Diabeto is a combining form used in medical terms to indicate a relationship to diabetes, a condition characterized by excessive urination, thirst, and hunger, often accompanied by weight loss. It can also refer to diabetes insipidus, a condition characterized by excessive thirst and urination due to a deficiency of antidiuretic hormone.
Diabeto is derived from the Greek word “diabetes,” which means “siphon.” This term was first used to describe the excessive flow of urine that is a characteristic symptom of diabetes. Today, diabeto is used in a variety of medical terms, including diabetes mellitus, diabetes insipidus, and diabetic ketoacidosis.
Understanding diabeto is important for healthcare professionals and patients alike. By understanding the meaning of this term, healthcare professionals can better diagnose and treat diabetes and related conditions. Patients can also benefit from understanding diabeto, as it can help them to better understand their condition and make informed decisions about their care.
Diabeto
Diabeto is a combining form used in medical terms to indicate a relationship to diabetes, a condition characterized by excessive urination, thirst, and hunger, often accompanied by weight loss. It can also refer to diabetes insipidus, a condition characterized by excessive thirst and urination due to a deficiency of antidiuretic hormone.
- Etymology: Greek “diabetes,” meaning “siphon”
- Medical term: diabetes mellitus
- Medical term: diabetes insipidus
- Medical term: diabetic ketoacidosis
- Symptom: excessive urination
- Symptom: excessive thirst
- Symptom: weight loss
These key aspects of diabeto provide a comprehensive overview of the term and its relationship to diabetes and related conditions. By understanding these aspects, healthcare professionals and patients can gain a deeper understanding of diabetes and its management.
Etymology
The term “diabetes” is derived from the Greek word “diabetes,” which means “siphon.” This term was first used to describe the excessive flow of urine that is a characteristic symptom of diabetes. The word “siphon” is used to describe a tube that is used to draw liquid from one container to another. In the case of diabetes, the “siphon” is the kidneys, which are responsible for filtering waste products from the blood and producing urine. In diabetes, the kidneys are unable to filter out all of the glucose in the blood, which leads to an increase in the amount of urine produced.
-
Facet 1: Historical Context
The term “diabetes” was first used by the Greek physician Aretaeus of Cappadocia in the 2nd century AD. Aretaeus described diabetes as a condition characterized by excessive thirst, frequent urination, and weight loss. He also noted that the urine of people with diabetes was sweet to the taste, which is why the condition was later called “mellitus” (meaning “honey”).
-
Facet 2: Pathophysiology
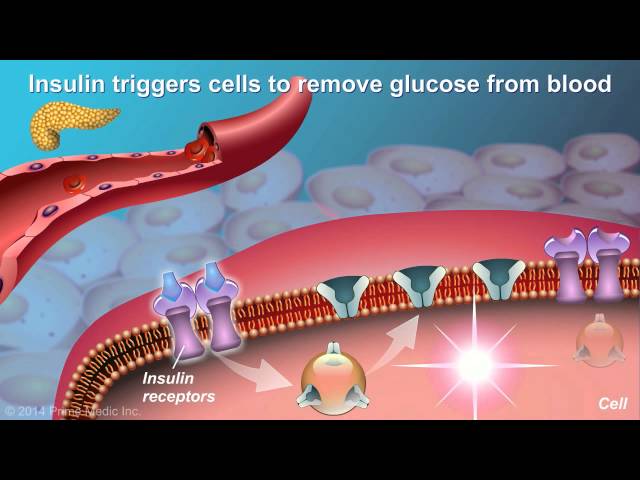
In diabetes, the body is unable to produce or use insulin, a hormone that is responsible for regulating blood sugar levels. Without insulin, the body is unable to take glucose from the blood and use it for energy. This leads to a build-up of glucose in the blood, which can cause a variety of symptoms, including excessive thirst, frequent urination, and weight loss.
-
Facet 3: Clinical Presentation
The symptoms of diabetes can vary depending on the type of diabetes and the severity of the condition. Some people with diabetes may only experience mild symptoms, while others may experience more severe symptoms that can lead to complications. Common symptoms of diabetes include excessive thirst, frequent urination, weight loss, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow-healing sores.
-
Facet 4: Treatment
The treatment for diabetes depends on the type of diabetes and the severity of the condition. Treatment options may include lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, as well as medication and insulin therapy. The goal of treatment is to control blood sugar levels and prevent complications.
The etymology of the term “diabetes” provides a valuable insight into the history and pathophysiology of this condition. By understanding the meaning of the term “diabetes,” healthcare professionals and patients can gain a better understanding of the condition and its management.
Medical term
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood sugar levels. It is the most common type of diabetes, accounting for about 90% of all cases. Diabetes mellitus is caused by the body’s inability to produce or use insulin, a hormone that is responsible for regulating blood sugar levels.
-
Facet 1: Pathophysiology
In diabetes mellitus, the body is unable to produce or use insulin, a hormone that is responsible for regulating blood sugar levels. Without insulin, the body is unable to take glucose from the blood and use it for energy. This leads to a build-up of glucose in the blood, which can cause a variety of symptoms, including excessive thirst, frequent urination, and weight loss.
-
Facet 2: Symptoms
The symptoms of diabetes mellitus can vary depending on the type of diabetes and the severity of the condition. Some people with diabetes mellitus may only experience mild symptoms, while others may experience more severe symptoms that can lead to complications. Common symptoms of diabetes mellitus include excessive thirst, frequent urination, weight loss, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow-healing sores.
-
Facet 3: Treatment
The treatment for diabetes mellitus depends on the type of diabetes and the severity of the condition. Treatment options may include lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, as well as medication and insulin therapy. The goal of treatment is to control blood sugar levels and prevent complications.
-
Facet 4: Complications
Diabetes mellitus can lead to a number of complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness. These complications are caused by the damage that high blood sugar levels can do to the blood vessels and organs.
Diabetes mellitus is a serious condition that can lead to a number of complications. However, with proper treatment and management, people with diabetes mellitus can live long and healthy lives.
Medical term
Diabetes insipidus is a condition characterized by excessive thirst and urination. It is caused by a deficiency of antidiuretic hormone (ADH), a hormone that helps the kidneys to reabsorb water. Diabetes insipidus is less common than diabetes mellitus, but it can be just as serious if left untreated.
-
Facet 1: Causes
Diabetes insipidus can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Damage to the pituitary gland, which produces ADH
- Damage to the hypothalamus, which controls the pituitary gland
- Certain medications, such as lithium and diuretics
- Genetic disorders
-
Facet 2: Symptoms
The symptoms of diabetes insipidus can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
- Excessive thirst
- Frequent urination
- Dehydration
- Fatigue
- Headaches
- Constipation
-
Facet 3: Diagnosis
Diabetes insipidus is diagnosed with a blood test that measures ADH levels. A urine test can also be used to measure the amount of water in the urine.
-
Facet 4: Treatment
The treatment for diabetes insipidus depends on the cause of the condition. Treatment options may include:
- ADH replacement therapy
- Medications to reduce urine output
- Lifestyle changes, such as increasing fluid intake
Diabetes insipidus is a serious condition that can lead to dehydration and other complications. However, with proper treatment, people with diabetes insipidus can live long and healthy lives.
Medical term
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body is unable to use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This process produces ketones, which can build up in the blood and cause DKA.
DKA is a medical emergency that can lead to coma and death if it is not treated promptly. Symptoms of DKA include:
- High blood sugar levels
- Ketones in the urine
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Dehydration
- Confusion
- Loss of consciousness
DKA is treated with fluids, insulin, and electrolytes. Treatment is typically given in a hospital setting. Once DKA is treated, the underlying cause of the condition must be addressed. This may involve changing the diabetes medication regimen, increasing physical activity, or losing weight.
DKA is a serious complication of diabetes, but it can be prevented with proper management of the condition. People with diabetes should monitor their blood sugar levels closely and follow their doctor’s instructions for managing their diabetes.
Symptom
Excessive urination is a common symptom of diabetes, a condition in which the body is unable to properly regulate blood sugar levels. When blood sugar levels are high, the kidneys work harder to filter out the excess glucose, which leads to increased urination. This can cause dehydration, fatigue, and other problems.
In some cases, excessive urination can be a sign of a more serious underlying condition, such as diabetes insipidus. Diabetes insipidus is a condition in which the body is unable to produce or respond to antidiuretic hormone (ADH), a hormone that helps the kidneys to reabsorb water. This can lead to excessive urination and dehydration.
If you are experiencing excessive urination, it is important to see a doctor to determine the cause and get appropriate treatment.
Symptom
Excessive thirst, also known as polydipsia, is a common symptom of diabetes, a condition in which the body is unable to properly regulate blood sugar levels. When blood sugar levels are high, the body tries to get rid of the excess glucose by excreting it in the urine. This leads to increased urination, which in turn can cause dehydration. Dehydration can lead to excessive thirst, as the body tries to replenish its fluids.
Excessive thirst is an important symptom of diabetes because it can be a sign that blood sugar levels are too high. If you are experiencing excessive thirst, it is important to see a doctor to get your blood sugar levels checked. Early diagnosis and treatment of diabetes can help to prevent serious complications, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness.
In some cases, excessive thirst can also be a sign of other underlying conditions, such as diabetes insipidus, a condition in which the body is unable to produce or respond to antidiuretic hormone (ADH). ADH is a hormone that helps the kidneys to reabsorb water. If you are experiencing excessive thirst and you do not have diabetes, it is important to see a doctor to rule out other possible causes.
Symptom
Weight loss is a common symptom of diabetes, a condition in which the body is unable to properly regulate blood sugar levels. When blood sugar levels are high, the body tries to get rid of the excess glucose by excreting it in the urine. This leads to increased urination, which in turn can cause dehydration and weight loss.
Weight loss can also be a sign of other underlying conditions, such as cancer, thyroid disease, or Addison’s disease. However, in people with diabetes, weight loss is often one of the first symptoms to appear. This is because the body is unable to use glucose for energy, so it starts to break down fat and muscle for energy instead. This process can lead to significant weight loss, even in people who are not eating less.
Weight loss can be a serious complication of diabetes, as it can lead to malnutrition and other health problems. It is important for people with diabetes to maintain a healthy weight and to monitor their blood sugar levels closely. If you are experiencing weight loss and you have diabetes, it is important to see a doctor to rule out other possible causes and to get your blood sugar levels under control.
FAQs about Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how the body turns food into energy. The main types of diabetes are type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes. Diabetes can cause many health problems, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, blindness, and amputation.
Question 1: What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how the body turns food into energy. It is caused by the pancreas not producing enough insulin, or the body not being able to use insulin properly.
Question 2: What are the symptoms of diabetes?
The symptoms of diabetes can include feeling very thirsty, needing to urinate often, feeling very hungry, losing weight without trying, having blurry vision, and feeling very tired.
Question 3: What are the risk factors for diabetes?
The risk factors for diabetes include being overweight or obese, having a family history of diabetes, being physically inactive, and having high blood pressure or high cholesterol.
Question 4: How is diabetes treated?
Diabetes is treated with a healthy diet, regular exercise, and medication. In some cases, insulin therapy may be necessary.
Question 5: Can diabetes be prevented?
There is no sure way to prevent diabetes, but there are things you can do to reduce your risk, such as eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Question 6: What are the complications of diabetes?
Diabetes can lead to a number of complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, blindness, and amputation.
Summary of key takeaways: Diabetes is a serious condition that can lead to many health problems. However, it can be managed with a healthy diet, regular exercise, and medication. If you have diabetes, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions and to make healthy lifestyle choices.
Transition to the next article section: If you have any questions about diabetes, please talk to your doctor or visit the website of the American Diabetes Association.
Tips for Managing Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic condition that can lead to many health problems. However, it can be managed with a healthy diet, regular exercise, and medication. If you have diabetes, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions and to make healthy lifestyle choices.
Tip 1: Eat a healthy diet.
A healthy diet for people with diabetes includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It also includes lean protein and low-fat dairy products. Limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats can help to control blood sugar levels.
Tip 2: Get regular exercise.
Regular exercise helps to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
Tip 3: Take your medication as prescribed.
If you have been prescribed medication for diabetes, it is important to take it as directed. Skipping doses or not taking your medication properly can lead to high blood sugar levels.
Tip 4: Monitor your blood sugar levels.
Monitoring your blood sugar levels can help you to track your progress and make necessary adjustments to your diet, exercise, or medication regimen. Talk to your doctor about how often you should check your blood sugar levels.
Tip 5: Make healthy lifestyle choices.
In addition to eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and taking your medication, there are other healthy lifestyle choices you can make to manage your diabetes. These include getting enough sleep, managing stress, and avoiding smoking.
Summary of key takeaways or benefits:
- Following these tips can help you to manage your diabetes and prevent serious health problems.
- It is important to talk to your doctor about the best way to manage your diabetes.
- Making healthy lifestyle choices can help you to live a long and healthy life with diabetes.
Transition to the article’s conclusion:
If you have any questions about diabetes, please talk to your doctor or visit the website of the American Diabetes Association.
Diabeto
This exploration of “diabeto” has illuminated its significance in the medical field, particularly in relation to diabetes and related conditions. The term “diabeto” serves as a valuable tool for healthcare professionals and patients alike, providing a common language for discussing and understanding the complexities of diabetes.
As we continue to unravel the intricacies of diabetes, the role of “diabeto” will undoubtedly remain central. By embracing a comprehensive approach that encompasses the latest research and advancements, we can empower individuals with diabetes to live healthier and more fulfilling lives.
Youtube Video: