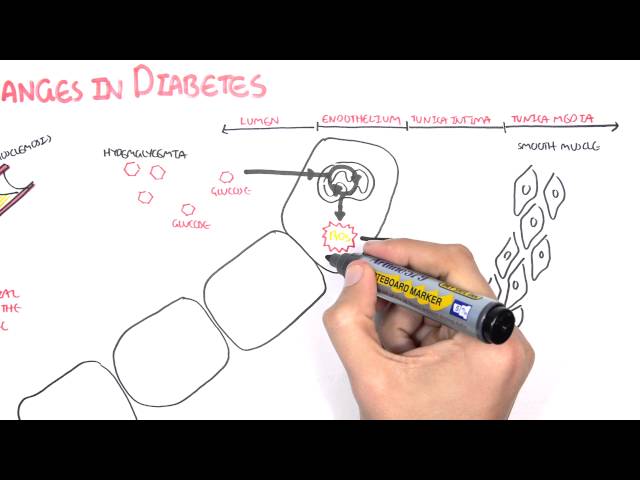
Diabetic complications are a group of conditions that can occur in people with diabetes. They are caused by high blood sugar levels, which can damage the blood vessels and nerves over time. Diabetic complications can affect many parts of the body, including the heart, eyes, kidneys, and feet.
Some of the most common diabetic complications include:
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Kidney disease
- Eye damage, including diabetic retinopathy and macular degeneration
- Nerve damage, including diabetic neuropathy
- Foot problems, including diabetic foot ulcers and amputations
Diabetic complications can be serious and even life-threatening. However, they can often be prevented or delayed with proper diabetes management. This includes keeping blood sugar levels under control, eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and taking medication as prescribed.
If you have diabetes, it is important to be aware of the risks of diabetic complications and to take steps to prevent them. Talk to your doctor about what you can do to stay healthy and reduce your risk of developing these complications.
diabetic complications
Diabetic complications are a group of conditions that can occur in people with diabetes. They are caused by high blood sugar levels, which can damage the blood vessels and nerves over time. Diabetic complications can affect many parts of the body, including the heart, eyes, kidneys, and feet.
- Heart disease: High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels that supply blood to the heart, increasing the risk of heart disease.
- Stroke: High blood sugar levels can also damage the blood vessels in the brain, increasing the risk of stroke.
- Kidney disease: High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys, leading to kidney failure.
- Eye damage: High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to eye damage, including diabetic retinopathy and macular degeneration.
- Nerve damage: High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves, leading to nerve damage, including diabetic neuropathy.
- Foot problems: High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves and blood vessels in the feet, leading to foot problems, including diabetic foot ulcers and amputations.
- Premature death: Diabetic complications can lead to premature death.
Diabetic complications can be serious and even life-threatening. However, they can often be prevented or delayed with proper diabetes management. This includes keeping blood sugar levels under control, eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and taking medication as prescribed.
Heart disease
High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels that supply blood to the heart, leading to a buildup of plaque in the arteries. This plaque buildup can narrow the arteries and restrict blood flow to the heart, increasing the risk of heart disease. Heart disease is a major complication of diabetes and is the leading cause of death in people with diabetes.
There are a number of things that people with diabetes can do to reduce their risk of heart disease, including:
- Keeping blood sugar levels under control
- Eating a healthy diet
- Getting regular exercise
- Taking medication as prescribed
- Quitting smoking
- Managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels
By following these steps, people with diabetes can reduce their risk of heart disease and other diabetic complications.
Stroke
Stroke is a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when high blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the brain. This damage can lead to a stroke, which occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted. Strokes can cause a variety of symptoms, including sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the body, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, and problems with vision or balance. Strokes can be life-threatening and can lead to permanent disability.
-
Facet 1: Risk factors for stroke in people with diabetes
There are a number of risk factors for stroke in people with diabetes, including:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
-
Facet 2: Symptoms of stroke
The symptoms of stroke can vary depending on the part of the brain that is affected. Some common symptoms of stroke include:
- Sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the body
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- Problems with vision or balance
- Sudden headache
- Confusion
- Loss of consciousness
-
Facet 3: Treatment for stroke
The treatment for stroke depends on the type of stroke and the severity of the symptoms. Treatment may include:
- Medication to dissolve the blood clot and restore blood flow to the brain
- Surgery to remove the blood clot or repair a damaged blood vessel
- Rehabilitation to help the person regain function after a stroke
-
Facet 4: Prevention of stroke
There are a number of things that people with diabetes can do to prevent stroke, including:
- Keeping blood sugar levels under control
- Eating a healthy diet
- Getting regular exercise
- Taking medication as prescribed
- Quitting smoking
- Managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels
Stroke is a serious complication of diabetes, but it can be prevented or managed with proper care. By following these tips, people with diabetes can reduce their risk of stroke and other diabetic complications.
Kidney disease
Kidney disease is a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when high blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the kidneys. This damage can lead to kidney failure, which is a life-threatening condition. Kidney failure can cause a buildup of waste products in the blood, which can lead to a variety of health problems, including heart disease, stroke, and death.
-
Facet 1: Risk factors for kidney disease in people with diabetes
There are a number of risk factors for kidney disease in people with diabetes, including:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
-
Facet 2: Symptoms of kidney disease
The symptoms of kidney disease can vary depending on the stage of the disease. Some common symptoms of kidney disease include:
- Swelling in the hands, feet, and ankles
- High blood pressure
- Frequent urination
- Foamy urine
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue
-
Facet 3: Treatment for kidney disease
The treatment for kidney disease depends on the stage of the disease. Treatment may include:
- Medication to lower blood pressure
- Medication to lower cholesterol
- Dialysis
- Kidney transplant
-
Facet 4: Prevention of kidney disease
There are a number of things that people with diabetes can do to prevent kidney disease, including:
- Keeping blood sugar levels under control
- Eating a healthy diet
- Getting regular exercise
- Taking medication as prescribed
- Quitting smoking
- Managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels
Kidney disease is a serious complication of diabetes, but it can be prevented or managed with proper care. By following these tips, people with diabetes can reduce their risk of kidney disease and other diabetic complications.
Eye damage
Eye damage is a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to blindness. High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, causing them to leak fluid and blood. This can lead to a number of eye problems, including diabetic retinopathy and macular degeneration.
Diabetic retinopathy is the most common eye complication of diabetes. It occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. Diabetic retinopathy can cause a number of vision problems, including blurred vision, floaters, and blind spots. If left untreated, diabetic retinopathy can lead to blindness.
Macular degeneration is another serious eye complication of diabetes. It occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp central vision. Macular degeneration can cause blurred vision, distorted vision, and difficulty reading or recognizing faces. If left untreated, macular degeneration can lead to blindness.
Eye damage is a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to blindness. However, it can often be prevented or delayed with proper diabetes management. This includes keeping blood sugar levels under control, eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and taking medication as prescribed. By following these steps, people with diabetes can reduce their risk of eye damage and other diabetic complications.
In conclusion, eye damage is a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to blindness. However, it can often be prevented or delayed with proper diabetes management. People with diabetes should have regular eye exams to check for signs of eye damage and to get treatment as early as possible.
Nerve damage
Nerve damage is a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when high blood sugar levels damage the nerves. This damage can lead to a variety of symptoms, including pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness. Nerve damage can affect any part of the body, but it is most common in the hands, feet, and legs.
-
Facet 1: Symptoms of nerve damage
The symptoms of nerve damage can vary depending on the nerves that are affected. Some common symptoms of nerve damage include:
- Pain
- Numbness
- Tingling
- Weakness
- Burning sensation
- Muscle cramps
- Loss of coordination
- Difficulty walking
-
Facet 2: Causes of nerve damage
Nerve damage can be caused by a number of factors, including diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and smoking. Diabetes is the most common cause of nerve damage, and it is estimated that up to 50% of people with diabetes will develop some form of nerve damage.
-
Facet 3: Treatment for nerve damage
There is no cure for nerve damage, but there are treatments that can help to relieve the symptoms. Treatment options for nerve damage include:
- Medication
- Physical therapy
- Occupational therapy
- Surgery
-
Facet 4: Prevention of nerve damage
There are a number of things that people with diabetes can do to prevent nerve damage, including:
- Keeping blood sugar levels under control
- Eating a healthy diet
- Getting regular exercise
- Taking medication as prescribed
- Quitting smoking
Nerve damage is a serious complication of diabetes, but it can be prevented or managed with proper care. By following these tips, people with diabetes can reduce their risk of nerve damage and other diabetic complications.
Foot problems
Foot problems are a common complication of diabetes. High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves and blood vessels in the feet, leading to a number of problems, including:
- Diabetic foot ulcers: These are open sores on the feet that can occur when high blood sugar levels damage the nerves and blood vessels in the feet. Diabetic foot ulcers can be difficult to heal and can lead to serious infections.
- Amputations: In some cases, diabetic foot ulcers can become so severe that amputation is necessary. Amputation is the surgical removal of a limb or part of a limb.
Foot problems are a serious complication of diabetes, but they can be prevented or managed with proper care. People with diabetes should inspect their feet daily for any signs of problems, such as cuts, blisters, or redness. They should also wear comfortable shoes that fit well and protect their feet from injury. If you have diabetes, it is important to see your doctor regularly for foot exams.
In addition to the above, here are some other important points to consider:
- Foot problems are more likely to occur in people with diabetes who have poor blood sugar control.
- People with diabetes who smoke are at an increased risk for foot problems.
- Foot problems can lead to serious complications, including infection, amputation, and even death.
If you have diabetes, it is important to take steps to prevent foot problems. This includes keeping your blood sugar levels under control, quitting smoking, and wearing comfortable shoes that fit well. If you have any foot problems, see your doctor right away.
Premature death
Diabetic complications are a major cause of premature death. In fact, people with diabetes are two to four times more likely to die prematurely than people without diabetes.
- Cardiovascular disease: Diabetic complications can lead to cardiovascular disease, which is the leading cause of death in people with diabetes. High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels and heart, increasing the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular problems.
- Kidney disease: Diabetic complications can also lead to kidney disease, which is another major cause of death in people with diabetes. High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys, leading to kidney failure and other serious health problems.
- Infections: People with diabetes are also more susceptible to infections, which can be life-threatening. High blood sugar levels can weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections.
- Other complications: Diabetic complications can also lead to other serious health problems, such as blindness, amputation, and nerve damage. These complications can significantly reduce quality of life and can contribute to premature death.
Premature death is a serious consequence of diabetic complications. However, it is important to note that these complications can be prevented or delayed with proper diabetes management. People with diabetes should work closely with their healthcare team to keep their blood sugar levels under control and to manage other risk factors for diabetic complications.
FAQs about Diabetic Complications
Diabetic complications are a group of conditions that can occur in people with diabetes. They are caused by high blood sugar levels, which can damage the blood vessels and nerves over time. Diabetic complications can affect many parts of the body, including the heart, eyes, kidneys, and feet.
Here are some frequently asked questions about diabetic complications:
Question 1: What are the most common diabetic complications?
The most common diabetic complications include heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, eye damage, nerve damage, and foot problems.
Question 2: Are diabetic complications serious?
Yes, diabetic complications can be serious and even life-threatening. They can lead to heart attack, stroke, kidney failure, blindness, amputation, and premature death.
Question 3: Can diabetic complications be prevented?
Yes, diabetic complications can often be prevented or delayed with proper diabetes management. This includes keeping blood sugar levels under control, eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and taking medication as prescribed.
Question 4: How can I reduce my risk of developing diabetic complications?
You can reduce your risk of developing diabetic complications by keeping your blood sugar levels under control, eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, taking medication as prescribed, quitting smoking, and managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
Question 5: What should I do if I think I have a diabetic complication?
If you think you have a diabetic complication, see your doctor right away. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent serious problems.
Question 6: How can I live a healthy life with diabetic complications?
If you have diabetic complications, it is important to work closely with your healthcare team to manage your condition and reduce your risk of developing further complications. This may include taking medication, following a special diet, and getting regular exercise.
Diabetic complications are a serious concern, but they can be prevented or managed with proper care. By following these tips, you can reduce your risk of developing diabetic complications and live a long, healthy life.
To learn more about diabetic complications, talk to your doctor or visit the website of the American Diabetes Association.
Tips for Managing Diabetic Complications
Diabetic complications are a group of conditions that can occur in people with diabetes. They are caused by high blood sugar levels, which can damage the blood vessels and nerves over time. Diabetic complications can affect many parts of the body, including the heart, eyes, kidneys, and feet.
There are a number of things that people with diabetes can do to reduce their risk of developing diabetic complications. These include:
Tip 1: Keep blood sugar levels under control
Keeping blood sugar levels under control is the most important thing you can do to prevent diabetic complications. This means following your doctor’s recommendations for diet, exercise, and medication.
Tip 2: Eat a healthy diet
Eating a healthy diet is another important way to prevent diabetic complications. This means eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It also means limiting your intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and saturated and unhealthy fats.
Tip 3: Get regular exercise
Getting regular exercise is another important way to prevent diabetic complications. Exercise helps to lower blood sugar levels and improve blood flow. It also helps to strengthen the heart and lungs.
Tip 4: Take medication as prescribed
If you are taking medication for diabetes, it is important to take it as prescribed. Your doctor will have prescribed the medication to help you control your blood sugar levels and prevent complications.
Tip 5: Quit smoking
Smoking is a major risk factor for diabetic complications. If you smoke, quitting is one of the best things you can do for your health.
Tip 6: Manage blood pressure and cholesterol levels
High blood pressure and high cholesterol are both risk factors for diabetic complications. It is important to manage these conditions if you have them.
Tip 7: Get regular eye exams
People with diabetes should get regular eye exams to check for signs of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetic retinopathy is a serious eye condition that can lead to blindness if it is not treated.
Tip 8: Get regular foot exams
People with diabetes should get regular foot exams to check for signs of diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetic foot ulcers are a serious foot condition that can lead to amputation if they are not treated.
By following these tips, you can reduce your risk of developing diabetic complications and live a long, healthy life.
Conclusion:
Diabetic complications are a serious concern, but they can be prevented or managed with proper care. By following these tips, you can reduce your risk of developing diabetic complications and live a long, healthy life.
Conclusion
Diabetic complications are a serious threat to the health and well-being of people with diabetes. They can affect many parts of the body, including the heart, eyes, kidneys, and feet. Diabetic complications can lead to disability and even death.
However, diabetic complications can be prevented or delayed with proper diabetes management. This includes keeping blood sugar levels under control, eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and taking medication as prescribed. By following these steps, people with diabetes can reduce their risk of developing diabetic complications and live long, healthy lives.
If you have diabetes, it is important to be aware of the risks of diabetic complications and to take steps to prevent them. Talk to your doctor about what you can do to stay healthy and reduce your risk of developing these complications.
Youtube Video: