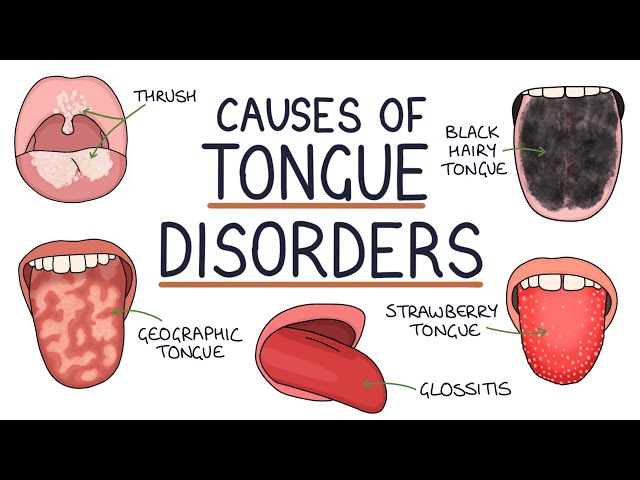
We use the term “diabetes tongue” to describe a condition characterized by a smooth, red, and glazed tongue. It often results from diabetes but can also stem from other underlying health issues, such as pernicious anemia or Plummer-Vinson syndrome.
Diabetes tongue is significant because it can indicate uncontrolled blood sugar levels, potentially leading to severe complications if left untreated. Historically, physicians have recognized the link between diabetes and tongue health, leading to the term “diabetes tongue.”
If you notice signs of diabetes tongue, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment. Early diagnosis and proper management of diabetes can help prevent or minimize complications associated with the condition
diabetes tongue
Understanding the different aspects of “diabetes tongue” is crucial for its comprehensive analysis. Six key aspects to consider include:
- Medical sign: Diabetes tongue is a potential indicator of uncontrolled blood sugar levels.
- Underlying causes: Diabetes is a primary cause, but other conditions can contribute.
- Smooth and red appearance: The tongue’s surface becomes abnormally smooth and red.
- Diagnostic tool: Historically, physicians have used tongue appearance to assess diabetes.
- Symptom: Diabetes tongue can manifest as a symptom of uncontrolled diabetes.
- Preventable: Early diagnosis and management of diabetes can help prevent diabetes tongue.
By exploring these various dimensions, healthcare professionals can better understand the significance of diabetes tongue in diabetes management and overall patient health. Early identification and appropriate treatment of the underlying condition are essential to prevent or minimize complications associated with diabetes tongue.
Medical sign
The connection between diabetes tongue and uncontrolled blood sugar levels is significant because it highlights the potential role of tongue examination in diabetes management. The tongue’s appearance can provide valuable clues about a person’s glycemic control, making diabetes tongue a potentially useful screening tool.
When blood sugar levels are consistently high, as in uncontrolled diabetes, it can lead to changes in the tongue’s appearance. These changes, such as a smooth and red tongue, may indicate underlying health issues that require medical attention. Therefore, recognizing diabetes tongue can prompt individuals to seek professional evaluation and appropriate treatment, potentially preventing or minimizing complications associated with diabetes.
In conclusion, understanding the connection between diabetes tongue and uncontrolled blood sugar levels underscores the importance of regular tongue examinations as part of routine diabetes care. By being aware of this potential sign, healthcare professionals and individuals with diabetes can take proactive steps to manage blood sugar levels effectively and maintain overall health.
Underlying causes
The connection between underlying causes and diabetes tongue lies in the recognition that while diabetes is a primary cause of diabetes tongue, other medical conditions can also contribute to its development. Understanding this broader spectrum of potential causes is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management of diabetes tongue.
Beyond diabetes, conditions that may cause or contribute to diabetes tongue include pernicious anemia, Plummer-Vinson syndrome, and certain medications. Pernicious anemia, an autoimmune condition that affects the absorption of vitamin B12, can lead to a smooth and red tongue similar to diabetes tongue. Plummer-Vinson syndrome, a rare condition characterized by difficulty swallowing, can also cause a smooth tongue. Additionally, certain medications, such as chemotherapy drugs, can cause inflammation and changes in the tongue’s appearance.
Identifying the underlying cause of diabetes tongue is essential for appropriate treatment. If diabetes is the underlying cause, managing blood sugar levels through medication, lifestyle changes, or both is crucial. In cases where other medical conditions are contributing to diabetes tongue, addressing those conditions may be necessary to improve tongue health.
In conclusion, understanding the connection between underlying causes and diabetes tongue is vital for a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and management. Considering the various potential causes beyond diabetes allows healthcare professionals to provide personalized treatment plans tailored to each individual’s specific needs, ultimately improving patient outcomes and overall well-being.
Smooth and red appearance
The smooth and red appearance of the tongue is a characteristic feature of diabetes tongue, providing valuable insights into the condition’s underlying mechanisms and implications for diabetes management. This abnormal tongue presentation results from a combination of factors related to diabetes and its impact on oral health.
-
Increased inflammation
Diabetes can lead to chronic inflammation throughout the body, including the oral cavity. This inflammation contributes to the tongue’s smooth appearance by damaging the filiform papillae, small projections on the tongue’s surface responsible for its rough texture.
-
Reduced saliva production
Diabetes can also cause a reduction in saliva production, leading to a dry mouth. This dryness further contributes to the smooth tongue appearance, as saliva plays a crucial role in lubricating and protecting the tongue’s surface.
-
Altered taste perception
The smooth and red tongue in diabetes tongue can also affect taste perception. The filiform papillae contain taste buds, which are responsible for sensing different tastes. Damage to these papillae can lead to a decreased ability to taste, potentially impacting an individual’s dietary choices and overall nutritional status.
-
Risk factor for oral health issues
The smooth and red tongue associated with diabetes tongue is often accompanied by other oral health issues, such as gum disease and tooth decay. This increased risk stems from the underlying factors contributing to diabetes tongue, including inflammation and reduced saliva production, which can compromise the oral environment’s health.
Understanding the connection between the smooth and red appearance of the tongue and diabetes tongue not only aids in the diagnosis and management of diabetes but also highlights the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental checkups for individuals with diabetes. By addressing these oral health concerns, individuals with diabetes can improve their overall well-being and reduce the risk of developing severe complications.
Diagnostic tool
The use of tongue appearance as a diagnostic tool for diabetes, termed “diabetes tongue,” holds significant historical and practical value in understanding the condition. Historically, physicians have relied on visual examination of the tongue to assess a person’s overall health, including their diabetic status. This practice stems from the belief that the tongue’s appearance can reflect internal imbalances or disease processes within the body.
In the context of diabetes, the characteristic smooth and red appearance of the tongue, known as diabetes tongue, has been associated with uncontrolled blood sugar levels. This observation arises from the fact that diabetes can lead to chronic inflammation and reduced saliva production, both of which contribute to the tongue’s altered appearance. By recognizing diabetes tongue, physicians can gain valuable insights into a person’s glycemic control and potential underlying health issues.
While tongue examination remains a part of traditionalmedicine practices, modern medicine has largely moved away from relying solely on tongue appearance for diabetes diagnosis. However, the connection between diabetes tongue and uncontrolled blood sugar levels serves as a reminder of the importance of comprehensive patient assessment, considering both subjective and objective findings. In contemporary clinical practice, tongue examination may complement other diagnostic tests, such as blood glucose measurements and HbA1c levels, to provide a more holistic evaluation of a person’s diabetic status.
Understanding the connection between diabetes tongue and diabetes management holds practical significance for healthcare professionals and individuals with diabetes. By recognizing the potential implications of diabetes tongue, healthcare providers can encourage regular tongue examinations as part of routine diabetes care. This simple and non-invasive procedure can contribute to early detection of uncontrolled blood sugar levels, prompting timely interventions to prevent or minimize diabetes-related complications.
In conclusion, the connection between diabetes tongue and diabetes assessment underscores the historical and practical value of tongue examination in understanding a person’s diabetic status. While modern medicine relies on more advanced diagnostic tools, recognizing diabetes tongue can complement comprehensive patient evaluation, contributing to early detection of uncontrolled blood sugar levels and promoting timely management of diabetes.
Symptom
The connection between diabetes tongue and its manifestation as a symptom of uncontrolled diabetes lies at the heart of understanding the condition’s significance in diabetes management. Diabetes tongue is a visible indicator of underlying health issues, particularly uncontrolled blood sugar levels. Recognizing this connection empowers individuals with diabetes and healthcare professionals to take proactive steps in managing the condition and preventing potential complications.
- Early detection: Diabetes tongue can serve as an early warning sign of uncontrolled diabetes. By recognizing the characteristic smooth and red appearance of the tongue, individuals can seek medical attention promptly. Early detection allows for timely intervention and lifestyle modifications to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
- Monitoring disease progression: Monitoring changes in the appearance of the tongue can provide insights into the progression of diabetes. Improvements in tongue health may indicate better glycemic control, while worsening tongue appearance may signal a need for adjustments in treatment plans.
- Guiding treatment decisions: Diabetes tongue can guide treatment decisions by providing additional information about a person’s diabetic status. For example, the presence of diabetes tongue may warrant closer monitoring of blood sugar levels, medication adjustments, or referral to a specialist for further evaluation.
- Promoting self-care: Understanding the connection between diabetes tongue and uncontrolled diabetes empowers individuals to take an active role in their self-care. Regular tongue examinations can enhance self-awareness and encourage proactive measures to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
In conclusion, the connection between diabetes tongue as a symptom of uncontrolled diabetes underscores its importance in diabetes management. By recognizing this relationship, individuals with diabetes and healthcare professionals can work together to monitor disease progression, guide treatment decisions, and promote self-care practices. This comprehensive approach contributes to improved outcomes and a better quality of life for individuals living with diabetes.
Preventable
Understanding the connection between “Preventable: Early diagnosis and management of diabetes can help prevent diabetes tongue.” and “diabetes tongue” requires exploring the role of early intervention in managing diabetes and preventing its complications, including diabetes tongue. By recognizing the potential consequences of uncontrolled diabetes on oral health, we can appreciate the significance of early diagnosis and effective diabetes management.
- Early Intervention: Early diagnosis of diabetes is crucial for preventing the development of diabetes tongue. Regular checkups and screenings can help identify individuals at risk or with early signs of diabetes, allowing for timely intervention and treatment.
- Glycemic Control: Effective management of diabetes involves maintaining optimal blood sugar levels. This can be achieved through a combination of lifestyle modifications, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, along with medication when necessary. Good glycemic control helps prevent the chronic inflammation and reduced saliva production associated with diabetes tongue.
- Oral Hygiene: Maintaining good oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing, flossing, and dental checkups, is essential for preventing diabetes tongue. Proper oral hygiene helps remove bacteria and plaque, reducing the risk of gum disease and other oral health issues that can contribute to diabetes tongue.
- Regular Tongue Examination: Regular examination of the tongue can aid in early detection of diabetes tongue. Individuals with diabetes should be encouraged to examine their tongues regularly and report any changes in appearance or texture to their healthcare provider.
In conclusion, the connection between “Preventable: Early diagnosis and management of diabetes can help prevent diabetes tongue.” and “diabetes tongue” highlights the importance of early intervention, effective diabetes management, and good oral hygiene practices. By understanding this connection, individuals with diabetes and healthcare professionals can work together to prevent the development of diabetes tongue and promote overall oral health.
FAQs on Diabetes Tongue
The following are frequently asked questions about diabetes tongue, a condition that can indicate uncontrolled blood sugar levels in people with diabetes.
Question 1: What causes diabetes tongue?
Diabetes tongue is primarily caused by uncontrolled blood sugar levels in people with diabetes. When blood sugar levels remain high over time, it can lead to inflammation and reduced saliva production in the mouth, resulting in a smooth and red tongue.
Question 2: What are the symptoms of diabetes tongue?
The main symptom of diabetes tongue is a smooth and red tongue. It may also be accompanied by other oral symptoms, such as dryness, burning, or soreness.
Question 3: How is diabetes tongue diagnosed?
Diabetes tongue is typically diagnosed by a healthcare professional during a physical examination. The healthcare professional will examine the tongue’s appearance and texture and ask about any other symptoms the person may be experiencing.
Question 4: How is diabetes tongue treated?
The treatment for diabetes tongue involves managing blood sugar levels effectively. This may include lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, and/or medication to lower blood sugar levels. Good oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing and flossing, are also important for preventing and treating diabetes tongue.
Question 5: Can diabetes tongue be prevented?
Diabetes tongue can be prevented by managing blood sugar levels effectively. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, following a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and taking prescribed medications as directed can help prevent uncontrolled blood sugar levels and the development of diabetes tongue.
Question 6: What are the complications of diabetes tongue?
Diabetes tongue itself is usually not a serious condition, but it can be a sign of uncontrolled diabetes. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to serious complications, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and nerve damage. Therefore, it is important for people with diabetes to manage their blood sugar levels effectively to prevent these complications.
Summary: Diabetes tongue is a condition that can indicate uncontrolled blood sugar levels in people with diabetes. It is characterized by a smooth and red tongue and can be accompanied by other oral symptoms. Diabetes tongue is diagnosed through a physical examination and treated by managing blood sugar levels effectively. Good oral hygiene practices can also help prevent and treat diabetes tongue. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, a healthy lifestyle, and proper medication adherence are crucial for preventing uncontrolled blood sugar levels and the development of diabetes tongue.
Transition to the next article section: For more information on diabetes tongue and its management, please refer to the following resources:
Tips for Managing Diabetes Tongue
Managing diabetes tongue involves addressing the underlying cause, which is typically uncontrolled blood sugar levels. Here are some practical tips for individuals with diabetes to help prevent and manage diabetes tongue:
Tip 1: Monitor blood sugar levels regularly: Keeping blood sugar levels within the target range is crucial for preventing diabetes tongue. Regular blood sugar monitoring allows individuals to track their progress and make necessary adjustments to their diabetes management plan.
Tip 2: Follow a healthy diet: A balanced diet that is low in sugar and processed foods can help control blood sugar levels. Focus on consuming fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
Tip 3: Engage in regular physical activity: Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week.
Tip 4: Take prescribed medications as directed: If lifestyle changes alone are not enough to control blood sugar levels, medications may be necessary. Take medications as prescribed by your healthcare provider and follow their instructions carefully.
Tip 5: Practice good oral hygiene: Maintaining good oral hygiene, including brushing twice daily, flossing regularly, and using an antiseptic mouthwash, can help prevent oral infections and contribute to a healthy oral environment.
Tip 6: Quit smoking: Smoking can worsen diabetes and its complications, including diabetes tongue. Quitting smoking can significantly improve overall health and reduce the risk of developing diabetes-related complications.
Tip 7: See your dentist regularly: Regular dental checkups and cleanings are essential for maintaining good oral health. Your dentist can assess the health of your tongue and provide guidance on proper oral hygiene practices.
Tip 8: Report changes to your healthcare provider: If you notice any changes in the appearance or texture of your tongue, such as increased smoothness or redness, report these changes to your healthcare provider promptly.
Summary: Managing diabetes tongue requires a multifaceted approach that includes regular blood sugar monitoring, a healthy lifestyle, proper medication adherence, good oral hygiene practices, smoking cessation, regular dental checkups, and prompt reporting of any changes in tongue appearance. By following these tips, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage diabetes tongue and maintain good oral health.
Transition to the article’s conclusion: In conclusion, diabetes tongue is a common condition that can indicate uncontrolled blood sugar levels. By understanding the causes and following these practical tips, individuals with diabetes can prevent and manage diabetes tongue, promoting overall health and well-being. Regular consultation with healthcare providers and dentists is crucial for ongoing support and guidance.
Conclusion
Throughout this article, we have explored the topic of diabetes tongue, a condition characterized by a smooth and red tongue. We have discussed its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and preventive measures. Diabetes tongue is primarily caused by uncontrolled blood sugar levels in people with diabetes, leading to inflammation and reduced saliva production in the mouth.
Effective management of diabetes tongue involves maintaining optimal blood sugar levels through lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise, and/or medication. Good oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing and flossing, are also crucial for preventing and treating diabetes tongue. By understanding the significance of diabetes tongue and following the practical tips outlined in this article, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage this condition and maintain good oral health.
Youtube Video: