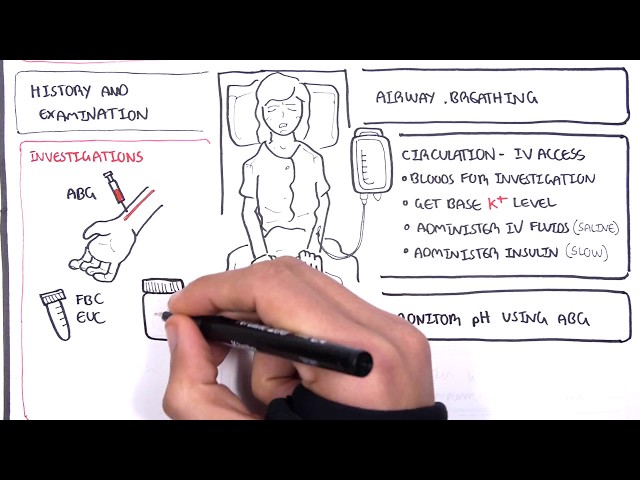
Definition and example of “diabetes dka symptoms”
Symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) can include:
- Excessive thirst
- Frequent urination
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Confusion or lethargy
DKA is a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
Importance, benefits, and historical context
DKA is a medical emergency that can lead to serious health problems, including death. It is important to recognize the symptoms of DKA and seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of them. Treatment for DKA typically involves fluids, electrolytes, and insulin.
Transition to main article topics
The main article topics will cover the following areas:
- Causes of DKA
- Risk factors for DKA
- Treatment for DKA
- Prevention of DKA
diabetes dka symptoms
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
The symptoms of DKA can include:
- Excessive thirst
- Frequent urination
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Confusion or lethargy
DKA is a medical emergency that can lead to serious health problems, including death. It is important to recognize the symptoms of DKA and seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of them.
The key aspects of diabetes dka symptoms are:
- Onset: DKA can develop suddenly, often within a few hours.
- Progression: The symptoms of DKA can worsen rapidly if not treated.
- Severity: DKA can be a life-threatening condition if not treated promptly.
- Causes: DKA is most commonly caused by uncontrolled diabetes, but it can also be triggered by other factors, such as infection or injury.
- Treatment: DKA is treated with fluids, electrolytes, and insulin.
- Prevention: DKA can be prevented by managing diabetes carefully and avoiding triggers.
- Complications: DKA can lead to a number of serious complications, including diabetic coma and death.
It is important to be aware of the symptoms of DKA and to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of them. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent serious complications.
Excessive thirst
Excessive thirst, also known as polydipsia, is a common symptom of diabetes dka symptoms. When a person is dehydrated, the body produces a hormone called antidiuretic hormone (ADH). ADH causes the kidneys to reabsorb water from the urine, which helps to keep the body hydrated. In people with diabetes, the kidneys are unable to respond to ADH properly, which leads to excessive thirst and frequent urination.
Excessive thirst can be a sign of DKA, a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
It is important to be aware of the symptoms of DKA and to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of them. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent serious complications.
Here are some tips for managing excessive thirst:
- Drink plenty of fluids, especially water.
- Avoid sugary drinks, as they can worsen dehydration.
- Eat fruits and vegetables that are high in water content, such as watermelon and cucumber.
- Talk to your doctor about medications that can help to reduce thirst.
Frequent urination
Frequent urination, also known as polyuria, is a common symptom of diabetes dka symptoms. When a person has diabetes, their body is unable to properly use glucose for energy. This causes the body to break down fat and muscle for energy instead, which produces ketones. Ketones are acidic and can build up in the blood, leading to a condition called ketoacidosis. Frequent urination is one of the body’s ways of trying to get rid of excess ketones.
- Dehydration: Frequent urination can lead to dehydration, which can worsen the symptoms of DKA. Dehydration can also lead to electrolyte imbalances, which can be dangerous.
- Infection: Frequent urination can also be a sign of a urinary tract infection (UTI). UTIs are more common in people with diabetes because high blood sugar levels can damage the nerves that control the bladder.
- Other causes: Frequent urination can also be caused by other factors, such as drinking too much caffeine or alcohol, or taking certain medications.
It is important to be aware of the symptoms of DKA and to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of them. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent serious complications.
Nausea and vomiting
Nausea and vomiting are common symptoms of diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA), a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
Nausea and vomiting can be caused by a number of factors, including:
- The buildup of ketones in the blood
- Dehydration
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Gastric paresis, a condition that slows down the emptying of the stomach
Nausea and vomiting can be a sign that DKA is developing, so it is important to seek medical attention immediately if you experience these symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment of DKA can help to prevent serious complications.
Here are some tips for managing nausea and vomiting:
- Drink plenty of fluids, such as water or clear broth.
- Eat small, frequent meals.
- Avoid foods that are high in fat or sugar.
- Talk to your doctor about medications that can help to reduce nausea and vomiting.
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain is a common symptom of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
- Ketone-induced inflammation: Ketones can cause inflammation in the pancreas and other abdominal organs, leading to pain.
- Dehydration: DKA can cause dehydration, which can lead to abdominal pain and constipation.
- Electrolyte imbalances: DKA can also cause electrolyte imbalances, which can lead to muscle cramps and abdominal pain.
- Gastric paresis: DKA can cause gastric paresis, a condition that slows down the emptying of the stomach. This can lead to abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
Abdominal pain is a serious symptom of DKA and should be evaluated by a doctor immediately. Treatment for DKA typically involves fluids, electrolytes, and insulin.
Confusion or lethargy
Confusion or lethargy are serious symptoms of diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA), a life-threatening complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
- Neurological effects: Ketones can have a toxic effect on the brain, leading to confusion, lethargy, and even coma.
- Dehydration: DKA can cause dehydration, which can also lead to confusion and lethargy.
- Electrolyte imbalances: DKA can also cause electrolyte imbalances, which can lead to muscle weakness, fatigue, and confusion.
- Hypoglycemia: DKA can sometimes be mistaken for hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), which can also cause confusion and lethargy.
Confusion or lethargy are serious symptoms of DKA and should be evaluated by a doctor immediately. Treatment for DKA typically involves fluids, electrolytes, and insulin.
Onset
The sudden onset of DKA is a hallmark of this serious complication of diabetes. Unlike other complications that may develop gradually over time, DKA can progress rapidly, often within a matter of hours. This rapid progression highlights the importance of recognizing the symptoms of DKA and seeking medical attention immediately.
The sudden onset of DKA is often triggered by an event that stresses the body, such as an infection, injury, or missed insulin dose. When the body is stressed, it produces hormones like glucagon and cortisol, which increase blood sugar levels. If the body cannot use glucose for energy due to a lack of insulin, it will break down fat and muscle for energy instead. This process produces ketones, which can build up in the blood and lead to DKA.
The rapid onset of DKA can make it difficult to recognize and treat in its early stages. However, it is important to be aware of the symptoms of DKA, such as excessive thirst, frequent urination, nausea and vomiting, and confusion or lethargy. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
Early diagnosis and treatment of DKA is essential to prevent serious complications, including diabetic coma and death. Treatment typically involves fluids, electrolytes, and insulin to correct dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and high blood sugar levels.
Progression
The progression of DKA symptoms is a critical aspect of understanding the severity and urgency of this condition. DKA is a life-threatening complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. If left untreated, the symptoms of DKA can worsen rapidly, leading to serious complications and even death.
- Rapid Dehydration: DKA causes excessive thirst and frequent urination, leading to rapid dehydration. Dehydration can worsen the symptoms of DKA, such as confusion, lethargy, and electrolyte imbalances.
- Electrolyte Imbalances: DKA can cause electrolyte imbalances, such as low potassium and high sodium levels. These imbalances can affect heart function, muscle function, and nerve function. Severe electrolyte imbalances can be life-threatening.
- Ketoacidosis: The buildup of ketones in the blood can lead to ketoacidosis, a condition in which the blood becomes acidic. Ketoacidosis can damage the brain and other organs.
- Coma and Death: If DKA is not treated promptly, it can lead to diabetic coma and death. Diabetic coma is a life-threatening condition in which the person loses consciousness due to high blood sugar levels and ketoacidosis.
The rapid progression of DKA symptoms highlights the importance of recognizing the early signs and seeking medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent serious complications and improve the chances of a successful outcome.
FAQs on Diabetes DKA Symptoms
Understanding the symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is crucial for people with diabetes and their caregivers. Here are some frequently asked questions and answers to provide clarity and guidance:
Question 1: What are the most common symptoms of DKA?
Answer: The classic symptoms of DKA include excessive thirst, frequent urination, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, confusion or lethargy, and fruity-smelling breath.
Question 2: How quickly can DKA develop?
Answer: DKA can develop rapidly, often within a few hours. It is important to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any symptoms of DKA.
Question 3: What causes DKA?
Answer: DKA is caused by a severe lack of insulin, which leads to the body breaking down fat for energy and producing ketones. Common triggers include infections, missed insulin doses, and dehydration.
Question 4: How is DKA treated?
Answer: Treatment for DKA typically involves fluids, electrolytes, and insulin to correct dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and high blood sugar levels. It is essential to seek medical attention promptly to prevent serious complications.
Question 5: Can DKA be prevented?
Answer: While DKA cannot always be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk, such as managing your blood sugar levels effectively, taking insulin as prescribed, and recognizing and treating infections early on.
Question 6: What are the potential complications of DKA?
Answer: Untreated DKA can lead to serious complications, including diabetic coma, brain swelling, and even death. It is crucial to seek medical attention immediately if you suspect DKA.
Summary of key takeaways or final thought:
Recognizing and promptly addressing the symptoms of DKA is essential for people with diabetes. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent severe complications and improve overall outcomes. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, adherence to insulin therapy, and seeking medical attention when necessary are vital in managing diabetes and minimizing the risk of DKA.
Transition to the next article section:
For more information on diabetes management and DKA prevention, refer to the following resources:
Tips for Managing Diabetes DKA Symptoms
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that requires prompt recognition and treatment. Here are some crucial tips to help manage DKA symptoms effectively:
Tip 1: Recognize the Symptoms:
Familiarize yourself with the classic symptoms of DKA: excessive thirst, frequent urination, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, confusion or lethargy, and fruity-smelling breath. Early recognition allows for timely medical intervention.
Tip 2: Seek Immediate Medical Attention:
If you experience any DKA symptoms, seek medical attention immediately. DKA is a life-threatening condition that requires prompt treatment in a hospital setting.
Tip 3: Monitor Blood Sugar Levels Regularly:
Regular blood sugar monitoring is essential for diabetes management. Consistent tracking helps identify patterns, adjust insulin doses, and minimize the risk of DKA.
Tip 4: Adhere to Insulin Regimen:
Taking insulin as prescribed is crucial to prevent DKA. Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions carefully and never miss or delay insulin injections.
Tip 5: Stay Hydrated:
Dehydration can worsen DKA symptoms. Drink plenty of fluids, especially water, to maintain adequate hydration levels.
Tip 6: Manage Infections Promptly:
Infections can trigger DKA. If you develop any signs of infection, such as fever, chills, or pain, seek medical attention promptly to prevent DKA.
Summary of key takeaways or benefits:
By following these tips, you can effectively manage DKA symptoms and reduce the risk of severe complications. Remember, early recognition and prompt medical attention are crucial in treating DKA and ensuring a positive outcome.
Transition to the article’s conclusion:
Managing diabetes DKA symptoms requires a proactive approach. By understanding the symptoms, seeking timely medical care, and adhering to proper diabetes management practices, you can minimize the impact of DKA and maintain good health.
Conclusion
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that requires prompt recognition and management. Understanding the symptoms of DKA is crucial for individuals with diabetes and their caregivers to initiate timely medical intervention. The classic symptoms of DKA include excessive thirst, frequent urination, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, confusion or lethargy, and fruity-smelling breath.
Early diagnosis and treatment of DKA are essential to prevent severe complications and life-threatening consequences. Individuals with diabetes should monitor their blood sugar levels regularly, adhere to their prescribed insulin regimen, stay adequately hydrated, and promptly address any signs of infection to minimize the risk of DKA. Healthcare professionals play a vital role in educating patients about DKA symptoms and empowering them with self-management strategies.
Ongoing research and advancements in diabetes management continue to improve the care and outcomes for individuals with diabetes. By raising awareness, promoting early intervention, and supporting ongoing management efforts, we can collectively strive to reduce the incidence and impact of DKA, empowering individuals with diabetes to live healthier, more fulfilling lives.
Youtube Video: