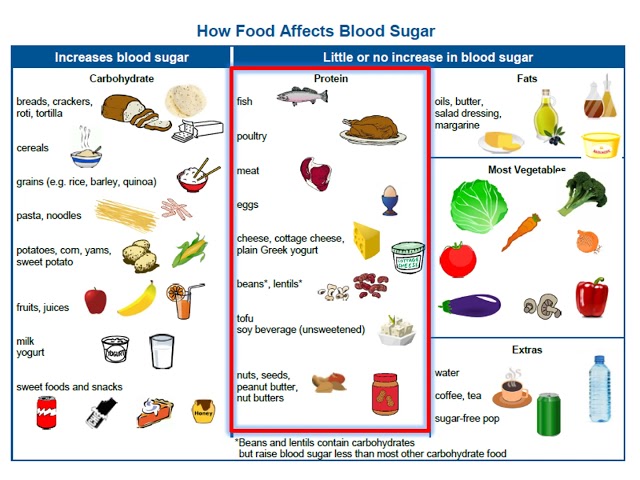
When we talk about “foods diabetics can eat,” we refer to foods that are suitable for individuals with diabetes, a condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels. These foods help manage blood sugar levels, promoting overall health and well-being.
Following a diabetes-friendly diet is essential for managing blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes. A balanced diet rich in fiber, lean protein, and healthy fats can help individuals with diabetes maintain optimal blood sugar control. Fruits, vegetables, and whole grains are excellent sources of fiber, while fish, poultry, and beans provide lean protein. Including healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil can also support heart health, often a concern for individuals with diabetes.
Navigating food choices with diabetes can be challenging, but with proper guidance and support, individuals can make informed decisions that align with their dietary needs and health goals. Registered dietitians or other qualified healthcare professionals can provide personalized advice and create tailored meal plans to meet specific dietary requirements.
Foods Diabetics Can Eat
For individuals with diabetes, managing blood sugar levels is crucial for maintaining good health. Following a diabetes-friendly diet is essential in achieving this goal. Here are six key aspects to consider when selecting foods diabetics can eat:
- Blood Sugar Control: Choose foods that help regulate blood sugar levels, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Fiber Intake: Include plenty of fiber in your diet to slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream.
- Lean Protein: Opt for lean protein sources like fish, poultry, and beans to promote satiety and help manage blood sugar levels.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporate healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil to support heart health.
- Portion Control: Pay attention to portion sizes to avoid consuming excessive calories and carbohydrates.
- Glycemic Index: Consider the glycemic index of foods to choose those that have a lower impact on blood sugar levels.
These aspects are interconnected and play a vital role in managing diabetes. By focusing on blood sugar control, fiber intake, lean protein, healthy fats, portion control, and glycemic index, individuals with diabetes can make informed food choices that support their overall health and well-being.
Blood Sugar Control
Managing blood sugar levels is paramount for individuals with diabetes. Consuming foods that help regulate blood sugar levels is a cornerstone of a diabetes-friendly diet. Fruits, vegetables, and whole grains are excellent choices in this regard.
Fruits and vegetables are naturally low in carbohydrates and calories, making them ideal for individuals with diabetes who need to monitor their carbohydrate intake. They are also rich in fiber, which slows down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, preventing spikes in blood sugar levels. Whole grains, such as brown rice, quinoa, and oatmeal, are also good sources of fiber and have a lower glycemic index compared to refined grains. This means they release sugar more slowly into the bloodstream, helping to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Including plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in the diet can significantly improve blood sugar control and reduce the risk of developing diabetes-related complications. These foods are not only nutritious but also versatile and can be incorporated into various meals and snacks throughout the day.
Fiber Intake
Fiber intake is a crucial aspect of “foods diabetics can eat.” Dietary fiber plays a vital role in regulating blood sugar levels, making it an essential component of a diabetes-friendly diet. When individuals with diabetes consume high-fiber foods, the fiber content slows down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, preventing spikes in blood sugar levels after meals.
Soluble fiber, a type of fiber found in foods like oatmeal, beans, and apples, forms a gel-like substance in the digestive tract, further delaying the absorption of sugar. This helps maintain stable blood sugar levels and reduces the risk of developing diabetes-related complications such as heart disease and stroke.
Incorporating adequate fiber into the diet can be achieved by consuming a variety of fiber-rich foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. By making smart food choices and including plenty of fiber in their daily meals and snacks, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their blood sugar levels and improve their overall health and well-being.
Lean Protein
In the context of “foods diabetics can eat,” lean protein plays a significant role in managing blood sugar levels and overall health. Unlike carbohydrates, which can cause spikes in blood sugar levels, lean protein is digested and absorbed more slowly, promoting satiety and helping to regulate blood sugar levels.
Including lean protein sources like fish, poultry, and beans in a diabetes-friendly diet offers several benefits. Firstly, these foods are low in carbohydrates, making them suitable for individuals with diabetes who need to monitor their carbohydrate intake. Secondly, lean protein helps slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, preventing post-meal spikes in blood sugar levels. Additionally, lean protein promotes satiety and fullness, reducing the likelihood of overeating and helping individuals maintain a healthy weight.
Incorporating lean protein into the diet can be achieved through various meal planning strategies. For breakfast, individuals can include eggs, Greek yogurt, or tofu in their meals. During lunch and dinner, lean protein sources like grilled chicken, fish, or beans can be paired with non-starchy vegetables and whole grains. By making smart food choices and including adequate lean protein in their daily meals and snacks, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their blood sugar levels and improve their overall health and well-being.
Healthy Fats
In the context of “foods diabetics can eat,” healthy fats play a crucial role in supporting heart health and overall well-being. While individuals with diabetes need to be mindful of their carbohydrate and sugar intake, incorporating healthy fats into their diet is essential for several reasons.
Unlike saturated and trans fats, which can raise cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease, healthy fats have the opposite effect. They help lower LDL (bad) cholesterol and raise HDL (good) cholesterol, thus promoting heart health.
Additionally, healthy fats are digested and absorbed more slowly than carbohydrates, which helps prevent spikes in blood sugar levels after meals. This slow and steady release of energy can help individuals with diabetes manage their blood sugar levels more effectively.
Good sources of healthy fats for individuals with diabetes include avocados, nuts, olive oil, and fatty fish like salmon and tuna. By incorporating these foods into their daily meals and snacks, individuals with diabetes can support their heart health, improve their blood sugar control, and reduce their risk of developing diabetes-related complications.
Portion Control
Individuals with diabetes need to be mindful of their calorie and carbohydrate intake to manage their blood sugar levels effectively. Portion control is a crucial aspect of “foods diabetics can eat” because it helps prevent overconsumption and supports blood sugar control.
- Understanding Serving Sizes: Understanding recommended serving sizes for different food groups is essential for portion control. Food labels and measuring cups/spoons can help individuals accurately measure portions to avoid consuming excessive amounts.
- Plate Method: The plate method is a simple visual guide for portion control. Fill half the plate with non-starchy vegetables, one-quarter with lean protein, and one-quarter with whole grains or starchy vegetables.
- Mindful Eating: Paying attention to hunger cues and eating slowly can help individuals avoid overeating. Eating meals without distractions and taking breaks during meals can promote mindful eating.
- Meal Planning: Planning meals and snacks ahead of time can help individuals make healthier choices and avoid impulsive eating. Pre-portioning snacks and meals can also support portion control.
By practicing portion control, individuals with diabetes can better manage their calorie and carbohydrate intake, leading to improved blood sugar control and reduced risk of diabetes-related complications.
Glycemic Index
When considering “foods diabetics can eat,” understanding the glycemic index (GI) of foods is crucial. The GI measures the impact of carbohydrate-containing foods on blood sugar levels. Foods with a high GI release sugar rapidly into the bloodstream, causing spikes in blood sugar levels. In contrast, foods with a low GI release sugar more slowly, resulting in a more gradual rise in blood sugar levels.
- GI and Blood Sugar Control: Individuals with diabetes need to be mindful of the GI of foods they consume. Choosing foods with a low GI can help prevent blood sugar spikes and promote better blood sugar control.
- GI and Diabetes Management: Eating a diet rich in low-GI foods has been shown to improve glycemic control in individuals with type 2 diabetes. It can also reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes in individuals at risk.
- GI and Heart Health: High-GI foods have been linked to an increased risk of heart disease. Consuming a diet rich in low-GI foods may benefit heart health in individuals with diabetes, who are at an increased risk of cardiovascular complications.
- GI and Weight Management: Low-GI foods promote satiety and fullness, which can aid in weight management. This is beneficial for individuals with diabetes who are overweight or obese, as weight loss can improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control.
Incorporating the glycemic index into food choices is an important aspect of diabetes management. By opting for foods with a lower GI, individuals with diabetes can better manage their blood sugar levels, reduce their risk of diabetes-related complications, and improve their overall health and well-being.
FAQs
Understanding “foods diabetics can eat” is crucial for individuals with diabetes to manage their blood sugar levels and maintain good health. Here are answers to some frequently asked questions on this topic:
Question 1: What types of foods should diabetics focus on eating?
Individuals with diabetes should focus on consuming foods that are low in carbohydrates and have a low glycemic index (GI). These include non-starchy vegetables, lean protein, and healthy fats. Whole grains and fruits can also be included in moderation.
Question 2: What foods should diabetics avoid or limit?
Diabetics should limit their intake of foods high in carbohydrates, such as sugary drinks, processed foods, and white bread. They should also avoid foods high in saturated and trans fats, as these can increase cholesterol levels and raise the risk of heart disease.
Question 3: How does fiber help diabetics?
Fiber slows down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, which helps prevent spikes in blood sugar levels after meals. Soluble fiber, found in foods like oats and beans, is particularly beneficial for diabetics.
Question 4: What is the glycemic index and why is it important for diabetics?
The glycemic index measures how quickly a carbohydrate-containing food raises blood sugar levels. Diabetics should opt for foods with a low GI, as these foods release sugar more slowly into the bloodstream.
Question 5: Can diabetics eat fruit?
Yes, diabetics can eat fruit in moderation. Fruits contain natural sugars, but they also provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Choosing fruits with a low GI, such as berries and apples, is recommended.
Question 6: How can diabetics make healthy food choices when eating out?
When eating out, diabetics should look for restaurants that offer grilled, baked, or steamed dishes. They should also check the menu for nutritional information and opt for dishes that are lower in carbohydrates and fat.
Understanding these FAQs can help individuals with diabetes make informed food choices and effectively manage their condition.
Transition to the next article section:
In addition to dietary considerations, regular exercise and monitoring blood sugar levels are essential for managing diabetes. Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and support.
Tips for Choosing Foods Diabetics Can Eat
Managing diabetes effectively requires careful attention to diet. Here are some tips to guide individuals with diabetes in making informed food choices:
Tip 1: Focus on Non-Starchy Vegetables:
Non-starchy vegetables, such as broccoli, cauliflower, and leafy greens, are low in carbohydrates and rich in fiber. They help regulate blood sugar levels and promote satiety.
Tip 2: Choose Lean Protein Sources:
Lean protein sources, such as chicken, fish, and beans, help stabilize blood sugar levels by slowing down the absorption of glucose. They also promote muscle growth and repair.
Tip 3: Opt for Healthy Fats:
Healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil support heart health and can help improve insulin sensitivity. They also promote satiety and reduce cravings.
Tip 4: Include Whole Grains in Moderation:
Whole grains, such as brown rice and quinoa, contain fiber and essential nutrients. Consuming them in moderation can help manage blood sugar levels and provide sustained energy.
Tip 5: Limit Processed Foods and Sugary Drinks:
Processed foods and sugary drinks are often high in carbohydrates and added sugars, which can rapidly raise blood sugar levels. Limiting their intake is crucial for effective diabetes management.
Tip 6: Read Food Labels Carefully:
Paying attention to food labels helps individuals understand the nutritional content of foods and make informed choices. Checking the carbohydrate content, glycemic index, and serving size is essential.
Tip 7: Consult with a Healthcare Professional:
A registered dietitian or other healthcare professional can provide personalized dietary guidance and support. They can help create a meal plan tailored to individual needs and goals.
Tip 8: Monitor Blood Sugar Levels Regularly:
Regular blood sugar monitoring allows individuals to track the impact of their food choices and make necessary adjustments to their diet and medication regimen.
By following these tips, individuals with diabetes can make informed food choices that support their blood sugar management, overall health, and well-being.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes effectively requires careful attention to dietary choices. Understanding “foods diabetics can eat” is paramount, as it empowers individuals to make informed decisions that support their blood sugar control and overall well-being.
This article explored the key aspects of diabetes-friendly foods, emphasizing the importance of focusing on non-starchy vegetables, lean protein sources, and healthy fats. It highlighted the significance of limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and understanding food labels to make informed choices.
Remember, dietary management is an integral part of diabetes care. By incorporating these principles into their daily lives, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their condition, reduce the risk of complications, and enjoy a healthier, more fulfilling life.
Youtube Video: