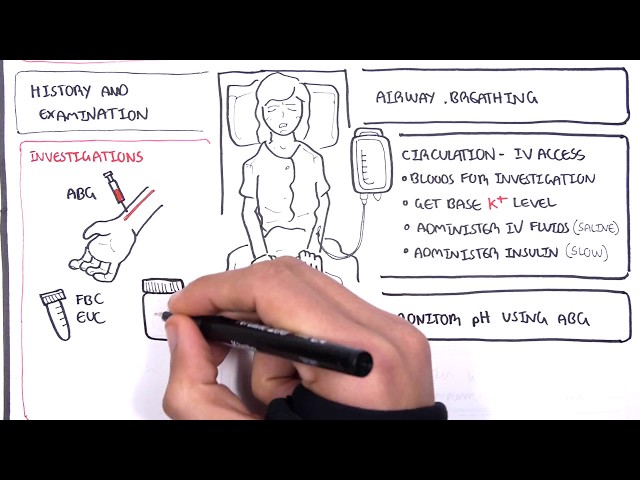
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This process produces ketones.
DKA can be life-threatening if it is not treated. Symptoms of DKA include:
- High blood sugar levels
- High levels of ketones in the blood or urine
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Confusion
- Loss of consciousness
DKA is treated with insulin and fluids. Insulin helps the body to use glucose for energy, which lowers blood sugar levels and ketone levels. Fluids help to prevent dehydration.
People with diabetes can prevent DKA by:
- Taking insulin as prescribed
- Monitoring blood sugar levels
- Eating a healthy diet
- Getting regular exercise
Diabetic Ketosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This process produces ketones. DKA can be life-threatening if it is not treated.
- Ketones: Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy.
- Insulin: Insulin helps the body to use glucose for energy.
- Blood sugar: High blood sugar levels can lead to DKA.
- Dehydration: DKA can lead to dehydration.
- Treatment: DKA is treated with insulin and fluids.
- Prevention: People with diabetes can prevent DKA by taking insulin as prescribed, monitoring blood sugar levels, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise.
- Complications: DKA can lead to serious complications, such as coma and death.
The key aspects of diabetic ketosis are all interconnected. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. This process is stimulated by high blood sugar levels. Insulin helps to lower blood sugar levels by allowing the body to use glucose for energy. Dehydration can occur when the body loses too much fluid, which can happen during DKA. Treatment for DKA involves administering insulin and fluids. People with diabetes can prevent DKA by taking insulin as prescribed, monitoring blood sugar levels, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise.
Ketones
Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. This process is called ketogenesis. Ketogenesis occurs when the body does not have enough glucose to use for energy. Glucose is the body’s preferred source of energy. When glucose levels are low, the body will start to break down fat for energy. This process produces ketones.
- Role of ketones: Ketones are a type of fuel that the body can use for energy. Ketones are produced in the liver. They are then released into the bloodstream and transported to cells throughout the body. Cells can use ketones for energy in the absence of glucose.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis: Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. DKA can occur when the body does not have enough insulin to use glucose for energy. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose enter cells.
- Symptoms of DKA: Symptoms of DKA include high blood sugar levels, high levels of ketones in the blood or urine, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, confusion, and loss of consciousness. DKA is a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment.
- Treatment of DKA: DKA is treated with insulin and fluids. Insulin helps the body to use glucose for energy, which lowers blood sugar levels and ketone levels. Fluids help to prevent dehydration.
Ketones are an important source of energy for the body. However, high levels of ketones can lead to DKA. People with diabetes need to be aware of the symptoms of DKA and seek medical attention immediately if they experience any of these symptoms.
Insulin
Insulin is a hormone that helps the body to use glucose for energy. Glucose is the body’s preferred source of energy. When glucose levels are low, the body will start to break down fat for energy. This process produces ketones. Ketones are a type of fuel that the body can use for energy. However, high levels of ketones can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA).
- Role of insulin in preventing DKA: Insulin helps to prevent DKA by allowing the body to use glucose for energy. When insulin levels are low, the body cannot use glucose for energy and will start to break down fat for energy. This process produces ketones. High levels of ketones can lead to DKA.
- Symptoms of DKA: Symptoms of DKA include high blood sugar levels, high levels of ketones in the blood or urine, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, confusion, and loss of consciousness. DKA is a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment.
- Treatment of DKA: DKA is treated with insulin and fluids. Insulin helps the body to use glucose for energy, which lowers blood sugar levels and ketone levels. Fluids help to prevent dehydration.
- Prevention of DKA: People with diabetes can prevent DKA by taking insulin as prescribed, monitoring blood sugar levels, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise.
Insulin is an important hormone that helps to prevent DKA. People with diabetes need to be aware of the symptoms of DKA and seek medical attention immediately if they experience any of these symptoms.
Blood sugar
High blood sugar levels are a major cause of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). DKA is a serious complication of diabetes that can be life-threatening if it is not treated. When blood sugar levels are high, the body cannot use glucose for energy. This causes the body to break down fat for energy, which produces ketones. Ketones are a type of acid that can build up in the blood and cause DKA.
Symptoms of DKA include:
- High blood sugar levels
- High levels of ketones in the blood or urine
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Confusion
- Loss of consciousness
DKA is treated with insulin and fluids. Insulin helps the body to use glucose for energy, which lowers blood sugar levels and ketone levels. Fluids help to prevent dehydration.
People with diabetes can prevent DKA by:
- Taking insulin as prescribed
- Monitoring blood sugar levels
- Eating a healthy diet
- Getting regular exercise
High blood sugar levels are a serious complication of diabetes. People with diabetes need to be aware of the symptoms of DKA and seek medical attention immediately if they experience any of these symptoms.
Dehydration
Dehydration is a serious complication of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). DKA is a condition that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. This process can lead to dehydration because the body loses fluids through the production of ketones.
Dehydration can also occur in people with diabetes who are not experiencing DKA. This is because high blood sugar levels can cause the body to lose fluids through urination.
Symptoms of dehydration include:
- Thirst
- Dry mouth
- Dark urine
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Confusion
- Loss of consciousness
Dehydration is a serious condition that can lead to organ damage and even death. It is important to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any symptoms of dehydration.
People with diabetes can prevent dehydration by:
- Drinking plenty of fluids
- Monitoring blood sugar levels
- Taking insulin as prescribed
- Eating a healthy diet
- Getting regular exercise
Dehydration is a serious complication of diabetic ketoacidosis. People with diabetes need to be aware of the symptoms of dehydration and seek medical attention immediately if they experience any of these symptoms.
Treatment
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can be life-threatening if it is not treated. DKA occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. This process can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
The primary treatment for DKA is insulin and fluids. Insulin helps the body to use glucose for energy, which lowers blood sugar levels and ketone levels. Fluids help to prevent dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
Treatment for DKA typically involves hospitalization. Intravenous (IV) fluids are given to correct dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. Insulin is also given intravenously to lower blood sugar levels and ketone levels.
Once blood sugar levels and ketone levels have been stabilized, the patient may be switched to oral medications. These medications may include insulin, oral diabetes medications, and fluids.
Treatment for DKA is essential to prevent serious complications, such as coma and death. People with diabetes need to be aware of the symptoms of DKA and seek medical attention immediately if they experience any of these symptoms.
Prevention
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can be life-threatening if it is not treated. DKA occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. This process can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
The primary treatment for DKA is insulin and fluids. Insulin helps the body to use glucose for energy, which lowers blood sugar levels and ketone levels. Fluids help to prevent dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
People with diabetes can prevent DKA by taking the following steps:
- Taking insulin as prescribed: Insulin is a hormone that helps the body to use glucose for energy. People with diabetes need to take insulin as prescribed in order to keep their blood sugar levels under control.
- Monitoring blood sugar levels: People with diabetes need to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly to make sure that they are within a healthy range. Monitoring blood sugar levels can help to prevent DKA by identifying high blood sugar levels early on.
- Eating a healthy diet: Eating a healthy diet can help to prevent DKA by keeping blood sugar levels under control. A healthy diet for people with diabetes includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Getting regular exercise: Getting regular exercise can help to prevent DKA by improving insulin sensitivity. Insulin sensitivity is the body’s ability to use insulin effectively.
By following these steps, people with diabetes can help to prevent DKA and other serious complications of diabetes.
Complications
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can be life-threatening if it is not treated. DKA occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. This process can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
- Coma: Coma is a state of unconsciousness from which a person cannot be awakened. DKA can lead to coma if it is not treated. Coma can occur when the body’s blood sugar levels become too low or too high.
- Death: DKA can be fatal if it is not treated. Death can occur from complications of DKA, such as coma, heart attack, or stroke.
It is important for people with diabetes to be aware of the symptoms of DKA and to seek medical attention immediately if they experience any of these symptoms.
FAQs on Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about DKA:
Question 1: What is diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)?
Answer: DKA is a condition that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones, which are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. This can happen when the body does not have enough insulin to use glucose for energy.
Question 2: What are the symptoms of DKA?
Answer: Symptoms of DKA include high blood sugar levels, high levels of ketones in the blood or urine, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, confusion, and loss of consciousness.
Question 3: What causes DKA?
Answer: DKA is most often caused by uncontrolled diabetes. It can also be triggered by other factors, such as infection, injury, or surgery.
Question 4: How is DKA treated?
Answer: DKA is treated with insulin and fluids. Insulin helps the body to use glucose for energy, which lowers blood sugar levels and ketone levels. Fluids help to prevent dehydration.
Question 5: How can DKA be prevented?
Answer: DKA can be prevented by managing diabetes carefully. This includes taking insulin as prescribed, monitoring blood sugar levels, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise.
Question 6: What are the complications of DKA?
Answer: DKA can lead to serious complications, such as coma and death. It is important to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any symptoms of DKA.
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious condition, but it can be managed with proper treatment and care. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment of DKA, you can help to prevent this life-threatening complication.
Talk to your doctor or diabetes care team for more information about DKA and how to prevent it.
Tips on Managing Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. Here are some tips for managing DKA:
Tip 1: Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly.
Monitoring your blood sugar levels regularly is the best way to prevent DKA. This is especially important if you are sick or under stress, as these factors can increase your risk of developing DKA.
Tip 2: Take your insulin as prescribed.
Insulin is a hormone that helps the body to use glucose for energy. People with diabetes need to take insulin to keep their blood sugar levels under control. If you do not take your insulin as prescribed, you are at increased risk of developing DKA.
Tip 3: Drink plenty of fluids.
Dehydration can worsen DKA. Drink plenty of fluids, such as water, broth, or clear juice. Avoid sugary drinks, as these can raise your blood sugar levels.
Tip 4: Eat a healthy diet.
Eating a healthy diet can help to keep your blood sugar levels under control and reduce your risk of developing DKA. Choose foods that are low in carbohydrates and high in fiber.
Tip 5: Get regular exercise.
Exercise can help to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. Get at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
Tip 6: See your doctor regularly.
See your doctor regularly for checkups and to discuss your diabetes management plan. Your doctor can help you to adjust your insulin dosage and make other changes to your treatment plan as needed.
Tip 7: Know the signs and symptoms of DKA.
Know the signs and symptoms of DKA so that you can seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of them. Symptoms of DKA include high blood sugar levels, high levels of ketones in the blood or urine, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, confusion, and loss of consciousness.
Tip 8: Carry a glucagon kit.
Carry a glucagon kit with you at all times in case of a severe hypoglycemic episode. Glucagon is a hormone that can raise blood sugar levels quickly.
By following these tips, you can help to manage your diabetes and reduce your risk of developing DKA.
Summary
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious complication of diabetes, but it can be managed with proper treatment and care. By following these tips, you can help to keep your blood sugar levels under control and reduce your risk of developing DKA.
Diabetic Ketosis
Diabetic ketosis is a serious complication of diabetes that can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. It occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones, which are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. This can happen when the body does not have enough insulin to use glucose for energy.
Symptoms of diabetic ketosis include high blood sugar levels, high levels of ketones in the blood or urine, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, confusion, and loss of consciousness. Diabetic ketosis is treated with insulin and fluids. Insulin helps the body to use glucose for energy, which lowers blood sugar levels and ketone levels. Fluids help to prevent dehydration.
Diabetic ketosis can be prevented by managing diabetes carefully. This includes taking insulin as prescribed, monitoring blood sugar levels, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise. If you have diabetes, it is important to be aware of the symptoms of diabetic ketosis and to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of them.
Youtube Video: