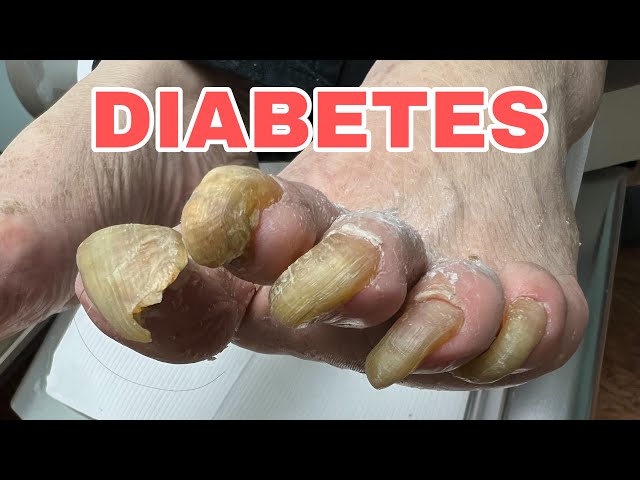
Diabetic toenails is a condition that affects people with diabetes. It is characterized by thick, yellowed, and brittle toenails. In severe cases, the toenails may become infected and even fall off.
Diabetic toenails are caused by poor circulation and nerve damage, both of which are common complications of diabetes. Poor circulation can lead to a lack of oxygen and nutrients to the toenails, which can cause them to become thick and brittle. Nerve damage can lead to a loss of sensation in the toes, which can make it difficult to notice injuries or infections.
Diabetic toenails can be a serious problem, as they can lead to infections and other complications. It is important for people with diabetes to take care of their feet and to see a doctor regularly for checkups.
There are a number of things that people with diabetes can do to prevent and treat diabetic toenails. These include:
- Keeping blood sugar levels under control
- Wearing comfortable shoes that fit well
- Inspecting feet daily for injuries or infections
- Trimming toenails carefully
- Seeing a doctor regularly for checkups
diabetic toenails
Diabetic toenails are a common complication of diabetes. They can be caused by a number of factors, including poor circulation, nerve damage, and high blood sugar levels. Diabetic toenails can be painful and unsightly, and they can also lead to more serious problems, such as infections and ulcers.
- Thickened: Diabetic toenails are often thicker than normal toenails.
- Discolored: Diabetic toenails may be yellowed, brown, or black.
- Brittle: Diabetic toenails are often brittle and.
- Painful: Diabetic toenails can be painful, especially if they are infected.
- Infected: Diabetic toenails can become infected if they are not properly cared for.
- Ulcerated: Diabetic toenails can lead to ulcers, which are open sores on the skin.
- Amputation: In severe cases, diabetic toenails can lead to amputation of the toe.
It is important for people with diabetes to take care of their feet and to see a doctor regularly for checkups. Diabetic toenails can be prevented and treated with proper care.
Thickened
Thickened toenails are a common symptom of diabetic toenails. This is because high blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels and nerves in the feet, which can lead to poor circulation and nerve damage. Poor circulation can cause a lack of oxygen and nutrients to the toenails, which can cause them to become thick and brittle. Nerve damage can lead to a loss of sensation in the toes, which can make it difficult to notice injuries or infections.
Thickened toenails can be a problem because they can make it difficult to wear shoes and can also be a sign of more serious problems, such as infections or ulcers. It is important for people with diabetes to take care of their feet and to see a doctor regularly for checkups.
There are a number of things that people with diabetes can do to prevent and treat thickened toenails. These include:
- Keeping blood sugar levels under control
- Wearing comfortable shoes that fit well
- Inspecting feet daily for injuries or infections
- Trimming toenails carefully
- Seeing a doctor regularly for checkups
Discolored
Discoloration of toenails is a common symptom of diabetic toenails. This is because high blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels and nerves in the feet, which can lead to poor circulation and nerve damage. Poor circulation can cause a lack of oxygen and nutrients to the toenails, which can cause them to become discolored.
-
Fungal infection
One of the most common causes of discolored toenails in people with diabetes is a fungal infection. Fungal infections can cause the toenails to become yellow, brown, or black. They can also cause the toenails to become thick and brittle.
-
Bacterial infection
Another common cause of discolored toenails in people with diabetes is a bacterial infection. Bacterial infections can cause the toenails to become red, swollen, and painful. They can also cause the toenails to discharge pus.
-
Trauma
Trauma to the toenails can also cause them to become discolored. Trauma can occur from stubbing the toe, wearing shoes that are too tight, or dropping something on the foot. Trauma to the toenails can cause them to become black and blue.
-
Medication side effects
Some medications can cause the toenails to become discolored. These medications include antibiotics, antimalarial drugs, and chemotherapy drugs.
It is important for people with diabetes to take care of their feet and to see a doctor regularly for checkups. Discolored toenails can be a sign of a more serious problem, such as an infection or ulcer. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent serious complications.
Brittle
Brittle toenails are a common symptom of diabetic toenails. This is because high blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels and nerves in the feet, which can lead to poor circulation and nerve damage. Poor circulation can cause a lack of oxygen and nutrients to the toenails, which can cause them to become brittle and easily broken.
Brittle toenails can be a problem because they can make it difficult to wear shoes and can also be a sign of more serious problems, such as infections or ulcers. It is important for people with diabetes to take care of their feet and to see a doctor regularly for checkups.
There are a number of things that people with diabetes can do to prevent and treat brittle toenails. These include:
- Keeping blood sugar levels under control
- Wearing comfortable shoes that fit well
- Inspecting feet daily for injuries or infections
- Trimming toenails carefully
- Seeing a doctor regularly for checkups
Painful
Diabetic toenails can be painful for a number of reasons. First, the thickened and discolored nails can put pressure on the surrounding skin and nerves, causing pain. Second, diabetic toenails are often more susceptible to infection, which can also cause pain. Finally, the nerve damage that is common in diabetes can lead to a loss of sensation in the feet, which can make it difficult to notice injuries or infections that could be causing pain.
It is important for people with diabetes to be aware of the potential for painful diabetic toenails and to take steps to prevent and treat them. This includes keeping blood sugar levels under control, wearing comfortable shoes that fit well, inspecting feet daily for injuries or infections, and trimming toenails carefully. If you have any pain in your toenails, it is important to see a doctor to rule out any underlying problems.
Painful diabetic toenails can be a serious problem, but they can be prevented and treated with proper care. By following these tips, you can help to keep your feet healthy and pain-free.
Infected
Diabetic toenails are a common complication of diabetes. They can be caused by a number of factors, including poor circulation, nerve damage, and high blood sugar levels. Diabetic toenails can be painful and unsightly, and they can also lead to more serious problems, such as infections and ulcers.
One of the most common problems associated with diabetic toenails is infection. Fungal and bacterial infections are particularly common in people with diabetes, and they can lead to a number of serious complications. Fungal infections can cause the toenails to become thick, discolored, and brittle. Bacterial infections can cause the toenails to become red, swollen, and painful. In severe cases, infections can spread to the bone and cause serious health problems.
It is important for people with diabetes to take care of their feet and to see a doctor regularly for checkups. Proper foot care can help to prevent infections and other complications. People with diabetes should also be aware of the signs and symptoms of infection, and they should seek medical attention if they suspect that they have an infection.
There are a number of things that people with diabetes can do to prevent and treat infections of the toenails. These include:
- Keeping blood sugar levels under control
- Wearing comfortable shoes that fit well
- Inspecting feet daily for injuries or infections
- Trimming toenails carefully
- Seeing a doctor regularly for checkups
Ulcerated
Diabetic toenails are a common complication of diabetes. They can be caused by a number of factors, including poor circulation, nerve damage, and high blood sugar levels. Diabetic toenails can be painful and unsightly, and they can also lead to more serious problems, such as infections and ulcers.
Ulcers are open sores on the skin that can develop when the skin is damaged. In people with diabetes, ulcers can develop on the feet due to poor circulation and nerve damage. Poor circulation can cause a lack of oxygen and nutrients to the skin, which can make it more susceptible to damage. Nerve damage can lead to a loss of sensation in the feet, which can make it difficult to notice injuries or infections that could lead to ulcers.
Ulcers on the feet can be a serious problem for people with diabetes. They can be painful and difficult to heal, and they can also lead to infections and other complications. In severe cases, ulcers can even lead to amputation of the toe or foot.
It is important for people with diabetes to take care of their feet and to see a doctor regularly for checkups. Proper foot care can help to prevent ulcers and other complications. People with diabetes should also be aware of the signs and symptoms of ulcers, and they should seek medical attention if they suspect that they have an ulcer.
Amputation
Diabetic toenails are a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to amputation of the toe. This is because diabetic toenails can cause infections and ulcers, which can eventually lead to tissue death and amputation. Amputation is a serious surgery that can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. It is important for people with diabetes to take care of their feet and to see a doctor regularly for checkups to prevent serious complications like amputation.
-
Infection
One of the most common complications of diabetic toenails is infection. Infections can occur when bacteria or fungi enter the nail bed through a crack or other opening in the nail. Infections can cause the nail to become discolored, swollen, and painful. If left untreated, infections can spread to the bone and other parts of the foot, leading to serious complications, including amputation.
-
Ulcers
Ulcers are open sores on the skin that can develop on the feet of people with diabetes due to poor circulation and nerve damage. Ulcers can be painful and difficult to heal, and they can also become infected. If left untreated, ulcers can lead to amputation of the toe or foot.
-
Tissue death
Tissue death can occur when the blood supply to a part of the body is cut off. In people with diabetes, tissue death can occur in the toes due to poor circulation. Tissue death can lead to amputation of the toe or foot.
-
Amputation
Amputation is the surgical removal of a body part. In people with diabetes, amputation may be necessary to remove a toe or foot that has been damaged by infection, ulcers, or tissue death. Amputation is a serious surgery that can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life.
It is important for people with diabetes to take care of their feet and to see a doctor regularly for checkups to prevent serious complications like amputation. People with diabetes should also be aware of the signs and symptoms of infection and ulcers, and they should seek medical attention if they suspect that they have either of these conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions About Diabetic Toenails
Diabetic toenails are a common complication of diabetes that can be painful, unsightly, and even lead to serious health problems. Here are some frequently asked questions about diabetic toenails:
Question 1: What causes diabetic toenails?
Diabetic toenails are caused by a combination of factors, including poor circulation, nerve damage, and high blood sugar levels. Poor circulation can cause a lack of oxygen and nutrients to the toenails, which can make them thick, discolored, and brittle. Nerve damage can lead to a loss of sensation in the toes, which can make it difficult to notice injuries or infections. High blood sugar levels can also contribute to the development of diabetic toenails.
Question 2: What are the symptoms of diabetic toenails?
Diabetic toenails can cause a variety of symptoms, including thickening of the nails, discoloration of the nails, brittleness of the nails, pain, and infection.
Question 3: How are diabetic toenails treated?
Treatment for diabetic toenails typically involves managing blood sugar levels, taking medication, and practicing good foot care. Managing blood sugar levels can help to prevent the development and progression of diabetic toenails. Medication can be used to treat infections or pain associated with diabetic toenails. Good foot care includes wearing comfortable shoes, inspecting the feet daily for injuries or infections, and trimming toenails carefully.
Question 4: Can diabetic toenails be prevented?
There is no sure way to prevent diabetic toenails, but there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing them. These steps include managing blood sugar levels, practicing good foot care, and wearing comfortable shoes.
Question 5: What are the complications of diabetic toenails?
Diabetic toenails can lead to a number of complications, including infections, ulcers, and amputation. Infections can occur when bacteria or fungi enter the nail bed through a crack or other opening in the nail. Ulcers are open sores on the skin that can develop on the feet of people with diabetes due to poor circulation and nerve damage. Amputation may be necessary to remove a toe or foot that has been damaged by infection, ulcers, or tissue death.
Question 6: When should I see a doctor about diabetic toenails?
You should see a doctor about diabetic toenails if you have any of the following symptoms: pain, swelling, redness, drainage, or changes in the appearance of the nail. You should also see a doctor if you have any underlying health conditions, such as diabetes, that increase your risk of developing diabetic toenails.
Summary of key takeaways or final thought:
Diabetic toenails are a common complication of diabetes that can be painful, unsightly, and even lead to serious health problems. It is important to manage blood sugar levels, practice good foot care, and see a doctor regularly for checkups to prevent and treat diabetic toenails.
Transition to the next article section:
If you have any questions or concerns about diabetic toenails, please speak to your doctor.
Tips for Managing Diabetic Toenails
Diabetic toenails are a common complication of diabetes that can be painful, unsightly, and even lead to serious health problems. However, there are a number of things that people with diabetes can do to prevent and treat diabetic toenails.
Tip 1: Keep blood sugar levels under control
High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels and nerves in the feet, which can lead to poor circulation and nerve damage. Poor circulation can cause a lack of oxygen and nutrients to the toenails, which can make them thick, discolored, and brittle. Nerve damage can lead to a loss of sensation in the toes, which can make it difficult to notice injuries or infections.
Tip 2: Wear comfortable shoes that fit well
Wearing shoes that are too tight or too loose can put pressure on the toenails and cause them to become damaged. It is important to wear shoes that fit well and that provide support for the feet.
Tip 3: Inspect feet daily for injuries or infections
People with diabetes should inspect their feet daily for any signs of injuries or infections. This includes checking for cuts, blisters, redness, swelling, and drainage. If you notice any changes in the appearance of your toenails or feet, it is important to see a doctor right away.
Tip 4: Trim toenails carefully
Trimming toenails too short or too irregularly can increase the risk of developing ingrown toenails or other nail problems. It is important to trim toenails straight across and to file any sharp edges.
Tip 5: See a doctor regularly for checkups
People with diabetes should see a doctor regularly for checkups to monitor their blood sugar levels and to check for any signs of nerve damage or other complications. Early diagnosis and treatment of diabetic toenails can help to prevent serious complications.
Summary of key takeaways or benefits
Following these tips can help to prevent and treat diabetic toenails and to keep your feet healthy.
Transition to the article’s conclusion
If you have any questions or concerns about diabetic toenails, please speak to your doctor.
Conclusion
Diabetic toenails are a common complication of diabetes that can lead to serious health problems. However, there are a number of things that people with diabetes can do to prevent and treat diabetic toenails.
By following the tips outlined in this article, you can help to keep your feet healthy and prevent the development of diabetic toenails. If you have any questions or concerns about diabetic toenails, please speak to your doctor.
Youtube Video: