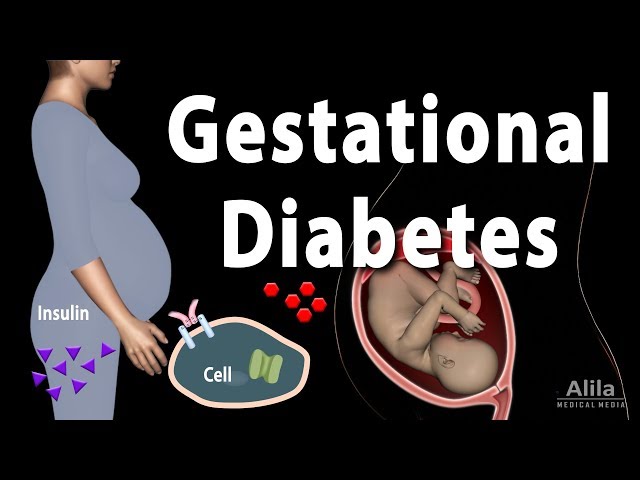
Diabetes while pregnant, also known as gestational diabetes, is a condition in which a woman develops high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. This can happen even if the woman has never had diabetes before. Gestational diabetes usually develops in the second or third trimester of pregnancy, and it can cause a number of health problems for both the mother and the baby.
Importance and Benefits
- Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can lead to a number of health problems, including premature birth, birth defects, and even death.
- However, gestational diabetes can be managed with diet, exercise, and medication, and most women with gestational diabetes go on to have healthy pregnancies and babies.
- It is important for women with gestational diabetes to follow their doctor’s instructions carefully to help prevent these complications.
Historical Context
Gestational diabetes has been recognized for centuries, but it was not until the 1960s that researchers began to understand the causes and effects of the condition. In the past, women with gestational diabetes were often treated with bed rest and a strict diet. However, today, there are a number of different treatment options available, and most women with gestational diabetes are able to have healthy pregnancies and babies.
Main Article Topics
- Causes of gestational diabetes
- Symptoms of gestational diabetes
- Treatment options for gestational diabetes
- Risks and complications of gestational diabetes
- Prevention of gestational diabetes
Diabetes While Pregnant
Diabetes while pregnant, or gestational diabetes, is a serious condition that can lead to a number of health problems for both the mother and the baby. It is important to be aware of the key aspects of diabetes while pregnant in order to prevent and manage the condition.
- Causes: Gestational diabetes is caused by the hormones of pregnancy, which can make it difficult for the body to use insulin.
- Symptoms: Many women with gestational diabetes do not have any symptoms, but some may experience increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue.
- Treatment: Gestational diabetes can be managed with diet, exercise, and medication.
- Risks: Gestational diabetes can increase the risk of premature birth, birth defects, and even death.
- Prevention: There is no sure way to prevent gestational diabetes, but eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the risk.
- Diagnosis: Gestational diabetes is diagnosed with a blood sugar test.
- Management: Gestational diabetes can be managed with diet, exercise, and medication.
These are just some of the key aspects of diabetes while pregnant. It is important to be aware of these aspects in order to prevent and manage the condition. If you are pregnant, talk to your doctor about your risk of developing gestational diabetes and how to manage the condition if you are diagnosed.
Causes
Gestational diabetes is caused by the hormones of pregnancy, which can make it difficult for the body to use insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps the body use glucose for energy. When the body cannot use insulin properly, glucose builds up in the blood. This can lead to a number of health problems, including premature birth, birth defects, and even death.
- Hormonal Changes: During pregnancy, the placenta produces hormones that can make the body less sensitive to insulin. This can lead to high blood sugar levels.
- Increased Glucose Production: The liver also produces more glucose during pregnancy. This can further contribute to high blood sugar levels.
- Decreased Insulin Production: The pancreas may not produce enough insulin during pregnancy to meet the increased demand.
These factors can all contribute to gestational diabetes. It is important for women with gestational diabetes to follow their doctor’s instructions carefully to help prevent these complications.
Symptoms
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can lead to a number of health problems for both the mother and the baby. It is important to be aware of the symptoms of gestational diabetes so that you can get diagnosed and treated as early as possible.
Many women with gestational diabetes do not have any symptoms. However, some women may experience:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
These symptoms are often mild and can be easily mistaken for other pregnancy symptoms. However, it is important to see your doctor if you are experiencing any of these symptoms, especially if you have other risk factors for gestational diabetes, such as obesity, a family history of diabetes, or being over the age of 35.
Gestational diabetes is diagnosed with a blood sugar test. If you are diagnosed with gestational diabetes, you will need to follow a treatment plan that may include diet, exercise, and medication. By following your doctor’s instructions, you can help prevent the serious health problems that can be caused by gestational diabetes.
Treatment
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can lead to a number of health problems for both the mother and the baby. It is important to follow a treatment plan that includes diet, exercise, and medication in order to manage gestational diabetes and prevent these complications.
Diet: Eating a healthy diet is an important part of managing gestational diabetes. A healthy diet for gestational diabetes includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It is also important to limit your intake of sugary foods and drinks.
Exercise: Regular exercise is another important part of managing gestational diabetes. Exercise helps to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. It is important to talk to your doctor about which types of exercise are safe for you during pregnancy.
Medication: Some women with gestational diabetes may need to take medication to help control their blood sugar levels. There are a number of different medications that can be used to treat gestational diabetes, and your doctor will work with you to choose the best medication for you.
By following a treatment plan that includes diet, exercise, and medication, you can help manage your gestational diabetes and prevent the serious health problems that can be caused by the condition.
Risks
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can lead to a number of health problems for both the mother and the baby. One of the most significant risks of gestational diabetes is that it can increase the risk of premature birth, birth defects, and even death.
- Premature birth: Gestational diabetes can increase the risk of premature birth by up to 50%. Premature babies are at an increased risk of a number of health problems, including respiratory problems, feeding difficulties, and developmental delays.
- Birth defects: Gestational diabetes can also increase the risk of birth defects, such as heart defects, neural tube defects, and cleft lip and palate. Birth defects can cause lifelong health problems for the child.
- Death: In severe cases, gestational diabetes can even lead to the death of the baby. This is most likely to happen if the baby is born prematurely or if the mother has poorly controlled blood sugar levels.
These are just some of the serious risks associated with gestational diabetes. It is important for women with gestational diabetes to follow their doctor’s instructions carefully to help prevent these complications.
Prevention
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can lead to a number of health problems for both the mother and the baby. While there is no sure way to prevent gestational diabetes, there are a number of things that women can do to reduce their risk, including eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight.
- Eating a healthy diet: Eating a healthy diet is one of the best ways to reduce your risk of gestational diabetes. A healthy diet includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It is also important to limit your intake of sugary foods and drinks.
- Exercising regularly: Regular exercise is another important way to reduce your risk of gestational diabetes. Exercise helps to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. It is important to talk to your doctor about which types of exercise are safe for you during pregnancy.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Maintaining a healthy weight is also important for reducing your risk of gestational diabetes. If you are overweight or obese, losing weight before you become pregnant can help to reduce your risk of developing gestational diabetes.
By following these tips, you can help reduce your risk of developing gestational diabetes and protect the health of your baby.
Diagnosis
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can lead to a number of health problems for both the mother and the baby. It is important to diagnose and treat gestational diabetes as early as possible to prevent these complications.
- The Role of Blood Sugar Tests: Blood sugar tests are used to diagnose gestational diabetes by measuring the amount of glucose in the blood. High blood sugar levels may indicate gestational diabetes.
- Timing of Blood Sugar Tests: Blood sugar tests are typically performed during the second trimester of pregnancy, between 24 and 28 weeks.
- Types of Blood Sugar Tests: There are two main types of blood sugar tests used to diagnose gestational diabetes: the fasting blood sugar test and the glucose tolerance test.
- Importance of Early Diagnosis: Early diagnosis and treatment of gestational diabetes is crucial to prevent complications such as premature birth, birth defects, and even death.
By understanding the importance of blood sugar tests in diagnosing gestational diabetes, we can ensure that women receive timely and appropriate care to protect the health of both the mother and the baby.
Management
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can lead to a number of health problems for both the mother and the baby. It is important to follow a treatment plan that includes diet, exercise, and medication in order to manage gestational diabetes and prevent these complications.
- Diet: Eating a healthy diet is an important part of managing gestational diabetes. A healthy diet for gestational diabetes includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It is also important to limit your intake of sugary foods and drinks.
- Exercise: Regular exercise is another important part of managing gestational diabetes. Exercise helps to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. It is important to talk to your doctor about which types of exercise are safe for you during pregnancy.
- Medication: Some women with gestational diabetes may need to take medication to help control their blood sugar levels. There are a number of different medications that can be used to treat gestational diabetes, and your doctor will work with you to choose the best medication for you.
By following a treatment plan that includes diet, exercise, and medication, you can help manage your gestational diabetes and prevent the serious health problems that can be caused by the condition.
FAQs on Diabetes While Pregnant
This section provides answers to frequently asked questions about diabetes while pregnant, also known as gestational diabetes, to provide clear and informative guidance on the condition.
Question 1: What is diabetes while pregnant?
Diabetes while pregnant is a condition in which a woman develops high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. It can occur even in women with no prior history of diabetes.
Question 2: What causes diabetes while pregnant?
Gestational diabetes is caused by the hormonal changes of pregnancy, which can make the body less sensitive to insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels.
Question 3: What are the symptoms of diabetes while pregnant?
Many women with gestational diabetes experience no symptoms, but some may have increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue.
Question 4: How is diabetes while pregnant diagnosed?
Gestational diabetes is diagnosed through a blood sugar test, typically performed between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy.
Question 5: How is diabetes while pregnant treated?
Treatment for gestational diabetes involves managing blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and sometimes medication.
Question 6: What are the risks of diabetes while pregnant?
Uncontrolled diabetes while pregnant can increase the risk of premature birth, birth defects, and other health problems for both the mother and the baby.
By understanding these key questions and answers, individuals can gain a clearer understanding of diabetes while pregnant, its diagnosis, treatment, and potential risks.
Tips for Managing Diabetes While Pregnant
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can lead to a number of health problems for both the mother and the baby. By following these tips, you can help manage your gestational diabetes and reduce your risk of complications.
Tip 1: Follow a Healthy Diet
Eating a healthy diet is essential for managing gestational diabetes. A healthy diet includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It is also important to limit your intake of sugary foods and drinks.
Tip 2: Exercise Regularly
Regular exercise is another important part of managing gestational diabetes. Exercise helps to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Talk to your doctor about which types of exercise are safe for you during pregnancy.
Tip 3: Monitor Your Blood Sugar Levels
Monitoring your blood sugar levels is important for managing gestational diabetes. Your doctor will tell you how often to check your blood sugar levels and what your target blood sugar levels are.
Tip 4: Take Medication if Needed
Some women with gestational diabetes may need to take medication to help control their blood sugar levels. Your doctor will work with you to choose the best medication for you.
Tip 5: Attend Prenatal Appointments
It is important to attend all of your prenatal appointments. Your doctor will monitor your blood sugar levels and check for any complications.
Tip 6: Get Enough Sleep
Getting enough sleep is important for overall health, including managing gestational diabetes. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night.
Tip 7: Manage Stress
Stress can raise blood sugar levels. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, yoga, or meditation.
Tip 8: Quit Smoking
Smoking can worsen gestational diabetes. If you smoke, quit as soon as possible.
By following these tips, you can help manage your gestational diabetes and have a healthy pregnancy.
Conclusion
Diabetes while pregnant, also known as gestational diabetes, is a serious condition that requires careful management to protect the health of both the mother and the baby. This article has explored the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and management of diabetes while pregnant, providing comprehensive information for those affected by this condition.
Gestational diabetes is a temporary condition that usually resolves after pregnancy. However, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully to manage your blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications. By eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, taking medication if needed, and attending prenatal appointments, you can help ensure a healthy pregnancy and a healthy baby.
Youtube Video: