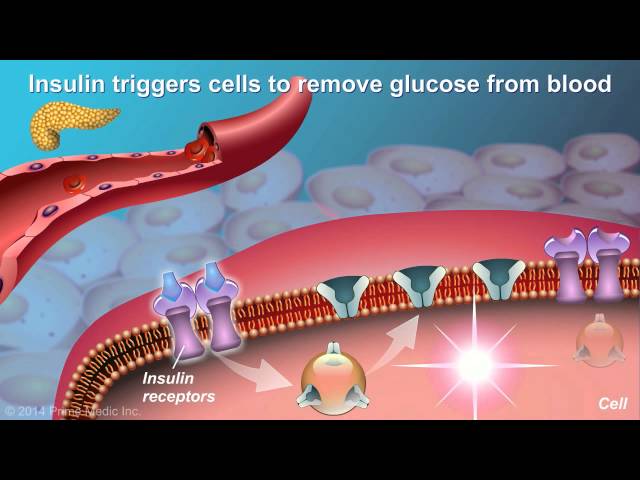
Diabetes tipo 2, also known as type 2 diabetes, is a chronic condition that affects the way the body processes sugar (glucose). In people with diabetes tipo 2, the body does not make enough insulin or does not use insulin well. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get from the blood into the cells. Without enough insulin, glucose builds up in the blood. Over time, high blood sugar levels can damage the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves.
Diabetes tipo 2 is the most common type of diabetes. It usually develops in adults over the age of 40, but it can also occur in children and adolescents. Diabetes tipo 2 is a major risk factor for heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness. However, it can be managed with healthy lifestyle changes, such as diet, exercise, and weight loss.
There is no cure for diabetes tipo 2, but it can be managed. Treatment typically involves lifestyle changes, such as diet, exercise, and weight loss. Medications may also be necessary to help control blood sugar levels.
diabetes tipo 2
Diabetes tipo 2 is a chronic condition that affects the body’s ability to process sugar (glucose). Key aspects of diabetes tipo 2 include:
- High blood sugar
- Insulin resistance
- Weight gain
- Physical inactivity
- Family history
- Age
- Race/ethnicity
- Gestational diabetes
High blood sugar levels can damage the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Insulin resistance is a condition in which the body does not respond well to insulin. Weight gain, physical inactivity, family history, age, race/ethnicity, and gestational diabetes are all risk factors for diabetes tipo 2. There is no cure for diabetes tipo 2, but it can be managed with healthy lifestyle changes, such as diet, exercise, and weight loss. Medications may also be necessary to help control blood sugar levels.
High blood sugar
High blood sugar, also known as hyperglycemia, is a condition in which the blood glucose level is above normal. It is a common symptom of diabetes tipo 2. There are several causes of high blood sugar, including:
- The body does not produce enough insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get from the blood into the cells. Without enough insulin, glucose builds up in the blood.
- The body does not respond well to insulin. This is known as insulin resistance. When the body is insulin resistant, glucose does not get into the cells as easily, and it builds up in the blood.
- The liver produces too much glucose. The liver is responsible for regulating blood sugar levels. When the liver produces too much glucose, it can lead to high blood sugar.
High blood sugar can damage the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves. It can also lead to other health problems, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness. Therefore, it is important to control blood sugar levels to prevent these complications.
Insulin resistance
Insulin resistance is a condition in which the body does not respond well to insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get from the blood into the cells. When the body is insulin resistant, glucose does not get into the cells as easily, and it builds up in the blood. This can lead to high blood sugar, which is a common symptom of diabetes tipo 2.
Insulin resistance is a major risk factor for diabetes tipo 2. In fact, it is estimated that up to 90% of people with diabetes tipo 2 are insulin resistant. Insulin resistance can also lead to other health problems, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness.
There are several things that can cause insulin resistance, including:
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Family history of diabetes
- Certain medications
- Certain medical conditions, such as Cushing’s syndrome and Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
There is no cure for insulin resistance, but it can be managed with healthy lifestyle changes, such as diet, exercise, and weight loss. Medications may also be necessary to help improve insulin sensitivity.
Weight gain
Weight gain is a major risk factor for diabetes tipo 2. People who are overweight or obese are more likely to develop diabetes tipo 2 than people who are at a healthy weight. There are several reasons for this, including:
- Excess weight can lead to insulin resistance. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get from the blood into the cells. When the body is overweight or obese, it can become resistant to insulin. This means that the body does not respond to insulin as well as it should, and glucose builds up in the blood.
- Excess weight can also lead to inflammation. Inflammation is a natural response to injury or infection. However, chronic inflammation can damage the cells and tissues in the body, including the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. This can lead to diabetes tipo 2.
- Excess weight can also lead to high blood pressure. High blood pressure can damage the blood vessels, including the blood vessels in the kidneys. This can lead to kidney disease, which is a major risk factor for diabetes tipo 2.
Losing weight can help to reduce the risk of developing diabetes tipo 2. Even a small amount of weight loss can make a difference. Losing weight can help to improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and lower blood pressure. If you are overweight or obese, talk to your doctor about ways to lose weight and improve your health.
Physical inactivity
Physical inactivity is a major risk factor for diabetes tipo 2. People who are physically inactive are more likely to develop diabetes tipo 2 than people who are physically active. There are several reasons for this, including:
- Physical inactivity can lead to weight gain. Weight gain is a major risk factor for diabetes tipo 2. People who are overweight or obese are more likely to develop diabetes tipo 2 than people who are at a healthy weight.
- Physical inactivity can lead to insulin resistance. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get from the blood into the cells. When the body is physically inactive, it can become resistant to insulin. This means that the body does not respond to insulin as well as it should, and glucose builds up in the blood.
- Physical inactivity can lead to inflammation. Inflammation is a natural response to injury or infection. However, chronic inflammation can damage the cells and tissues in the body, including the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. This can lead to diabetes tipo 2.
Getting regular physical activity can help to reduce the risk of developing diabetes tipo 2. Even a small amount of physical activity can make a difference. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity most days of the week. If you are new to exercise, start slowly and gradually increase the amount of time and intensity of your workouts over time.
Family history
Family history is a major risk factor for diabetes tipo 2. People who have a family history of diabetes tipo 2 are more likely to develop the condition themselves. This is because diabetes tipo 2 is a complex condition that is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Genes play a role in the development of diabetes tipo 2, and people who have a family history of the condition are more likely to inherit these genes. Additionally, people who have a family history of diabetes tipo 2 are more likely to share similar environmental factors, such as diet and lifestyle, which can also increase the risk of developing the condition.
There are several ways that family history can increase the risk of developing diabetes tipo 2. First, people who have a family history of diabetes tipo 2 are more likely to inherit genes that increase their risk of developing the condition. These genes can affect the way the body produces insulin, the way the body uses insulin, or the way the body regulates blood sugar levels. Second, people who have a family history of diabetes tipo 2 are more likely to share similar environmental factors, such as diet and lifestyle, which can also increase the risk of developing the condition. For example, people who have a family history of diabetes tipo 2 are more likely to be overweight or obese, to eat a diet high in processed foods and sugary drinks, and to be physically inactive. These factors can all increase the risk of developing diabetes tipo 2.
Knowing your family history of diabetes tipo 2 can help you to take steps to reduce your risk of developing the condition. If you have a family history of diabetes tipo 2, you should talk to your doctor about ways to reduce your risk, such as eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Age
Age is a major risk factor for diabetes tipo 2. The risk of developing diabetes tipo 2 increases with age, and people over the age of 45 are at the highest risk. There are several reasons for this, including:
- Age-related changes in body composition. As people age, they tend to lose muscle mass and gain body fat. This can lead to insulin resistance, which is a major risk factor for diabetes tipo 2.
- Age-related changes in hormone levels. As people age, their levels of certain hormones, such as growth hormone and testosterone, decline. These hormones help to regulate blood sugar levels, and their decline can lead to insulin resistance and diabetes tipo 2.
- Age-related changes in lifestyle. As people age, they are more likely to become less physically active and to eat a less healthy diet. These lifestyle factors can also increase the risk of developing diabetes tipo 2.
It is important to be aware of the increased risk of diabetes tipo 2 with age and to take steps to reduce your risk, such as eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight. If you are over the age of 45, talk to your doctor about your risk of developing diabetes tipo 2 and about ways to reduce your risk.
Race/ethnicity
Race and ethnicity are important factors to consider when discussing diabetes tipo 2, as certain racial and ethnic groups have a higher risk of developing the condition. For example, African Americans, Hispanic Americans, American Indians, and Asian Americans are all at an increased risk of developing diabetes tipo 2 compared to white Americans.
There are several reasons why race and ethnicity can affect the risk of developing diabetes tipo 2. One reason is that certain racial and ethnic groups are more likely to have certain genetic factors that increase the risk of diabetes tipo 2. For example, African Americans are more likely to have a variant of the PPARG gene, which has been linked to an increased risk of diabetes tipo 2. Additionally, Hispanic Americans are more likely to have a variant of the KCNJ11 gene, which has been linked to an increased risk of diabetes tipo 2.
Another reason why race and ethnicity can affect the risk of developing diabetes tipo 2 is that certain racial and ethnic groups are more likely to experience certain environmental factors that increase the risk of diabetes tipo 2. For example, African Americans and Hispanic Americans are more likely to live in poverty, which is a major risk factor for diabetes tipo 2. Additionally, African Americans and Hispanic Americans are more likely to be exposed to air pollution, which has been linked to an increased risk of diabetes tipo 2.
It is important to be aware of the increased risk of diabetes tipo 2 among certain racial and ethnic groups. This awareness can help to ensure that these groups have access to the resources and support they need to prevent and manage diabetes tipo 2.
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin to meet the increased demands of pregnancy. Gestational diabetes usually goes away after the baby is born, but it can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
-
Risk factors for gestational diabetes
Several factors can increase the risk of developing gestational diabetes, including obesity, being over the age of 35, having a family history of diabetes, and having had gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy.
-
Symptoms of gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes often has no symptoms. However, some women may experience increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue.
-
Diagnosis of gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is diagnosed with a blood sugar test. The test is usually done between the 24th and 28th weeks of pregnancy.
-
Treatment of gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is treated with diet, exercise, and, if necessary, medication. The goal of treatment is to keep blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can have both short-term and long-term health consequences. However, with proper treatment, most women with gestational diabetes can have a healthy pregnancy and deliver a healthy baby. Furthermore, by managing their weight, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise, women who have had gestational diabetes can reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Diabetes Tipo 2
Understanding diabetes tipo 2 is essential for proactive management. Here we address common concerns to empower individuals with knowledge and facilitate informed decision-making.
Question 1: What is diabetes tipo 2?
Diabetes tipo 2 is a chronic condition where the body struggles to effectively process sugar, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. This can result from insufficient insulin production or the body’s resistance to insulin.
Question 2: What are the symptoms of diabetes tipo 2?
Often, diabetes tipo 2 progresses without noticeable symptoms. However, some individuals may experience increased thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and blurred vision.
Question 3: What causes diabetes tipo 2?
The precise cause of diabetes tipo 2 is not fully understood, but risk factors include obesity, physical inactivity, family history, age, and certain ethnicities.
Question 4: How is diabetes tipo 2 diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves blood tests that measure fasting blood sugar levels or glucose tolerance during an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT).
Question 5: How is diabetes tipo 2 treated?
Treatment typically encompasses lifestyle modifications such as maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and adopting a balanced diet. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to manage blood sugar levels.
Question 6: What are the complications of diabetes tipo 2?
Uncontrolled diabetes tipo 2 can lead to severe complications affecting the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Regular monitoring and adherence to treatment plans are crucial for preventing or delaying these complications.
Remember, proactively managing diabetes tipo 2 requires a comprehensive approach involving medical guidance, lifestyle adjustments, and ongoing self-care. By staying informed and adhering to recommended treatment plans, individuals can effectively manage their condition and maintain a good quality of life.
Consult reputable healthcare sources or consult with a qualified healthcare professional for further information and personalized advice regarding diabetes tipo 2.
Tips for Managing Diabetes Tipo 2
Diabetes tipo 2, a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, requires careful management to maintain overall health and well-being. Here are some essential tips to assist individuals in effectively managing their diabetes tipo 2:
Tip 1: Prioritize a Nutritious Diet
Maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet is pivotal in managing diabetes tipo 2. Focus on consuming whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins while limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats. This dietary approach helps regulate blood sugar levels and promotes overall well-being.
Tip 2: Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is crucial for managing diabetes tipo 2. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week. Exercise enhances insulin sensitivity, aids in weight management, and improves cardiovascular health.
Tip 3: Maintain a Healthy Weight
Obesity is a significant risk factor for diabetes tipo 2. Maintaining a healthy weight through a combination of diet and exercise is essential for effective diabetes management. Even modest weight loss can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood sugar levels.
Tip 4: Monitor Blood Sugar Levels Regularly
Regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial for managing diabetes tipo 2. Use a glucometer to check blood sugar levels as directed by your healthcare provider. This monitoring allows for timely adjustments to medication or lifestyle to maintain optimal blood sugar control.
Tip 5: Take Medications as Prescribed
If prescribed medications for diabetes tipo 2, such as insulin or oral medications, adhere strictly to the dosage and schedule. These medications are essential for regulating blood sugar levels and preventing complications.
Tip 6: Quit Smoking
Smoking worsens insulin resistance and increases the risk of diabetes complications. Quitting smoking is highly recommended for individuals with diabetes tipo 2 to improve overall health and blood sugar control.
Tip 7: Manage Stress
Chronic stress can elevate blood sugar levels. Engage in stress-reducing activities such as exercise, yoga, or meditation to promote relaxation and improve diabetes management.
Tip 8: Get Enough Sleep
Sufficient sleep is vital for overall health, including diabetes management. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night to regulate hormones involved in blood sugar control and reduce the risk of insulin resistance.
Effectively managing diabetes tipo 2 requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses dietary modifications, regular physical activity, weight management, blood sugar monitoring, medication adherence, and healthy lifestyle practices. By incorporating these tips into daily routines, individuals can proactively manage their condition and maintain a good quality of life.
Remember to consult with qualified healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance on managing diabetes tipo 2 effectively.
Conclusin sobre la diabetes tipo 2
La diabetes tipo 2 es una afeccin crnica que afecta a millones de personas en todo el mundo. Se caracteriza por niveles elevados de azcar en sangre debido a la resistencia a la insulina o a la produccin insuficiente de insulina. Si no se trata, la diabetes tipo 2 puede provocar complicaciones graves como enfermedades cardacas, derrames cerebrales, ceguera, insuficiencia renal y amputaciones.
Afortunadamente, la diabetes tipo 2 se puede controlar con una combinacin de dieta saludable, ejercicio, medicacin y cambios de estilo de vida. Al adoptar un enfoque proactivo para controlar sus niveles de azcar en sangre, las personas con diabetes tipo 2 pueden vivir vidas largas y saludables. La investigacin en curso y los avances en el tratamiento ofrecen esperanza para un futuro an ms brillante para quienes viven con esta afeccin.
Youtube Video: