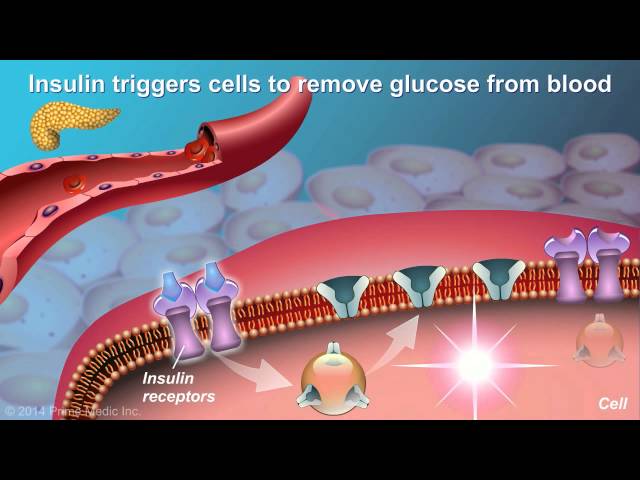
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition in which the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t make enough insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, get from the bloodstream into the cells. Without enough insulin, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels. Over time, high blood sugar levels can damage the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves.
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for about 90% of all cases. It usually develops in adults over the age of 35, but it can also occur in children and adolescents. There are a number of risk factors for type 2 diabetes, including obesity, physical inactivity, family history of diabetes, and certain ethnicities. However, type 2 diabetes can be prevented or delayed with healthy lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise.
There is no cure for type 2 diabetes, but it can be managed with lifestyle changes and medication. Treatment goals include lowering blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of complications, and improving overall health. Type 2 diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with proper care.
Define Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition in which the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t make enough insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, get from the bloodstream into the cells. Without enough insulin, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels. Over time, high blood sugar levels can damage the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves.
- Chronic condition: Type 2 diabetes is a lifelong condition that requires ongoing management.
- Insulin resistance: Type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance, which means that the body’s cells do not respond to insulin as well as they should.
- High blood sugar: Type 2 diabetes is characterized by high blood sugar levels, which can damage the body’s organs and tissues.
- Risk factors: Type 2 diabetes is more common in people who are overweight or obese, physically inactive, have a family history of diabetes, or are of certain ethnicities.
- Complications: Type 2 diabetes can lead to a number of serious complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness.
- Prevention: Type 2 diabetes can be prevented or delayed with healthy lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise.
- Treatment: Type 2 diabetes is treated with lifestyle changes and medication. Treatment goals include lowering blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of complications, and improving overall health.
- Management: Type 2 diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with proper care.
These are just a few of the key aspects of type 2 diabetes. By understanding these aspects, you can better understand the condition and how to manage it.
Chronic condition
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition, which means that it is a lifelong condition that requires ongoing management. This is because type 2 diabetes is a progressive disease, meaning that it tends to get worse over time. There is currently no cure for type 2 diabetes, but it can be managed with lifestyle changes and medication. Treatment goals include lowering blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of complications, and improving overall health.
-
Facet 1: Lifestyle changes
Lifestyle changes are an important part of managing type 2 diabetes. These changes include losing weight, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise. Losing weight can help to improve insulin sensitivity, which can help to lower blood sugar levels. Eating a healthy diet includes eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and limiting intake of sugary drinks and processed foods. Getting regular exercise can help to improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control.
-
Facet 2: Medication
Medication may be necessary to manage type 2 diabetes. There are a number of different types of medications that can be used to treat type 2 diabetes, including insulin, oral medications, and injectables. The type of medication that is best for a particular person will depend on their individual needs and circumstances.
-
Facet 3: Monitoring
Monitoring blood sugar levels is an important part of managing type 2 diabetes. This can be done with a blood glucose meter. Monitoring blood sugar levels can help to ensure that they are within a healthy range and can help to identify trends that may indicate a need for changes in treatment.
-
Facet 4: Complications
Type 2 diabetes can lead to a number of serious complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness. These complications can be prevented or delayed with proper management of type 2 diabetes.
Managing type 2 diabetes can be a challenge, but it is important to remember that it is a lifelong condition that can be managed with proper care. By following a healthy lifestyle, taking medication as prescribed, and monitoring blood sugar levels, people with type 2 diabetes can live long, healthy lives.
Insulin resistance
Insulin resistance is a key component of type 2 diabetes. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, get from the bloodstream into the cells. Without enough insulin, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels. Over time, high blood sugar levels can damage the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves.
There are a number of factors that can contribute to insulin resistance, including obesity, physical inactivity, and family history of diabetes. When a person is insulin resistant, their cells do not respond to insulin as well as they should. This means that the pancreas has to produce more insulin in order to get the same effect. Over time, the pancreas can become exhausted and unable to produce enough insulin, leading to type 2 diabetes.
Insulin resistance is a serious condition that can lead to a number of health problems. However, there are a number of things that can be done to improve insulin sensitivity and prevent or delay the development of type 2 diabetes. These include losing weight, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise.
If you are at risk for type 2 diabetes, it is important to talk to your doctor about ways to improve your insulin sensitivity and reduce your risk of developing the condition.
Conclusion
Insulin resistance is a key component of type 2 diabetes. By understanding the connection between insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes, you can better understand the condition and how to prevent or manage it.
High blood sugar
High blood sugar is a hallmark of type 2 diabetes. When blood sugar levels are high, they can damage the blood vessels and organs throughout the body. Some of the most common complications of high blood sugar include heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness.
There are a number of factors that can contribute to high blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes, including:
- Insulin resistance: Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, get from the bloodstream into the cells. In people with type 2 diabetes, the cells are resistant to insulin, which means that glucose builds up in the bloodstream.
- Lack of insulin: In some cases, people with type 2 diabetes do not produce enough insulin. This can also lead to high blood sugar levels.
- Certain medications: Some medications, such as steroids, can raise blood sugar levels.
- Stress: Stress can also lead to high blood sugar levels.
High blood sugar levels can be dangerous, so it is important to manage them carefully. There are a number of things that people with type 2 diabetes can do to manage their blood sugar levels, including:
- Taking medication: There are a number of different medications that can help to lower blood sugar levels.
- Eating a healthy diet: Eating a healthy diet can help to manage blood sugar levels. A healthy diet for people with type 2 diabetes includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Getting regular exercise: Getting regular exercise can help to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels.
- Losing weight: Losing weight can help to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels.
Managing blood sugar levels is an important part of managing type 2 diabetes. By managing blood sugar levels, people with type 2 diabetes can reduce their risk of developing complications.
Risk factors
The risk factors for type 2 diabetes are closely connected to the definition of the condition. Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition in which the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t make enough insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, get from the bloodstream into the cells. Without enough insulin, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels. Over time, high blood sugar levels can damage the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves.
The risk factors for type 2 diabetes include:
- Overweight or obesity: People who are overweight or obese are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes. This is because excess weight can lead to insulin resistance.
- Physical inactivity: People who are physically inactive are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes. This is because physical activity helps to improve insulin sensitivity.
- Family history of diabetes: People who have a family history of diabetes are more likely to develop the condition. This is because genes play a role in the development of type 2 diabetes.
- Certain ethnicities: People of certain ethnicities, such as African Americans, Hispanics, American Indians, and Asian Americans, are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes. This is because these groups have a higher risk of obesity and physical inactivity.
Understanding the risk factors for type 2 diabetes is important for preventing and managing the condition. By making healthy lifestyle choices, such as maintaining a healthy weight, getting regular exercise, and eating a healthy diet, people can reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
If you are at risk for type 2 diabetes, it is important to talk to your doctor about ways to reduce your risk and manage your blood sugar levels.
Complications
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the body’s ability to use insulin effectively. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, get from the bloodstream into the cells. Without enough insulin, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels. Over time, high blood sugar levels can damage the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves.
The complications of type 2 diabetes are a serious concern because they can lead to disability and even death. For example, heart disease is the leading cause of death in people with diabetes. Stroke, kidney disease, and blindness are also major health problems that can affect people with diabetes.
The good news is that the complications of type 2 diabetes can be prevented or delayed with proper management of the condition. This includes keeping blood sugar levels under control, eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and taking medication as prescribed. By following these recommendations, people with type 2 diabetes can live long, healthy lives.
Understanding the connection between type 2 diabetes and its complications is important for preventing and managing the condition. By making healthy lifestyle choices and working with your doctor to manage your blood sugar levels, you can reduce your risk of developing these serious complications.
Prevention
Preventing type 2 diabetes is an important part of defining the condition. Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition in which the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t make enough insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, get from the bloodstream into the cells. Without enough insulin, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels. Over time, high blood sugar levels can damage the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves.
The connection between prevention and the definition of type 2 diabetes is clear: if type 2 diabetes is a condition characterized by high blood sugar levels, then preventing type 2 diabetes means preventing high blood sugar levels. And one of the most effective ways to prevent high blood sugar levels is to make healthy lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise.
Losing weight can help to prevent type 2 diabetes by reducing insulin resistance. Insulin resistance is a condition in which the body’s cells do not respond to insulin as well as they should. This means that the pancreas has to produce more insulin in order to get the same effect. Over time, the pancreas can become exhausted and unable to produce enough insulin, leading to type 2 diabetes.
Eating a healthy diet can help to prevent type 2 diabetes by reducing the amount of glucose in the bloodstream. A healthy diet includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. These foods are low in glycemic index, which means that they do not cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels.
Getting regular exercise can help to prevent type 2 diabetes by improving insulin sensitivity. Insulin sensitivity is the ability of the body’s cells to respond to insulin. When insulin sensitivity is improved, the body is able to use insulin more effectively to lower blood sugar levels.
Making healthy lifestyle changes is not always easy, but it is one of the most effective ways to prevent type 2 diabetes. By losing weight, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise, you can reduce your risk of developing this serious condition.
Treatment
When we define type 2 diabetes, we are describing a chronic condition in which the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t make enough insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, get from the bloodstream into the cells. Without enough insulin, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels. Over time, high blood sugar levels can damage the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves.
Treatment for type 2 diabetes is essential to manage blood sugar levels and prevent complications. Treatment goals include lowering blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of complications, and improving overall health. There are two main components to treatment: lifestyle changes and medication.
Lifestyle changes include:
- Losing weight
- Eating a healthy diet
- Getting regular exercise
Medication may also be necessary to lower blood sugar levels. There are several different types of medications that can be used to treat type 2 diabetes, including insulin, oral medications, and injectables.
It is important to note that treatment for type 2 diabetes is an ongoing process. There is no cure for type 2 diabetes, but it can be managed with proper care. By following a healthy lifestyle and taking medication as prescribed, people with type 2 diabetes can live long, healthy lives.
The connection between treatment and the definition of type 2 diabetes is clear: treatment is essential to manage the condition and prevent complications. By understanding this connection, people with type 2 diabetes can make informed decisions about their care.
Management: Type 2 diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with proper care.
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management to prevent serious complications. Management of type 2 diabetes typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise, as well as taking medication to lower blood sugar levels.
- Healthy lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is an important part of managing type 2 diabetes. This involves eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight. A healthy diet includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It is also important to limit intake of sugary drinks and processed foods. Getting regular exercise helps to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. Maintaining a healthy weight can also help to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels.
- Medication: Medication may be necessary to lower blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes. There are several different types of medications that can be used to treat type 2 diabetes, including insulin, oral medications, and injectables. The type of medication that is best for a particular person will depend on their individual needs and circumstances.
- Monitoring: Monitoring blood sugar levels is an important part of managing type 2 diabetes. This can be done with a blood glucose meter. Monitoring blood sugar levels can help to ensure that they are within a healthy range and can help to identify trends that may indicate a need for changes in treatment.
- Complications: Type 2 diabetes can lead to a number of serious complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness. These complications can be prevented or delayed with proper management of type 2 diabetes.
Managing type 2 diabetes can be a challenge, but it is important to remember that it is a lifelong condition that can be managed with proper care. By following a healthy lifestyle, taking medication as prescribed, and monitoring blood sugar levels, people with type 2 diabetes can live long, healthy lives.
FAQs on Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a serious chronic condition. It’s caused by the body’s inability to effectively use insulin, a hormone that helps glucose get from the bloodstream into cells. Over time, high blood sugar levels associated with type 2 diabetes can damage the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves.
Question 1: What are the risk factors for type 2 diabetes?
Answer: Risk factors for type 2 diabetes include obesity, physical inactivity, family history of diabetes, and certain ethnicities.
Question 2: What are the symptoms of type 2 diabetes?
Answer: Symptoms of type 2 diabetes can include increased thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, increased hunger, fatigue, and blurred vision.
Question 3: How is type 2 diabetes diagnosed?
Answer: Type 2 diabetes is diagnosed with a blood test that measures blood sugar levels.
Question 4: How is type 2 diabetes treated?
Answer: Treatment for type 2 diabetes includes lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise, as well as taking medication to lower blood sugar levels.
Question 5: Can type 2 diabetes be prevented?
Answer: Type 2 diabetes can be prevented or delayed with healthy lifestyle choices, such as maintaining a healthy weight, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise.
Question 6: What are the complications of type 2 diabetes?
Answer: Complications of type 2 diabetes can include heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness.
If you have any concerns about your risk of type 2 diabetes or if you’ve been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, it’s important to talk to your doctor. Proper management of type 2 diabetes can help you live a long, healthy life.
Moving forward:
Understanding type 2 diabetes and its complications can help individuals make informed decisions about their health. In the next section, we will explore the topic of diabetes management and the importance of regular checkups and monitoring blood sugar levels.
Tips on Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a serious chronic condition that requires ongoing management to prevent serious complications. Management of type 2 diabetes typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise, as well as taking medication to lower blood sugar levels.
Here are five tips for managing type 2 diabetes:
Tip 1: Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly.
Monitoring your blood sugar levels is an important part of managing type 2 diabetes. This can be done with a blood glucose meter. Monitoring blood sugar levels can help to ensure that they are within a healthy range and can help to identify trends that may indicate a need for changes in treatment.Tip 2: Follow a healthy diet.
Eating a healthy diet is an important part of managing type 2 diabetes. A healthy diet includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It is also important to limit intake of sugary drinks and processed foods.Tip 3: Get regular exercise.
Getting regular exercise helps to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.Tip 4: Lose weight if you are overweight or obese.
Maintaining a healthy weight can help to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. If you are overweight or obese, talk to your doctor about ways to lose weight safely and effectively.Tip 5: Take your medication as prescribed.
Medication may be necessary to lower blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes. There are several different types of medications that can be used to treat type 2 diabetes, including insulin, oral medications, and injectables. The type of medication that is best for a particular person will depend on their individual needs and circumstances.
Following these tips can help you to manage your type 2 diabetes and live a long, healthy life.
Conclusion:
Type 2 diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with proper care. By following a healthy lifestyle, taking medication as prescribed, and monitoring blood sugar levels, people with type 2 diabetes can live long, healthy lives.
Conclusion
In this article, we have explored the definition of type 2 diabetes, its risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. Type 2 diabetes is a serious chronic condition that requires ongoing management to prevent serious complications. However, with proper care, people with type 2 diabetes can live long, healthy lives.
If you have any concerns about your risk of type 2 diabetes or if you’ve been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, it’s important to talk to your doctor. Together, you can develop a management plan that meets your individual needs and helps you to achieve your health goals.
Understanding and managing type 2 diabetes is an ongoing process. By staying informed about the latest advances in diabetes research and treatment, you can empower yourself to make informed decisions about your health and live your best life.
Youtube Video: