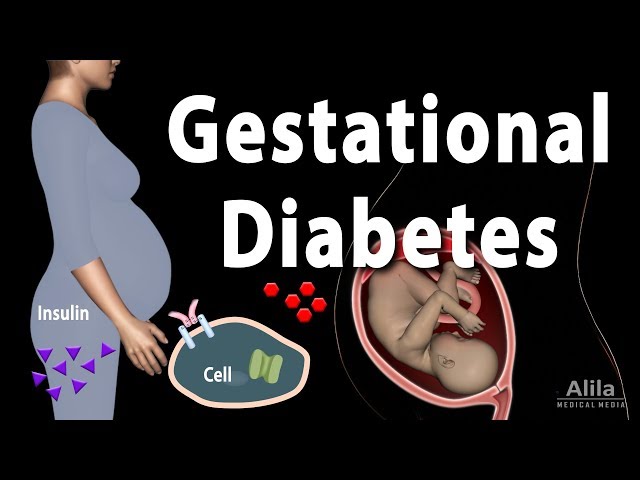
Gestational diabetes treatments encompass a range of interventions aimed at managing blood glucose levels during pregnancy. These treatments are crucial in preventing adverse outcomes for both the mother and the developing fetus.
Gestational diabetes, if left untreated, can lead to macrosomia (excessive birth weight), pre-eclampsia (high blood pressure during pregnancy), and premature birth. It also increases the risk of long-term health problems for the child, such as obesity and type 2 diabetes.
The primary treatment for gestational diabetes involves lifestyle modifications, including:
- Regular physical activity
- Dietary changes, such as reducing sugar intake and increasing fiber intake
- Blood glucose monitoring
In some cases, medication may be necessary to control blood glucose levels. Insulin is the most commonly used medication for gestational diabetes.
Gestational diabetes treatments have significantly improved the outcomes for both mothers and babies. By managing blood glucose levels, these treatments help to reduce the risk of pregnancy complications and ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
Gestational Diabetes Treatments
Gestational diabetes treatments are essential for managing blood glucose levels during pregnancy, ensuring the health of both the mother and the developing fetus.
- Lifestyle modifications: Regular exercise, dietary changes, and blood glucose monitoring.
- Medication: Insulin is the most commonly used medication for gestational diabetes.
- Prenatal care: Regular check-ups and monitoring are crucial for managing gestational diabetes.
- Blood glucose control: Maintaining blood glucose levels within target range is essential for preventing complications.
- Dietary management: A healthy diet is key to managing gestational diabetes.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity helps to control blood glucose levels.
- Monitoring: Regular blood glucose monitoring helps to track progress and adjust treatment as needed.
These key aspects of gestational diabetes treatments are interconnected and essential for ensuring a healthy pregnancy and delivery. By managing blood glucose levels, these treatments help to reduce the risk of pregnancy complications, such as macrosomia, pre-eclampsia, and premature birth. They also help to ensure the long-term health of both the mother and the child.
Lifestyle modifications
Lifestyle modifications are a cornerstone of gestational diabetes treatments, playing a crucial role in managing blood glucose levels and promoting a healthy pregnancy. These modifications include:
- Regular exercise: Physical activity helps to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood glucose levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Dietary changes: Eating a healthy diet is essential for managing gestational diabetes. Focus on consuming whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean protein. Limit your intake of sugary drinks, processed foods, and saturated and trans fats.
- Blood glucose monitoring: Regular blood glucose monitoring is essential for tracking your progress and adjusting your treatment plan as needed. Your doctor will recommend a specific monitoring schedule based on your individual needs.
By following these lifestyle modifications, you can help to manage your blood glucose levels and reduce your risk of pregnancy complications. It is important to work closely with your doctor or a registered dietitian to develop a personalized treatment plan that is right for you.
Medication
Insulin is a hormone that helps the body to use glucose for energy. In women with gestational diabetes, the placenta produces hormones that can block the effects of insulin, leading to high blood glucose levels. Insulin medication can help to lower blood glucose levels and manage gestational diabetes.
Insulin is typically given as an injection, either multiple times a day or as a continuous infusion. The dose of insulin is adjusted based on the individual’s blood glucose levels and response to treatment. Regular blood glucose monitoring is essential to ensure that insulin is working effectively and to prevent hypoglycemia (low blood sugar).
Insulin is a safe and effective medication for managing gestational diabetes. It can help to reduce the risk of pregnancy complications, such as macrosomia, pre-eclampsia, and premature birth. Insulin can also help to ensure the healthy growth and development of the baby.
If you are diagnosed with gestational diabetes, your doctor will work with you to develop a treatment plan that is right for you. This plan may include lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise, as well as insulin medication. By following your treatment plan, you can help to manage your blood glucose levels and reduce your risk of pregnancy complications.
Prenatal care
Prenatal care plays a vital role in the management of gestational diabetes, as regular check-ups and monitoring allow healthcare providers to assess the mother’s and baby’s health, identify any potential complications, and adjust treatment plans as needed.
- Monitoring blood glucose levels: Regular blood glucose monitoring is essential for managing gestational diabetes. Prenatal check-ups typically include blood glucose tests to track the mother’s blood sugar levels and ensure they are within target range. This monitoring helps to identify any fluctuations in blood glucose levels and allows for prompt adjustments to the treatment plan.
- Assessing fetal growth and well-being: Prenatal check-ups also involve assessing the growth and well-being of the fetus. Ultrasound scans are often used to monitor the baby’s growth, check for any abnormalities, and assess amniotic fluid levels. Additionally, fetal heart rate monitoring may be used to evaluate the baby’s health and detect any potential problems.
- Screening for pregnancy complications: Regular prenatal check-ups allow healthcare providers to screen for pregnancy complications that may be associated with gestational diabetes, such as pre-eclampsia, gestational hypertension, and premature birth. Early detection and management of these complications can help to improve outcomes for both the mother and the baby.
- Adjusting treatment plans: Based on the results of prenatal check-ups and monitoring, healthcare providers may adjust the mother’s treatment plan as needed. This may involve changes to diet, exercise, or medication regimens. Regular check-ups ensure that the treatment plan is optimized and tailored to the individual needs of the mother and baby.
In summary, prenatal care, including regular check-ups and monitoring, is crucial for managing gestational diabetes effectively. By closely monitoring the mother’s and baby’s health, identifying potential complications, and adjusting treatment plans as needed, healthcare providers can help to ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
Blood glucose control
Maintaining blood glucose levels within target range is a cornerstone of gestational diabetes treatments, as it is crucial for preventing pregnancy complications. Elevated blood glucose levels during pregnancy can lead to a number of adverse outcomes for both the mother and the baby.
For the mother, uncontrolled blood glucose levels can increase the risk of developing pre-eclampsia, gestational hypertension, and premature birth. Pre-eclampsia is a serious pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine, which can lead to seizures and other life-threatening complications if left untreated. Gestational hypertension is high blood pressure that develops during pregnancy and can also increase the risk of pre-eclampsia and premature birth.
For the baby, uncontrolled blood glucose levels can lead to macrosomia, which is excessive birth weight. Macrosomia can cause complications during delivery, such as shoulder dystocia and birth injuries. Additionally, high blood glucose levels in the mother can lead to hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) in the baby after birth.
By maintaining blood glucose levels within target range through gestational diabetes treatments, such as lifestyle modifications, medication, and prenatal care, the risks of these complications can be significantly reduced, ensuring a healthier pregnancy and delivery for both the mother and the baby.
Dietary management
Dietary management plays a crucial role in the treatment of gestational diabetes, as it involves making specific dietary changes to help control blood glucose levels and prevent pregnancy complications.
- Blood glucose control: A healthy diet can help to control blood glucose levels by reducing the intake of sugary foods and processed carbohydrates. This can help to prevent spikes in blood sugar levels and improve overall blood glucose management.
- Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight during pregnancy is important for managing gestational diabetes. A healthy diet can help to prevent excessive weight gain, which can contribute to insulin resistance and high blood glucose levels.
- Nutrient intake: A healthy diet can ensure that the mother and baby are getting the essential nutrients they need during pregnancy. This includes consuming plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated is important for overall health, including during pregnancy. Drinking plenty of water can help to prevent dehydration and maintain blood glucose levels.
By following a healthy diet, women with gestational diabetes can help to control their blood glucose levels, manage their weight, and ensure that they and their babies are getting the nutrients they need. This can help to reduce the risk of pregnancy complications and improve the overall health of both the mother and the baby.
Exercise
Exercise plays a crucial role in gestational diabetes treatments, as regular physical activity can effectively help to control blood glucose levels. Exercise improves insulin sensitivity, which allows the body to use insulin more efficiently to transport glucose from the blood into cells for energy. By improving insulin sensitivity and lowering blood glucose levels, exercise can help to prevent the development of gestational diabetes or manage the condition if it has already developed.
Real-life examples demonstrate the practical significance of exercise in gestational diabetes treatments. Studies have shown that women with gestational diabetes who participate in regular exercise programs have lower blood glucose levels, reduced insulin resistance, and a decreased risk of pregnancy complications, such as macrosomia and pre-eclampsia. Exercise can also help to improve overall fitness and well-being during pregnancy, which can benefit both the mother and the baby.
Understanding the connection between exercise and blood glucose control is essential for effective gestational diabetes treatments. By incorporating regular physical activity into their daily routines, women with gestational diabetes can help to manage their blood glucose levels, improve their overall health, and reduce the risk of pregnancy complications. Healthcare providers should encourage and support women with gestational diabetes to engage in regular exercise as part of their treatment plans.
Monitoring
Regular blood glucose monitoring is an essential component of gestational diabetes treatments, providing valuable information that guides treatment decisions and helps prevent complications. By tracking blood glucose levels, healthcare providers and individuals with gestational diabetes can assess the effectiveness of treatment strategies and make necessary adjustments to ensure optimal blood sugar management.
-
Tracking progress
Regular blood glucose monitoring allows individuals with gestational diabetes to track their progress over time. By monitoring blood sugar levels before and after meals, they can identify patterns and trends, assess the impact of dietary choices and exercise, and make informed decisions about their lifestyle and treatment plan. -
Adjusting treatment
The information gathered from regular blood glucose monitoring helps healthcare providers make informed decisions about treatment plans. Based on the monitoring results, they can adjust insulin doses, recommend dietary modifications, or suggest changes to physical activity levels to optimize blood sugar control and prevent complications. -
Preventing complications
Regular blood glucose monitoring is crucial for preventing pregnancy complications associated with gestational diabetes. By identifying blood sugar levels that are too high or too low, individuals can take prompt action to correct them, reducing the risk of developing serious complications such as pre-eclampsia, macrosomia, or premature birth. -
Empowering individuals
Regular blood glucose monitoring empowers individuals with gestational diabetes to take an active role in managing their condition. By providing them with real-time information about their blood sugar levels, they can make informed choices about their diet, exercise, and medication, promoting self-management and improving overall outcomes.
In conclusion, regular blood glucose monitoring is an integral part of gestational diabetes treatments, providing essential information for tracking progress, adjusting treatment plans, preventing complications, and empowering individuals to manage their condition effectively.
FAQs on Gestational Diabetes Treatments
Gestational diabetes treatments are an important part of managing blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about gestational diabetes treatments:
Question 1: What are the goals of gestational diabetes treatments?
Answer: The primary goal of gestational diabetes treatments is to maintain blood sugar levels within a healthy range throughout pregnancy. This helps to prevent complications for both the mother and the baby, such as premature birth, macrosomia (excessive birth weight), and pre-eclampsia (high blood pressure during pregnancy).
Question 2: What are the different types of gestational diabetes treatments?
Answer: Gestational diabetes treatments may include lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise, as well as medication, such as insulin. The specific treatment plan will vary depending on the individual’s needs and response to treatment.
Question 3: How often should I monitor my blood sugar levels?
Answer: The frequency of blood sugar monitoring will vary depending on the individual’s treatment plan and blood sugar levels. Your healthcare provider will recommend a specific monitoring schedule.
Question 4: What should I do if my blood sugar levels are too high or too low?
Answer: If your blood sugar levels are too high or too low, it is important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions. This may include adjusting your diet, exercise, or medication.
Question 5: Can gestational diabetes be cured?
Answer: Gestational diabetes typically goes away after pregnancy. However, women who have had gestational diabetes are at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Question 6: What are the long-term effects of gestational diabetes?
Answer: Gestational diabetes can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and other health problems later in life. It is important to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for managing your blood sugar levels and reducing your risk of long-term complications.
Summary: Gestational diabetes treatments are essential for managing blood sugar levels during pregnancy and preventing complications for both the mother and the baby. By following your healthcare provider’s instructions and maintaining healthy blood sugar levels, you can help to ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
Transition: For more information on gestational diabetes treatments, please consult with your healthcare provider or visit the website of the American Diabetes Association.
Gestational Diabetes Treatment Tips
Gestational diabetes treatments aim to manage blood sugar levels during pregnancy, ensuring the well-being of both the mother and the developing fetus. Here are some tips to effectively manage gestational diabetes:
Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly.
Regular blood sugar monitoring helps you track your progress and adjust your treatment plan as needed. Your healthcare provider will recommend a specific monitoring schedule based on your individual needs.
Follow a healthy diet.
Eating a healthy diet is essential for managing gestational diabetes. Focus on consuming whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean protein. Limit your intake of sugary drinks, processed foods, and saturated and trans fats.
Get regular exercise.
Physical activity helps to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
Take your medication as prescribed.
If medication is part of your treatment plan, take it exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Insulin is the most commonly used medication for gestational diabetes.
Attend all prenatal appointments.
Regular prenatal check-ups are crucial for monitoring your and your baby’s health, adjusting your treatment plan, and identifying any potential complications.
Get enough sleep.
Sleep deprivation can affect blood sugar control. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
Manage stress.
Stress can also affect blood sugar levels. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, yoga, or meditation.
Quit smoking.
Smoking can worsen gestational diabetes and increase the risk of pregnancy complications. If you smoke, quitting is the best thing you can do for your health and your baby’s health.
Summary: By following these tips and working closely with your healthcare provider, you can effectively manage your gestational diabetes, reduce the risk of complications, and ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
Transition: For more information and personalized guidance, consult with your healthcare provider or visit the website of the American Diabetes Association.
Gestational Diabetes Treatments
Gestational diabetes treatments are essential for managing blood glucose levels during pregnancy and reducing the risk of pregnancy complications for both the mother and the baby. Lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise, play a crucial role in managing gestational diabetes, and medication, such as insulin, may be necessary in some cases. Regular blood glucose monitoring, prenatal care, and close collaboration with healthcare providers are vital throughout the treatment process.
By effectively managing gestational diabetes, individuals can significantly improve pregnancy outcomes and ensure the health and well-being of both themselves and their babies. Continued research and advancements in gestational diabetes treatments hold promise for further improving care and reducing the impact of this condition on pregnant individuals and their families.
Youtube Video: