Ketoacidosis diabetes mellitus is a life-threatening complication of diabetes in which the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause ketoacidosis.
Ketoacidosis is a medical emergency. If left untreated, it can lead to coma and death. Symptoms of ketoacidosis include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Rapid breathing
- Confusion
- Loss of consciousness
Ketoacidosis is treated with fluids, insulin, and electrolytes. Treatment is usually given in a hospital setting.
Ketoacidosis can be prevented by managing diabetes carefully. This includes taking insulin as prescribed, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly.
Ketoacidosis diabetes mellitus
Ketoacidosis diabetes mellitus (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
- Cause: Diabetes
- Symptoms: Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, rapid breathing, confusion, loss of consciousness
- Treatment: Fluids, insulin, and electrolytes
- Prevention: Managing diabetes carefully, including taking insulin as prescribed, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly
- Emergency: DKA is a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment.
- Life-threatening: If left untreated, DKA can lead to coma and death.
DKA is a serious condition, but it can be prevented and treated. If you have diabetes, it is important to manage your blood sugar levels carefully. This will help to prevent DKA and other complications of diabetes.
Cause
Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects the body’s ability to produce or use insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, get from the blood into the cells. Without insulin, glucose builds up in the blood and can cause a number of health problems, including ketoacidosis diabetes mellitus (DKA).
- Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that make insulin. This type of diabetes usually develops in children and young adults, but it can occur at any age.
- Type 2 diabetes is a condition in which the body does not make enough insulin or does not use insulin well. This type of diabetes usually develops in adults over the age of 40, but it can occur at any age.
Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes can lead to DKA if they are not properly managed. DKA is a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Symptoms
The symptoms of ketoacidosis diabetes mellitus (DKA) are caused by the buildup of ketones in the blood. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
The symptoms of DKA can include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Rapid breathing
- Confusion
- Loss of consciousness
These symptoms can be very serious and can lead to coma or death if left untreated. If you have any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
DKA is a serious complication of diabetes, but it can be prevented and treated. If you have diabetes, it is important to manage your blood sugar levels carefully. This will help to prevent DKA and other complications of diabetes.
Treatment
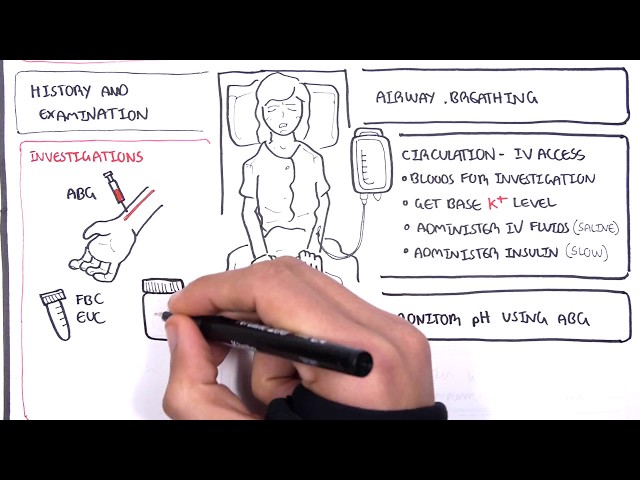
The treatment for ketoacidosis diabetes mellitus (DKA) involves replacing fluids, insulin, and electrolytes that are lost through excessive urination. Fluids are given intravenously (IV) to help rehydrate the body and correct electrolyte imbalances. Insulin is given to help lower blood sugar levels. Electrolytes, such as potassium, sodium, and chloride, are also given to correct imbalances that can occur as a result of DKA.
Fluids, insulin, and electrolytes are all essential components of DKA treatment. Without fluids, the body can become dehydrated and electrolyte imbalances can worsen. Without insulin, blood sugar levels can remain high and DKA can progress. Without electrolytes, the body can experience a number of problems, including muscle weakness, seizures, and heart arrhythmias.
The treatment of DKA is typically carried out in a hospital setting. The patient will be monitored closely and given fluids, insulin, and electrolytes until their condition improves. Once the patient’s condition has stabilized, they may be discharged from the hospital and continue treatment at home.
The treatment of DKA is essential to prevent serious complications and death. If you have diabetes, it is important to manage your blood sugar levels carefully to prevent DKA from developing.
Prevention
Preventing ketoacidosis diabetes mellitus (DKA) is essential for people with diabetes. DKA is a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
There are a number of things that people with diabetes can do to prevent DKA, including:
- Taking insulin as prescribed
- Eating a healthy diet
- Exercising regularly
Taking insulin as prescribed is essential for people with type 1 diabetes. Insulin helps the body to use glucose for energy. Without insulin, people with type 1 diabetes will develop DKA. People with type 2 diabetes may also need to take insulin if their blood sugar levels are not well controlled.
Eating a healthy diet is also important for people with diabetes. A healthy diet includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. These foods are low in carbohydrates and high in fiber, which helps to keep blood sugar levels stable. People with diabetes should also limit their intake of sugary foods and drinks.
Exercising regularly is another important part of diabetes management. Exercise helps to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. People with diabetes should aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
By following these tips, people with diabetes can help to prevent DKA and other complications of diabetes.
Conclusion
Preventing ketoacidosis diabetes mellitus (DKA) is essential for people with diabetes. DKA is a serious complication of diabetes that can be life-threatening. By taking insulin as prescribed, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly, people with diabetes can help to prevent DKA and other complications of diabetes.
Emergency
Ketoacidosis diabetes mellitus (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
- DKA is a medical emergency because it can lead to coma or death if it is not treated immediately.
- The symptoms of DKA include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, rapid breathing, confusion, and loss of consciousness.
- DKA is treated with fluids, insulin, and electrolytes.
- Preventing DKA is essential for people with diabetes.
If you have diabetes, it is important to manage your blood sugar levels carefully to prevent DKA from developing. This includes taking insulin as prescribed, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly.
Life-threatening
Ketoacidosis diabetes mellitus (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
- DKA is a life-threatening condition because it can lead to coma or death if it is not treated immediately.
- The symptoms of DKA include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, rapid breathing, confusion, and loss of consciousness.
- DKA is treated with fluids, insulin, and electrolytes.
- Preventing DKA is essential for people with diabetes.
If you have diabetes, it is important to manage your blood sugar levels carefully to prevent DKA from developing. This includes taking insulin as prescribed, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly.
FAQs about Ketoacidosis Diabetes Mellitus
Ketoacidosis diabetes mellitus (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
DKA is a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment. If left untreated, DKA can lead to coma or death.
Common Concerns or Misconceptions about DKA
Question 1: What are the symptoms of DKA?
Answer: The symptoms of DKA include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, rapid breathing, confusion, and loss of consciousness.Question 2: What causes DKA?
Answer: DKA is caused by a combination of factors, including high blood sugar levels, lack of insulin, and dehydration.Question 3: How is DKA treated?
Answer: DKA is treated with fluids, insulin, and electrolytes.Question 4: Can DKA be prevented?
Answer: DKA can be prevented by managing blood sugar levels carefully, taking insulin as prescribed, and eating a healthy diet.Question 5: What are the long-term risks of DKA?
Answer: DKA can lead to serious complications, including kidney damage, blindness, and heart disease.Question 6: How can I manage my diabetes to prevent DKA?
Answer: To manage your diabetes and prevent DKA, you should take your insulin as prescribed, eat a healthy diet, and exercise regularly. You should also monitor your blood sugar levels regularly and see your doctor for regular checkups.
Summary
DKA is a serious complication of diabetes, but it can be prevented and treated. By managing your blood sugar levels carefully, taking insulin as prescribed, and eating a healthy diet, you can help to prevent DKA from developing.
Transition to the next article section
Tips for Managing Ketoacidosis Diabetes Mellitus
Ketoacidosis diabetes mellitus (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
DKA is a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment. If left untreated, DKA can lead to coma or death.
Tips for Managing DKA
Tip 1: Take your insulin as prescribed.
Insulin is a hormone that helps the body use glucose for energy. People with diabetes need to take insulin to lower their blood sugar levels. Taking your insulin as prescribed will help to prevent DKA.
Tip 2: Eat a healthy diet.
A healthy diet includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. These foods are low in carbohydrates and high in fiber, which helps to keep blood sugar levels stable. Eating a healthy diet will help to prevent DKA.
Tip 3: Exercise regularly.
Exercise helps to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Exercising regularly will help to prevent DKA.
Tip 4: Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly.
Monitoring your blood sugar levels regularly will help you to identify when your blood sugar levels are too high. If your blood sugar levels are too high, you can take steps to lower them, such as taking more insulin or eating a snack.
Tip 5: See your doctor for regular checkups.
Seeing your doctor for regular checkups will help you to manage your diabetes and prevent complications, such as DKA.
Summary
DKA is a serious complication of diabetes, but it can be prevented and treated. By following these tips, you can help to manage your diabetes and prevent DKA.
Transition to the article’s conclusion
Conclusion
Ketoacidosis diabetes mellitus (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
DKA is a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment. If left untreated, DKA can lead to coma or death. However, DKA can be prevented and treated by managing blood sugar levels carefully, taking insulin as prescribed, and eating a healthy diet.
If you have diabetes, it is important to be aware of the symptoms of DKA and to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of these symptoms. By managing your diabetes carefully, you can help to prevent DKA and other complications of diabetes.
Youtube Video: