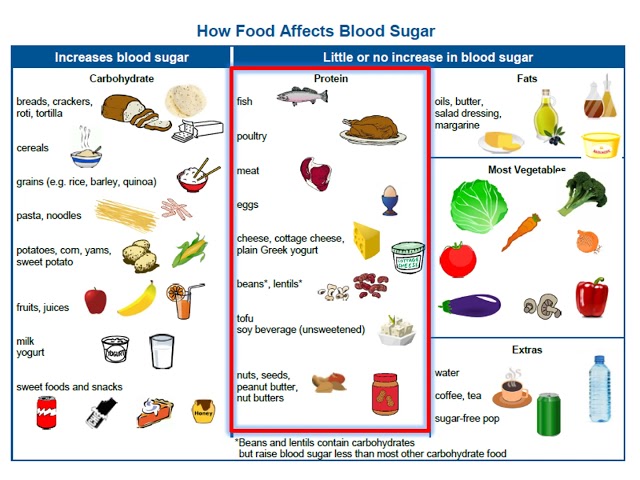
Foods for diabetics are foods that are safe for people with diabetes to eat. They are typically low in sugar and carbohydrates, and high in fiber. This helps to keep blood sugar levels stable and prevent spikes. Some examples of foods for diabetics include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
Eating a healthy diet is essential for people with diabetes. It can help to control blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of complications, and improve overall health. Foods for diabetics are an important part of a healthy diet. They can help people with diabetes to manage their condition and live a full and active life.
There is no one-size-fits-all diet for people with diabetes. The best diet for you will depend on your individual needs and preferences. However, there are some general guidelines that you can follow. These include:
- Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables.
- Choose whole grains over refined grains.
- Limit your intake of sugar and processed foods.
- Choose lean protein sources.
- Get regular exercise.
If you have diabetes, talk to your doctor or a registered dietitian about the best diet for you.
Foods for Diabetics
Foods for diabetics are an essential part of managing diabetes. They help to keep blood sugar levels stable and prevent complications. Key aspects of foods for diabetics include:
- Low in sugar
- Low in carbohydrates
- High in fiber
- Low in fat
- Low in sodium
- Rich in vitamins and minerals
These aspects are important because they help to control blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications. For example, foods that are low in sugar and carbohydrates help to prevent spikes in blood sugar levels. Foods that are high in fiber help to slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream. Foods that are low in fat and sodium help to reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke. Foods that are rich in vitamins and minerals help to maintain overall health and well-being.
Low in Sugar
Foods that are low in sugar are an important part of a diabetic diet. This is because sugar can cause blood sugar levels to spike, which can be dangerous for people with diabetes. Eating foods that are low in sugar helps to keep blood sugar levels stable and prevents complications.
There are many different ways to reduce your sugar intake. One way is to choose foods that are naturally low in sugar, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Another way is to limit your intake of processed foods, which often contain added sugar. You should also avoid sugary drinks, such as soda, juice, and sports drinks.
Eating a diet that is low in sugar can be challenging, but it is important for people with diabetes. By following these tips, you can help to keep your blood sugar levels under control and reduce your risk of complications.
Low in carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are an essential macronutrient that provides the body with energy. However, people with diabetes need to be careful about their carbohydrate intake because eating too many carbohydrates can cause blood sugar levels to spike. Foods that are low in carbohydrates are an important part of a diabetic diet because they help to keep blood sugar levels stable and prevent complications.
-
Glycemic index
The glycemic index (GI) is a measure of how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. Foods with a low GI release sugar slowly into the bloodstream, which helps to prevent spikes in blood sugar levels. Foods for diabetics should have a low GI.
-
Fiber
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that cannot be digested by the body. It helps to slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, which helps to keep blood sugar levels stable. Foods for diabetics should be high in fiber.
-
Portion size
The amount of carbohydrates you eat at one time can also affect your blood sugar levels. Eating large portions of carbohydrates can cause blood sugar levels to spike. People with diabetes should eat small, frequent meals to help keep their blood sugar levels stable.
Eating a diet that is low in carbohydrates can be challenging, but it is important for people with diabetes. By following these tips, you can help to keep your blood sugar levels under control and reduce your risk of complications.
High in fiber
Foods that are high in fiber are an important part of a diabetic diet. This is because fiber helps to slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, which helps to keep blood sugar levels stable. This is important for people with diabetes because high blood sugar levels can lead to a number of complications, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness.
There are two types of fiber: soluble fiber and insoluble fiber. Soluble fiber dissolves in water and forms a gel-like substance in the stomach. This gel helps to slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream. Insoluble fiber does not dissolve in water and adds bulk to the stool. This helps to keep the digestive system moving and can help to prevent constipation.
Good sources of soluble fiber include oats, beans, lentils, apples, and pears. Good sources of insoluble fiber include wheat bran, vegetables, and whole grains. People with diabetes should aim to eat 25-30 grams of fiber per day. This can be achieved by eating a variety of high-fiber foods throughout the day.
Eating a diet that is high in fiber can help people with diabetes to manage their blood sugar levels and reduce their risk of complications. It can also help to improve overall health and well-being.
Low in Fat
A crucial aspect of “foods for diabetics” lies in their low-fat content. Understanding this facet is essential in managing blood sugar levels and preventing diabetes-related complications.
-
Saturated and Trans Fats
Foods for diabetics should be low in saturated and trans fats. Saturated fats, primarily found in animal products, can raise LDL cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart disease. Trans fats, often found in processed foods, are even more harmful, contributing to inflammation and insulin resistance.
-
Healthy Fat Sources
While minimizing unhealthy fats is crucial, incorporating healthy fats into a diabetic diet is equally important. Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, found in olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds, can improve cholesterol levels and reduce inflammation.
-
Fat Reduction Techniques
To reduce fat intake, grilling, baking, or steaming cooking methods are recommended over frying. Removing visible fat from meats and choosing lean protein sources can also significantly lower fat consumption.
-
Mindful Food Choices
Making mindful food choices is essential. Reading food labels carefully, paying attention to serving sizes, and avoiding processed and fast foods can help individuals with diabetes manage their fat intake effectively.
In summary, consuming foods for diabetics that are low in fat, particularly saturated and trans fats, is crucial for maintaining optimal blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of cardiovascular complications commonly associated with diabetes.
Low in sodium
Understanding the significance of “low in sodium” in the context of “foods for diabetics” is crucial for effective diabetes management. Here’s a detailed exploration of this facet:
-
Elevated Blood Pressure
High sodium intake can contribute to elevated blood pressure, a common complication in diabetes. Excess sodium retains water in the body, increasing blood volume and putting strain on the heart. Maintaining a low-sodium diet helps regulate blood pressure and reduces the risk of heart disease.
-
Kidney Function
Kidneys play a vital role in regulating sodium levels in the body. Diabetes can impair kidney function, making it challenging for the kidneys to excrete excess sodium. A low-sodium diet reduces the burden on the kidneys and helps maintain their health.
-
Insulin Sensitivity
Research suggests that a high-sodium diet may impair insulin sensitivity, making it harder for the body to use insulin effectively. Insulin resistance can lead to elevated blood sugar levels, which is a primary concern in diabetes management.
-
Fluid Retention
Excessive sodium intake can cause fluid retention, leading to swelling in the hands, feet, and ankles. A low-sodium diet helps reduce fluid retention and promotes overall comfort.
In summary, adhering to a low-sodium diet is an essential aspect of “foods for diabetics.” It helps regulate blood pressure, supports kidney function, improves insulin sensitivity, and reduces fluid retention, all contributing to better diabetes management and overall health.
Rich in vitamins and minerals
In the context of “foods for diabetics,” understanding the significance of “rich in vitamins and minerals” is crucial for maintaining optimal health and managing blood sugar levels effectively.
-
Nutrient Absorption
Diabetes can affect the absorption and utilization of essential vitamins and minerals. Consuming foods rich in these micronutrients helps replenish depleted stores and ensures the body has the resources it needs to function properly.
-
Immunity and Infection
A diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports a healthy immune system, which is essential for fighting off infections and promoting overall well-being. Individuals with diabetes are more susceptible to infections, so a nutrient-dense diet is crucial.
-
Wound Healing
Proper wound healing is vital for people with diabetes. Vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin C and zinc, play a crucial role in collagen production and tissue repair, facilitating faster and more effective wound healing.
-
Nerve Health
Diabetes can damage nerves, leading to neuropathy. Vitamins like vitamin B12 and minerals like magnesium are essential for maintaining nerve health and preventing or slowing nerve damage.
In summary, consuming “foods for diabetics” that are rich in vitamins and minerals is essential for managing blood sugar levels, supporting overall health, and preventing or mitigating diabetes-related complications. By ensuring a balanced intake of essential micronutrients, individuals with diabetes can improve their quality of life and long-term health outcomes.
FAQs on Foods for Diabetics
Understanding the dietary needs and restrictions associated with diabetes can be crucial for effective management. Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about “foods for diabetics”:
Question 1: What are the key dietary considerations for people with diabetes?
Answer: Individuals with diabetes should focus on consuming foods that are low in sugar, carbohydrates, and fat, while being rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. This helps regulate blood sugar levels, prevents spikes, and supports overall health.
Question 2: Why is it important to limit sugar intake for diabetics?
Answer: Sugar can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels, making it difficult to manage diabetes. Consuming foods low in sugar helps prevent these spikes and promotes stable blood sugar levels.
Question 3: How does fiber benefit people with diabetes?
Answer: Fiber slows down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, helping to prevent blood sugar spikes and promoting a feeling of fullness. This aids in managing blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of complications.
Question 4: Why should diabetics be mindful of their fat intake?
Answer: Excessive fat intake, particularly saturated and trans fats, can contribute to high cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease, a common complication in diabetes.
Question 5: How can vitamins and minerals support diabetes management?
Answer: Vitamins and minerals play a crucial role in maintaining overall health and supporting the body’s functions. Consuming foods rich in these micronutrients helps prevent deficiencies, supports the immune system, and promotes nerve health, which is important for diabetics.
Question 6: What are some practical tips for following a diabetic diet?
Answer: Prioritize whole, unprocessed foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. Read food labels carefully to monitor sugar and carbohydrate content. Consider consulting with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
In summary, understanding the dietary considerations for “foods for diabetics” is essential for effective diabetes management. By adhering to these guidelines, individuals can maintain stable blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of complications, and improve their overall health and well-being.
Transition to the next article section:
For further insights and specific dietary recommendations, consult the following sections of this article: [Insert hyperlinks to relevant sections within the article]
Tips for Foods for Diabetics
Managing diabetes through dietary choices is essential for maintaining stable blood sugar levels and preventing complications. Here are some valuable tips to consider:
Tip 1: Prioritize Whole, Unprocessed Foods
Focus on consuming whole, unprocessed foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. These foods are rich in essential nutrients, fiber, and antioxidants, which support overall health and well-being.
Tip 2: Limit Sugar and Processed Carbohydrates
Sugar and processed carbohydrates can cause spikes in blood sugar levels. Limit sugary drinks, processed snacks, and white bread in favor of whole grains, fruits, and vegetables that provide sustained energy.
Tip 3: Choose Lean Protein Sources
Lean protein sources, such as fish, poultry, and beans, help manage blood sugar levels and promote satiety. They slow down digestion and prevent blood sugar spikes compared to fatty meats.
Tip 4: Include Healthy Fats
Incorporate healthy fats into your diet, such as those found in olive oil, avocados, and nuts. These fats support heart health, reduce inflammation, and promote a feeling of fullness.
Tip 5: Read Food Labels Carefully
Pay attention to food labels when selecting packaged foods. Monitor sugar content, carbohydrate count, and serving sizes to make informed choices and manage your blood sugar effectively.
Tip 6: Stay Hydrated
Staying hydrated is crucial for overall health and blood sugar control. Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help flush out excess sugar and support kidney function.
Tip 7: Consult a Healthcare Professional or Registered Dietitian
Seek guidance from a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized advice and support. They can provide tailored recommendations based on your individual needs and health goals.
By following these tips and adhering to a balanced diet, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their blood sugar levels and improve their overall health outcomes.
Transition to the article’s conclusion:
In conclusion, adopting these tips can empower you to make informed dietary choices that support your diabetes management plan. Remember to prioritize whole, unprocessed foods, limit sugar and processed carbohydrates, choose lean protein sources, and consult with healthcare professionals for personalized guidance. By taking control of your diet, you can live a healthier and more fulfilling life with diabetes.
Conclusion
In managing diabetes, understanding the significance of “foods for diabetics” is paramount. This article has explored the crucial aspects of such foods, emphasizing their low sugar, carbohydrate, and fat content, while highlighting their richness in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. By adhering to these dietary considerations, individuals with diabetes can effectively regulate blood sugar levels, prevent complications, and improve their overall health and well-being.
Remember, adopting a balanced diet tailored to your individual needs is essential. Consult with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians for personalized guidance. Empower yourself with knowledge and make informed choices about the foods you consume. By doing so, you can successfully manage your diabetes and live a fulfilling and healthy life.
Youtube Video: