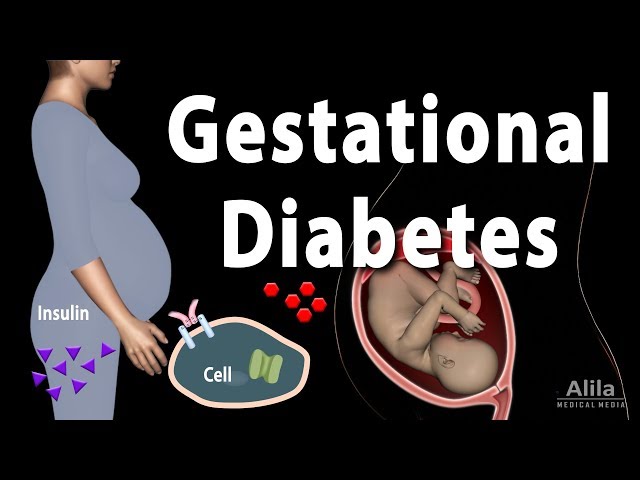
Gestational diabetes, also known as pregnant diabetes, is a condition characterized by high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. It typically develops during the second or third trimester and usually disappears after childbirth. Gestational diabetes occurs when the body is unable to produce enough insulin to meet the increased demands of pregnancy.
Pregnant diabetes can lead to several complications, including macrosomia (excessive birth weight), premature birth, and respiratory problems in the newborn. It can also increase the mother’s risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Treating pregnant diabetes typically involves diet and exercise. In some cases, insulin therapy may be necessary. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial to manage the condition and prevent complications.
Pregnant Diabetes
Pregnant diabetes, also known as gestational diabetes, is a condition that affects pregnant women. It is characterized by high blood sugar levels that develop during pregnancy and usually disappear after childbirth. Pregnant diabetes can have several implications for both the mother and the baby, making it crucial to understand its key aspects:
- Definition: High blood sugar during pregnancy
- Causes: Insufficient insulin production
- Symptoms: Often asymptomatic, may include frequent urination, thirst, fatigue
- Complications: Macrosomia, premature birth, respiratory problems in the baby; increased risk of type 2 diabetes for the mother
- Diagnosis: Glucose tolerance test during pregnancy
- Treatment: Diet, exercise, insulin therapy if necessary
- Prevention: Maintaining a healthy weight before and during pregnancy, regular exercise, healthy diet
- Management: Regular blood sugar monitoring, following treatment plan
Pregnant diabetes highlights the importance of prenatal care and managing blood sugar levels during pregnancy. By understanding these key aspects, expectant mothers can work with their healthcare providers to minimize the risks and ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
Definition
High blood sugar during pregnancy, also known as hyperglycemia, is a defining characteristic of pregnant diabetes, or gestational diabetes. It occurs when the body is unable to produce enough insulin to meet the increased demands of pregnancy. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, from the blood enter the body’s cells for energy. Without enough insulin, glucose builds up in the blood, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Pregnant diabetes typically develops during the second or third trimester and usually disappears after childbirth. However, if left untreated, high blood sugar during pregnancy can lead to several complications, including macrosomia (excessive birth weight), premature birth, and respiratory problems in the newborn. It can also increase the mother’s risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Therefore, it is crucial for pregnant women to understand the importance of managing blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Regular prenatal checkups and glucose tolerance tests can help identify and manage high blood sugar levels, reducing the risks associated with pregnant diabetes. Maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, and following the doctor’s recommendations can help expectant mothers keep their blood sugar levels within a healthy range, ensuring a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
Causes
Insufficient insulin production is a primary factor in the development of pregnant diabetes. During pregnancy, the body naturally develops a state of insulin resistance, which means that the cells become less responsive to insulin. This is a normal adaptation that allows the body to store more glucose for the baby’s growth and development.
However, in some women, the body is unable to produce enough insulin to overcome this insulin resistance, leading to high blood sugar levels. This can occur due to various reasons, including genetics, obesity, and certain medical conditions. Advanced maternal age also increases the risk of insufficient insulin production.
Understanding the link between insufficient insulin production and pregnant diabetes is crucial for managing and preventing this condition. Regular prenatal checkups and glucose tolerance tests can help identify women at risk of developing pregnant diabetes, allowing for early intervention and management.
Symptoms
Pregnant diabetes is often asymptomatic, making it crucial to be aware of potential symptoms. Frequent urination, excessive thirst, and fatigue are common indicators that may signal high blood sugar levels during pregnancy.
- Frequent urination: Increased blood sugar levels can lead to frequent urination as the body attempts to eliminate excess glucose through urine.
- Excessive thirst: Frequent urination can lead to dehydration, causing excessive thirst as the body tries to replenish lost fluids.
- Fatigue: High blood sugar levels can interfere with the body’s ability to use glucose for energy, resulting in fatigue and low energy levels.
While these symptoms can be common during pregnancy, it is important to consult a healthcare provider if they persist or become severe. Early detection and management of pregnant diabetes can help prevent complications for both the mother and the baby.
Complications
Pregnant diabetes, or gestational diabetes, can lead to several complications if left untreated. These complications can affect both the mother and the baby, highlighting the importance of managing blood sugar levels during pregnancy.
- Macrosomia: High blood sugar levels can cause excessive fetal growth, leading to macrosomia, or a large birth weight. Macrosomia can increase the risk of birth injuries and complications during delivery.
- Premature birth: Uncontrolled blood sugar levels can increase the risk of premature birth, which can lead to health problems for the baby, including respiratory distress syndrome and other complications.
- Respiratory problems in the baby: High blood sugar levels can affect the baby’s lung development, increasing the risk of respiratory problems after birth.
- Increased risk of type 2 diabetes for the mother: Women with pregnant diabetes have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Managing blood sugar levels during pregnancy can help reduce this risk.
Understanding these complications and their link to pregnant diabetes is crucial for proper prenatal care and management. Regular blood sugar monitoring, maintaining a healthy diet, and following the doctor’s recommendations can help prevent or minimize these complications, ensuring a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
Diagnosis
During pregnancy, a glucose tolerance test (GTT) is a crucial diagnostic tool for identifying pregnant diabetes, or gestational diabetes. This test involves measuring blood sugar levels after consuming a sugary drink. An elevated blood sugar level at specific time intervals during the test indicates impaired glucose tolerance, a characteristic of pregnant diabetes.
The importance of a GTT during pregnancy lies in its ability to detect high blood sugar levels that may not be apparent through routine prenatal care. Early detection and diagnosis of pregnant diabetes allow for timely intervention and management to prevent or minimize potential complications for both the mother and the baby.
For instance, managing blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and if necessary, insulin therapy can reduce the risk of macrosomia, premature birth, and respiratory problems in the baby. Additionally, it can lower the mother’s chances of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
In conclusion, the glucose tolerance test during pregnancy serves as an essential diagnostic tool for pregnant diabetes, enabling healthcare providers to identify and manage high blood sugar levels effectively. This understanding underscores the significance of prenatal care and regular monitoring to ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
Treatment
Managing pregnant diabetes, or gestational diabetes, involves a multifaceted approach that includes dietary modifications, regular exercise, and insulin therapy if required. Understanding the significance of these treatment components in relation to pregnant diabetes is crucial for ensuring a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
-
Dietary Modifications:
Adopting a balanced and nutritious diet forms the cornerstone of managing pregnant diabetes. Limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive carbohydrates helps control blood sugar levels. Incorporating fiber-rich fruits, vegetables, and whole grains promotes satiety and supports overall well-being.
-
Regular Exercise:
Engaging in regular physical activity, as recommended by a healthcare provider, plays a vital role in managing pregnant diabetes. Exercise enhances insulin sensitivity, allowing the body to utilize glucose more effectively. It also contributes to weight management and improves overall health.
-
Insulin Therapy:
In some cases, when diet and exercise alone are insufficient to control blood sugar levels, insulin therapy may be necessary. Insulin injections help regulate glucose metabolism, ensuring that blood sugar levels remain within a healthy range. Regular monitoring and medical supervision are crucial during insulin therapy.
The interplay of diet, exercise, and insulin therapy, when necessary, provides a comprehensive approach to managing pregnant diabetes. Adhering to these treatment components empowers individuals to maintain optimal blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of complications for both the mother and the baby. Effective management of pregnant diabetes leads to improved pregnancy outcomes and promotes the well-being of all parties involved.
Prevention
Preventing pregnant diabetes, also known as gestational diabetes, involves adopting a comprehensive approach that encompasses maintaining a healthy weight before and during pregnancy, engaging in regular exercise, and adhering to a healthy diet. Understanding the connection between these preventative measures and pregnant diabetes is crucial for promoting a healthy pregnancy and reducing the risk of complications.
Maintaining a healthy weight before and during pregnancy helps regulate blood sugar levels and reduces the risk of developing insulin resistance, a precursor to pregnant diabetes. Regular exercise enhances insulin sensitivity, allowing the body to utilize glucose more effectively, further lowering the risk of pregnant diabetes. Additionally, a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides essential nutrients while promoting satiety and stable blood sugar levels.
Adopting these preventative measures not only reduces the likelihood of developing pregnant diabetes but also contributes to overall well-being during pregnancy. By maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise, and following a healthy diet, individuals can empower themselves to manage their blood sugar levels, minimize the risk of complications, and promote a healthy pregnancy.
Management
Regular blood sugar monitoring and adherence to the prescribed treatment plan are essential components of managing pregnant diabetes, or gestational diabetes. Understanding this connection empowers individuals to maintain optimal blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of complications for both the mother and the baby.
Regular blood sugar monitoring allows individuals to track their glucose levels and identify patterns. This information helps healthcare providers make informed decisions about medication adjustments, dietary modifications, or physical activity recommendations. By closely monitoring blood sugar levels, pregnant women can proactively manage their condition and prevent blood sugar levels from reaching dangerous levels.
Following the prescribed treatment plan, which may include dietary changes, regular exercise, and in some cases, insulin therapy, is crucial for effectively managing pregnant diabetes. Adhering to the recommended diet helps control blood sugar levels by limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive carbohydrates. Regular exercise enhances insulin sensitivity and promotes overall well-being. Insulin therapy, when necessary, helps regulate glucose metabolism and maintain blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
The practical significance of understanding the connection between regular blood sugar monitoring and following the treatment plan lies in empowering individuals to take an active role in managing their pregnant diabetes. By diligently monitoring their blood sugar levels and adhering to the prescribed treatment plan, pregnant women can minimize the risk of developing complications such as macrosomia, premature birth, and respiratory problems in the baby. Additionally, managing blood sugar levels reduces the mother’s risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Frequently Asked Questions About Pregnant Diabetes
Pregnant diabetes, also known as gestational diabetes, is a condition characterized by high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. It typically develops during the second or third trimester and usually disappears after childbirth. Pregnant diabetes can have several implications for both the mother and the baby, making it crucial to understand its key aspects and address common concerns.
Question 1: What causes pregnant diabetes?
Pregnant diabetes occurs when the body is unable to produce enough insulin to meet the increased demands of pregnancy. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, from the blood enter the body’s cells for energy.
Question 2: What are the symptoms of pregnant diabetes?
Pregnant diabetes is often asymptomatic, but some common signs may include frequent urination, excessive thirst, and fatigue.
Question 3: How is pregnant diabetes diagnosed?
Pregnant diabetes is diagnosed through a glucose tolerance test, which measures blood sugar levels after consuming a sugary drink.
Question 4: How is pregnant diabetes treated?
Treatment for pregnant diabetes typically involves diet and exercise. In some cases, insulin therapy may be necessary to manage blood sugar levels.
Question 5: What are the risks of pregnant diabetes?
Pregnant diabetes can lead to several complications for both the mother and the baby, including macrosomia (excessive birth weight), premature birth, and respiratory problems in the newborn. It can also increase the mother’s risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Question 6: How can I prevent pregnant diabetes?
Maintaining a healthy weight before and during pregnancy, engaging in regular exercise, and following a healthy diet can help reduce the risk of developing pregnant diabetes.
Summary: Pregnant diabetes is a condition that requires monitoring and management during pregnancy. Understanding its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, risks, and prevention strategies empower expectant mothers to make informed choices and work with their healthcare providers to ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
Transition to the next article section: Managing pregnant diabetes involves regular blood sugar monitoring, adherence to the prescribed treatment plan, and open communication with healthcare providers. By understanding this connection and adopting proactive measures, expectant mothers can minimize the risks and improve pregnancy outcomes.
Pregnant Diabetes Management Tips
Pregnant diabetes, also known as gestational diabetes, requires careful management to ensure the health of both the mother and the baby. Here are some essential tips for managing pregnant diabetes:
Tip 1: Monitor Blood Sugar Regularly
Regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial for managing pregnant diabetes. It allows you to track your glucose levels and make necessary adjustments to your diet, exercise, or medication to keep your blood sugar within a healthy range.
Tip 2: Follow a Healthy Diet
A balanced and nutritious diet is essential for managing pregnant diabetes. Focus on consuming fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive carbohydrates.
Tip 3: Engage in Regular Exercise
Regular physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
Tip 4: Take Medication as Prescribed
If diet and exercise alone are not enough to control your blood sugar levels, your doctor may prescribe insulin or other medications. Take your medication exactly as prescribed and monitor your blood sugar regularly.
Tip 5: Attend Prenatal Appointments Regularly
Regular prenatal appointments are essential for monitoring your health and the baby’s growth. Your doctor will check your blood sugar levels, discuss your treatment plan, and provide guidance on diet, exercise, and any necessary lifestyle changes.
Summary: Managing pregnant diabetes requires a multifaceted approach involving regular blood sugar monitoring, a healthy diet, regular exercise, medication if needed, and regular prenatal care. By following these tips and working closely with your healthcare provider, you can effectively manage your blood sugar levels and promote a healthy pregnancy.
Transition to the article’s conclusion: Managing pregnant diabetes can be challenging, but by following these tips and seeking support from your healthcare team, you can optimize your health and the well-being of your baby.
Conclusion on Pregnant Diabetes
Pregnant diabetes, also known as gestational diabetes, is a serious condition that can affect pregnant women and their unborn children. It is characterized by high blood sugar levels during pregnancy and can lead to various complications if left untreated. This article has explored the definition, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, management, and frequently asked questions related to pregnant diabetes.
Understanding pregnant diabetes and its implications is crucial for expectant mothers and healthcare providers. By raising awareness about this condition, we empower individuals to make informed choices and take proactive measures to manage their blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Early detection, proper management, and a collaborative approach between healthcare providers and pregnant women are essential to ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
Youtube Video: