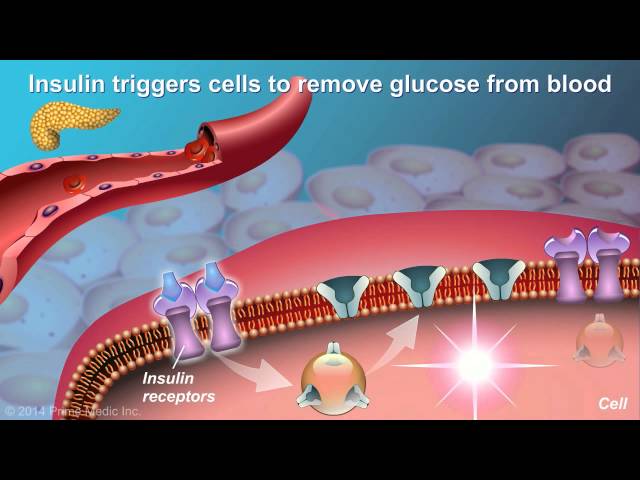
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way your body turns food into energy. With type 2 diabetes, your body doesn’t make enough insulin or doesn’t use insulin well. Glucose then stays in your blood instead of being absorbed by your cells.
There are many risk factors for type 2 diabetes, including obesity, family history, physical inactivity, and unhealthy diet. Type 2 diabetes can lead to serious health problems, including heart disease, stroke, blindness, and kidney failure. However, type 2 diabetes can be managed with diet, exercise, and medication.
If you have any of the risk factors for type 2 diabetes, it’s important to talk to your doctor. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent serious health problems.
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way your body turns food into energy. With type 2 diabetes, your body doesn’t make enough insulin or doesn’t use insulin well. Glucose then stays in your blood instead of being absorbed by your cells.
- Chronic: Type 2 diabetes is a lifelong condition that requires ongoing management.
- Progressive: Type 2 diabetes tends to get worse over time, requiring closer monitoring and treatment.
- Metabolic: Type 2 diabetes affects the way your body processes food, specifically glucose metabolism.
- Insulin Resistance: In type 2 diabetes, the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels.
- Blood Sugar Control: Managing type 2 diabetes involves controlling blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and medication.
- Lifestyle Management: Healthy lifestyle choices, such as regular exercise and a balanced diet, play a crucial role in managing type 2 diabetes.
- Complications: Uncontrolled type 2 diabetes can lead to serious health complications, including heart disease, stroke, blindness, and kidney failure.
Understanding these key aspects of type 2 diabetes is essential for effective management and prevention. By maintaining healthy blood sugar levels and adopting a healthy lifestyle, individuals with type 2 diabetes can live long, fulfilling lives.
Chronic
The chronic nature of type 2 diabetes is a defining characteristic that sets it apart from other types of diabetes. Unlike type 1 diabetes, which is an autoimmune condition that typically develops in childhood or adolescence, type 2 diabetes is a progressive condition that usually develops in adulthood and persists throughout a person’s lifetime.
- Continuous Monitoring: The ongoing nature of type 2 diabetes necessitates continuous monitoring of blood sugar levels, often through regular blood tests or glucose monitoring devices.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Managing type 2 diabetes requires sustained lifestyle modifications, including adherence to a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management techniques.
- Medication and Treatment: Depending on the severity of the condition, individuals with type 2 diabetes may require ongoing medication, such as insulin or oral medications, to regulate blood sugar levels.
- Regular Doctor Visits: Regular check-ups and consultations with healthcare professionals are crucial for monitoring progress, adjusting treatment plans, and preventing complications.
Understanding the chronic nature of type 2 diabetes is essential for effective disease management. It emphasizes the importance of adopting a long-term approach, prioritizing healthy lifestyle choices, and working closely with healthcare providers to maintain optimal blood sugar control and prevent potential complications.
Progressive
The progressive nature of type 2 diabetes is a crucial aspect to understand, as it underscores the importance of ongoing monitoring and treatment. Over time, the body’s ability to produce or effectively utilize insulin diminishes, leading to a gradual worsening of blood sugar control.
- Deteriorating Insulin Function: As type 2 diabetes progresses, the pancreas gradually loses its capacity to produce sufficient insulin, or the body’s cells become increasingly resistant to insulin’s effects. This leads to persistently elevated blood sugar levels.
- Increased Monitoring: The progressive nature of type 2 diabetes necessitates regular monitoring of blood sugar levels to assess the effectiveness of treatment and identify any necessary adjustments.
- Intensified Treatment: As the condition worsens, individuals with type 2 diabetes may require more intensive treatment, including increased medication dosages, additional medications, or even insulin therapy.
Understanding the progressive nature of type 2 diabetes empowers individuals to take proactive steps in managing their condition. Regular monitoring, adherence to treatment plans, and lifestyle modifications can help slow the progression of the disease, prevent complications, and maintain overall well-being.
In summary, the progressive nature of type 2 diabetes underscores the importance of ongoing monitoring and treatment to effectively manage blood sugar levels and prevent complications. This understanding empowers individuals to take an active role in their health and work closely with healthcare providers to achieve optimal outcomes.
Metabolic
The metabolic aspect of type 2 diabetes centers around the body’s impaired ability to process food, particularly glucose, which is the primary source of energy for the body.
-
Insulin Resistance
In type 2 diabetes, the body’s cells become resistant to insulin, a hormone that helps glucose enter cells for energy production. This resistance leads to a buildup of glucose in the bloodstream, resulting in hyperglycemia, a hallmark of type 2 diabetes.
-
Impaired Insulin Production
As type 2 diabetes progresses, the pancreas, responsible for producing insulin, gradually loses its capacity to produce sufficient insulin. This further exacerbates insulin resistance and contributes to elevated blood sugar levels.
-
Dysfunctional Glucose Metabolism
The combination of insulin resistance and impaired insulin production disrupts the normal metabolism of glucose. Glucose uptake into cells is hindered, leading to energy deprivation and a reliance on alternative fuel sources, such as fats, for energy production.
-
Long-Term Consequences
Chronic hyperglycemia associated with type 2 diabetes can lead to severe complications affecting various organs and systems, including the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves.
Understanding the metabolic basis of type 2 diabetes is crucial for developing effective management strategies. By addressing insulin resistance, improving insulin production, and promoting healthy glucose metabolism, individuals with type 2 diabetes can achieve better blood sugar control and minimize the risk of complications.
Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is a crucial aspect of type 2 diabetes, significantly contributing to the elevated blood sugar levels that characterize the condition. Understanding the connection between insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes is essential for developing effective management strategies and preventing complications.
-
Impaired Glucose Uptake
Insulin resistance impairs the ability of cells to absorb glucose from the bloodstream. This leads to a buildup of glucose in the blood, resulting in hyperglycemia, a hallmark of type 2 diabetes.
-
Metabolic Dysregulation
Insulin resistance disrupts the normal metabolic processes in the body. It affects carbohydrate, protein, and fat metabolism, leading to an imbalance that contributes to weight gain and other health issues.
-
Increased Risk of Complications
Chronic hyperglycemia associated with insulin resistance can damage blood vessels and organs over time. This increases the risk of developing serious complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and blindness.
-
Lifestyle and Genetic Factors
Insulin resistance can be influenced by lifestyle factors, such as obesity, physical inactivity, and unhealthy diet. Genetic factors also play a role, with some individuals being more prone to developing insulin resistance than others.
Understanding the connection between insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes is paramount for effective disease management. By adopting healthy lifestyle choices, such as maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and following a balanced diet, individuals can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes and its associated complications.
Blood Sugar Control
Blood sugar control is a critical aspect of managing type 2 diabetes. Elevated blood sugar levels, a hallmark of type 2 diabetes, can lead to severe complications if left unchecked. Therefore, maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is essential for preventing and managing the condition.
Diet plays a significant role in blood sugar control. Consuming a balanced diet that is low in refined carbohydrates and added sugars helps regulate blood sugar levels. Regular exercise is another important factor. Physical activity increases insulin sensitivity, allowing cells to better absorb glucose from the bloodstream. In some cases, medication may be necessary to control blood sugar levels. Medications such as insulin, metformin, and sulfonylureas work by either increasing insulin production, enhancing insulin sensitivity, or reducing glucose production in the liver.
Understanding the importance of blood sugar control in type 2 diabetes is crucial for effective disease management. By adopting healthy lifestyle choices and adhering to prescribed treatment plans, individuals with type 2 diabetes can maintain optimal blood sugar levels, reducing their risk of developing complications such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure.
Lifestyle Management
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels due to insulin resistance or impaired insulin production. Lifestyle management is a cornerstone of type 2 diabetes management, as healthy lifestyle choices can significantly impact blood sugar control and reduce the risk of complications.
-
Dietary Management
A balanced diet low in refined carbohydrates and added sugars helps regulate blood sugar levels. Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins promote satiety, provide essential nutrients, and support overall health.
-
Regular Exercise
Physical activity increases insulin sensitivity, allowing cells to better absorb glucose from the bloodstream. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week.
-
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces insulin resistance and improves blood sugar control. Excess weight, particularly abdominal fat, can contribute to insulin resistance and worsen type 2 diabetes.
-
Smoking Cessation
Smoking damages blood vessels and impairs insulin sensitivity. Quitting smoking can significantly improve blood sugar control and reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications.
Adopting healthy lifestyle habits can empower individuals with type 2 diabetes to manage their blood sugar levels, reduce their risk of complications, and improve their overall well-being. Healthcare professionals can provide personalized guidance and support to help individuals develop and maintain effective lifestyle management strategies.
Complications
Uncontrolled type 2 diabetes can lead to a range of serious health complications, including heart disease, stroke, blindness, and kidney failure. These complications are caused by the damage to blood vessels and organs that can occur when blood sugar levels are persistently high.
-
Heart disease
High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels that supply blood to the heart. This can lead to the development of heart disease, which can include angina (chest pain), heart attack, and heart failure.
-
Stroke
High blood sugar levels can also damage the blood vessels in the brain. This can lead to a stroke, which occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted. Strokes can cause a range of symptoms, including paralysis, speech problems, and vision problems.
-
Blindness
High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. This can lead to diabetic retinopathy, which can cause blurred vision, vision loss, and eventually blindness.
-
Kidney failure
High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys, which are responsible for filtering waste products from the blood. This can lead to kidney failure, which can be a life-threatening condition.
These are just some of the serious health complications that can occur as a result of uncontrolled type 2 diabetes. It is important to manage blood sugar levels carefully to reduce the risk of developing these complications.
Frequently Asked Questions about Type 2 Diabetes
This section addresses common questions and misconceptions surrounding type 2 diabetes, providing concise, evidence-based answers.
Question 1: What is the primary cause of type 2 diabetes?
Answer: Type 2 diabetes is primarily caused by insulin resistance, a condition in which the body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
Question 2: What are the key risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes?
Answer: Major risk factors include obesity, physical inactivity, family history of diabetes, certain ethnicities, and advancing age.
Question 3: Can type 2 diabetes be prevented?
Answer: While there is no guaranteed prevention, adopting a healthy lifestyle, including maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and following a balanced diet, can significantly reduce the risk.
Question 4: What are the common symptoms of type 2 diabetes?
Answer: Symptoms may include frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, increased hunger, fatigue, and blurred vision.
Question 5: How is type 2 diabetes diagnosed?
Answer: Diagnosis involves a comprehensive medical history, physical examination, and blood tests, such as a fasting plasma glucose test or an oral glucose tolerance test.
Question 6: Is type 2 diabetes a curable condition?
Answer: Currently, type 2 diabetes is considered a chronic condition that requires ongoing management. However, with proper treatment and lifestyle modifications, individuals can effectively control their blood sugar levels and prevent complications.
Summary: Understanding the causes, risk factors, symptoms, and management of type 2 diabetes is crucial for individuals at risk or living with this condition. Adopting a healthy lifestyle and adhering to prescribed treatment plans can significantly improve outcomes and prevent complications.
Transition: For further information on managing type 2 diabetes, refer to the following sections covering lifestyle modifications, treatment options, and potential complications.
Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Effectively managing type 2 diabetes involves adopting a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, medical treatment, and ongoing monitoring. Here are several crucial tips to consider:
Tip 1: Maintain a Healthy Diet
Adopting a balanced and nutritious diet is paramount. Focus on consuming fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats to regulate blood sugar levels.
Tip 2: Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Regular exercise plays a vital role in managing type 2 diabetes. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week. Physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and helps control blood sugar levels.
Tip 3: Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
Regular blood sugar monitoring is essential for effective diabetes management. Use a blood glucose meter to track your blood sugar levels at home. Keep a log of your readings to identify patterns and adjust your treatment plan accordingly.
Tip 4: Adhere to Medication Regimens
If prescribed, take your diabetes medications as directed by your healthcare provider. These medications can help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Do not alter your dosage or stop taking medications without consulting your doctor.
Tip 5: Manage Stress
Stress can contribute to elevated blood sugar levels. Engage in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature. Adequate sleep and relaxation techniques can also help manage stress levels.
Tip 6: Quit Smoking
Smoking damages blood vessels and impairs insulin sensitivity. Quitting smoking can significantly improve blood sugar control and reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications.
Summary: By incorporating these tips into your daily routine, you can effectively manage type 2 diabetes, maintain optimal blood sugar levels, and reduce the risk of complications. Remember to consult with your healthcare provider regularly to monitor your progress and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
Transition: For further insights into understanding type 2 diabetes and its management, refer to the following sections covering causes, risk factors, and potential complications.
Conclusion
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the body’s ability to process glucose, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. It is characterized by insulin resistance, where cells become less responsive to insulin, and impaired insulin production, where the pancreas gradually loses its capacity to produce sufficient insulin.
Understanding the causes, risk factors, symptoms, and management strategies of type 2 diabetes is crucial for individuals at risk or living with this condition. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, adhering to prescribed treatment plans, and monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, individuals can effectively manage their diabetes and prevent serious health complications.
Ongoing research and advancements in diabetes management continue to provide hope for improved outcomes. However, the key to successful diabetes management lies in empowering individuals with the knowledge and tools they need to take an active role in their health journey.
Youtube Video: