sugar monitoring allows individuals to:
- Track blood glucose patterns and identify trends
- Make informed decisions about insulin doses, diet, and exercise
- Detect and prevent episodes of high or low blood sugar
- Assess the effectiveness of diabetes management strategies
The recommended frequency of blood sugar checks varies depending on individual factors, such as the type of diabetes, treatment plan, and lifestyle. Generally, more frequent monitoring is recommended for individuals with:
- Type 1 diabetes
- Unstable blood glucose levels
- New or recently adjusted diabetes medications
- Certain medical conditions, such as kidney or liver disease
For most people with diabetes, it is recommended to check blood sugar levels:
- Before meals and snacks
- 2 hours after meals
- Before bedtime
- At other times as directed by a healthcare professional
Regular blood sugar monitoring empowers individuals with diabetes to take an active role in managing their condition and making informed decisions to maintain healthy blood glucose levels, reducing the risk of complications and improving overall well-being.
Timing
The timing of blood sugar checks is a crucial aspect of sugar level reading for diabetes. It is closely tied to effective diabetes management and helps individuals maintain healthy blood glucose levels.
Regular blood sugar monitoring allows individuals to:
- Track blood glucose patterns and identify trends
- Make informed decisions about insulin doses, diet, and exercise
- Detect and prevent episodes of high or low blood sugar
- Assess the effectiveness of diabetes management strategies
The recommended timing of blood sugar checks varies depending on individual factors, such as the type of diabetes, treatment plan, and lifestyle. Generally, more frequent monitoring is recommended for individuals with:
- Type 1 diabetes
- Unstable blood glucose levels
- New or recently adjusted diabetes medications
- Certain medical conditions, such as kidney or liver disease
For most people with diabetes, it is recommended to check blood sugar levels:
- Before meals and snacks
- 2 hours after meals
- Before bedtime
- At other times as directed by a healthcare professional
Regular blood sugar monitoring empowers individuals with diabetes to take an active role in managing their condition and making informed decisions to maintain healthy blood glucose levels, reducing the risk of complications and improving overall well-being.
Method
The method of blood sugar monitoring plays a significant role in accurate and effective sugar level reading for diabetes. Various methods are available, each with its own advantages and limitations.
-
Blood glucose meters
Blood glucose meters are small, portable devices that measure blood sugar levels from a drop of blood obtained by pricking a finger. They are widely used and provide quick results. However, they can be invasive and require multiple daily finger pricks, which can be painful or inconvenient.
-
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs)
CGMs are small, wearable devices that measure blood sugar levels continuously throughout the day and night. They use a tiny sensor inserted under the skin to measure interstitial fluid glucose levels, which correlate with blood glucose levels. CGMs provide real-time data and can alert users to high or low blood sugar levels, helping to prevent severe hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
-
Flash glucose monitors (FGMs)
FGMs are similar to CGMs but less invasive and more affordable. They provide glucose readings on demand with a quick scan of a sensor worn on the arm. FGMs offer a compromise between the convenience of CGMs and the simplicity of blood glucose meters, making them a popular choice for many people with diabetes.
The choice of blood sugar monitoring method depends on individual needs, preferences, and lifestyle factors. It is important to discuss the available options with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate method for effective diabetes management.
Accuracy
Accuracy is a crucial aspect of sugar level reading for diabetes. Accurate blood sugar readings are essential for making informed decisions about insulin doses, diet, and lifestyle choices. Inaccurate readings can lead to incorrect treatment decisions, which can have serious health implications.
The accuracy of blood sugar monitoring methods varies depending on the type of device and the technique used. Blood glucose meters are generally accurate within 10-15% of laboratory values, while continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and flash glucose monitors (FGMs) are typically more accurate. However, all methods can be affected by factors such as user error, skin irritation, and environmental conditions.
It is important to understand the accuracy limitations of different blood sugar monitoring methods and to use them correctly to obtain reliable readings. For example, blood glucose meters should be calibrated regularly, and fingers should be cleaned thoroughly before testing. CGMs and FGMs should be inserted and worn according to the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure accurate readings.
Accurate sugar level reading is essential for effective diabetes management. By using accurate monitoring methods and following proper techniques, individuals with diabetes can obtain reliable blood sugar readings and make informed decisions to manage their condition effectively.
Interpretation
Interpreting blood sugar readings is a critical aspect of sugar level reading for diabetes. Accurate interpretation allows individuals to understand the implications of their blood sugar levels and make informed decisions about their diabetes management.
-
Target Ranges:
Blood sugar readings should be interpreted in the context of target ranges established by healthcare professionals. These ranges vary depending on individual factors and the time of day. Understanding target ranges helps individuals identify when their blood sugar levels are within a healthy range or require attention.
-
Patterns and Trends:
Interpreting blood sugar readings involves analyzing patterns and trends over time. By tracking blood sugar levels regularly, individuals can identify patterns that may indicate the effectiveness of their diabetes management plan or the need for adjustments. This information helps healthcare professionals make informed decisions about medication, diet, and lifestyle changes.
-
Hypoglycemia and Hyperglycemia:
Blood sugar readings can indicate episodes of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or hyperglycemia (high blood sugar). Recognizing the symptoms and appropriate treatment for these conditions is crucial to prevent serious health complications. Accurate interpretation of blood sugar readings empowers individuals to take prompt action when necessary.
-
Lifestyle Factors:
Interpreting blood sugar readings also involves considering lifestyle factors that may influence blood sugar levels. Factors such as diet, exercise, stress, and medications can affect blood sugar readings. Understanding these relationships helps individuals make informed choices and adjust their lifestyle accordingly.
Overall, interpreting blood sugar readings is an essential skill for individuals with diabetes. By understanding target ranges, patterns, and trends, and considering lifestyle factors, individuals can effectively manage their blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications.
Goals
Establishing target blood sugar ranges is a crucial aspect of sugar level reading for diabetes. It provides a framework for interpreting blood sugar readings and making informed decisions about diabetes management.
-
Individualized Targets:
Target blood sugar ranges vary from person to person. Healthcare professionals determine individualized targets based on factors such as age, type of diabetes, overall health, and lifestyle. These targets help guide blood sugar management and reduce the risk of complications. -
HbA1c Levels:
HbA1c levels measure average blood sugar control over the past 2-3 months. Target HbA1c levels are typically set between 6.5% and 7.5%. Regularly monitoring HbA1c levels helps assess the effectiveness of diabetes management and identify areas for improvement. -
Pre-Meal and Post-Meal Targets:
Target blood sugar ranges are also set for specific times of the day, such as before meals and 1-2 hours after meals. These targets help ensure blood sugar levels remain within a healthy range throughout the day. -
Hypoglycemia and Hyperglycemia Prevention:
Establishing target blood sugar ranges aims to prevent episodes of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar). Hypoglycemia can occur when blood sugar levels drop below the target range, while hyperglycemia occurs when blood sugar levels rise above the target range. Both conditions can have serious health implications.
Overall, setting and monitoring target blood sugar ranges is essential for effective diabetes management. By aiming to keep blood sugar levels within these ranges, individuals can reduce the risk of complications and improve their overall health and well-being.
Action
Taking appropriate actions based on blood sugar readings is a crucial aspect of sugar level reading for diabetes. It involves interpreting the readings correctly and responding with necessary interventions to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
When blood sugar readings indicate levels outside the target range, individuals may need to adjust their insulin doses, diet, or physical activity. For example, if a blood sugar reading is high, an individual may need to increase their insulin dosage or engage in physical activity to lower their blood sugar levels. Conversely, if a blood sugar reading is low, they may need to consume a sugary snack or drink to raise their blood sugar levels.
Regular blood sugar monitoring empowers individuals to make informed decisions and take timely actions to prevent or address episodes of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. By understanding the implications of their blood sugar readings and taking appropriate actions, individuals can maintain healthy blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of long-term complications associated with diabetes.
Technology
Technological advancements have revolutionized sugar level reading for diabetes, leading to more accurate, convenient, and accessible blood sugar monitoring methods. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and flash glucose monitors (FGMs) are prime examples of these advancements, offering real-time data and eliminating the need for multiple daily finger pricks.
CGMs and FGMs use sensors inserted under the skin to measure glucose levels in the interstitial fluid, which closely correlates with blood glucose levels. This data is transmitted to a receiver or smartphone app, providing individuals with a continuous or near-continuous stream of blood sugar readings throughout the day and night. The ability to track blood sugar levels in real-time allows for proactive diabetes management, as individuals can identify trends, patterns, and potential issues before they become severe.
The practical significance of these technological advancements is immense. Real-time blood sugar monitoring empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their insulin doses, diet, and lifestyle choices, leading to improved glycemic control and reduced risk of complications. Additionally, CGMs and FGMs can provide peace of mind and reduce anxiety associated with diabetes management, as individuals have a better understanding of their blood sugar levels and can take steps to prevent or address fluctuations.
FAQs on Sugar Level Reading for Diabetes
Understanding sugar level reading is crucial for effective diabetes management. Here are answers to some common questions and misconceptions:
Question 1: How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
Answer: The frequency of blood sugar checks depends on individual factors and diabetes management plan. Generally, more frequent monitoring is recommended for individuals with Type 1 diabetes, unstable blood glucose levels, or new medications.
Question 2: What are the target blood sugar ranges?
Answer: Target blood sugar ranges vary based on factors such as age, type of diabetes, and overall health. Healthcare professionals set individualized targets to guide blood sugar management and minimize complications.
Question 3: What do I do if my blood sugar reading is too high or too low?
Answer: If your blood sugar reading is high, you may need to adjust your insulin dose or engage in physical activity. If your reading is low, consume a sugary snack or drink to raise your blood sugar levels.
Question 4: How accurate are blood sugar monitoring devices?
Answer: The accuracy of blood sugar monitoring devices varies depending on the type of device and technique used. Continuous glucose monitors and flash glucose monitors are generally more accurate than blood glucose meters.
Question 5: How can I prevent episodes of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia?
Answer: Regular blood sugar monitoring, understanding target ranges, and taking appropriate actions based on readings can help prevent episodes of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
Question 6: What technological advancements are available for blood sugar monitoring?
Answer: Technological advancements such as continuous glucose monitors and flash glucose monitors provide real-time blood sugar data, empowering individuals to make informed diabetes management decisions.
Summary:
Understanding sugar level reading for diabetes is essential for effective management. Regular monitoring, interpreting readings accurately, and taking appropriate actions can help maintain healthy blood sugar levels. Technological advancements have also improved the accuracy and convenience of blood sugar monitoring.
Transition:
For further information on diabetes management, consult your healthcare professional or explore reputable online resources.
Tips for Sugar Level Reading in Diabetes Management
Accurate and consistent sugar level reading is essential for effective diabetes management. Here are some tips to improve the accuracy and reliability of your readings:
Tip 1: Wash your hands before testing.
Unwashed hands can contaminate the test strip and lead to inaccurate readings. Always wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water before handling the test strip or lancing device.
Tip 2: Use a clean lancing device.
A dirty lancing device can cause pain and bleeding, and it can also transfer bacteria to the test site. Clean the lancing device regularly according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Tip 3: Apply enough blood to the test strip.
If you don’t apply enough blood to the test strip, the reading may be inaccurate. Make sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the amount of blood required.
Tip 4: Read the results within the specified time frame.
Most blood glucose meters have a specific time frame within which the results must be read. If you wait too long, the reading may be inaccurate.
Tip 5: Keep a log of your readings.
Keeping a log of your blood sugar readings can help you track your progress and identify patterns. This information can be helpful for your healthcare provider when making treatment decisions.
Summary:
By following these tips, you can improve the accuracy and reliability of your sugar level readings. This information is essential for effective diabetes management and can help you avoid complications.
Transition:
For more information on diabetes management, consult your healthcare provider or explore reputable online resources.
Conclusion
Sugar level reading for diabetes is an essential aspect of diabetes management, providing valuable information about how well diabetes is being controlled. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels helps individuals make informed decisions about their treatment plan, diet, and lifestyle, enabling them to maintain healthy blood sugar ranges, prevent complications, and improve their overall well-being.
Technological advancements, such as continuous glucose monitors and flash glucose monitors, have revolutionized blood sugar monitoring, offering real-time data and eliminating the need for multiple daily finger pricks. These advancements empower individuals with diabetes to take an active role in managing their condition and achieving optimal health outcomes.
Youtube Video: