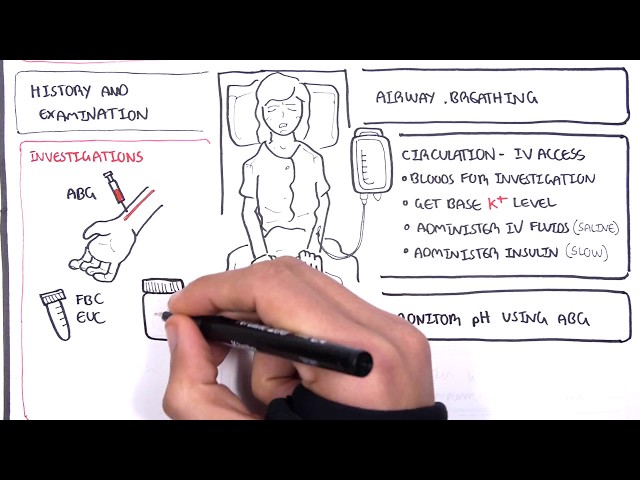
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This process produces ketones, which can build up in the blood and cause diabetic ketoacidosis.
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a medical emergency that can lead to coma or death if not treated promptly. Symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis include:
- High blood sugar levels
- Ketones in the blood or urine
- Dehydration
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Confusion
- Loss of consciousness
Treatment for diabetic ketoacidosis involves giving fluids, insulin, and electrolytes. Treatment is usually given in a hospital setting.
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This process produces ketones, which can build up in the blood and cause DKA.
- Emergency condition: DKA is a medical emergency that can lead to coma or death if not treated promptly.
- High blood sugar: DKA is caused by high blood sugar levels.
- Ketones in the blood: Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy.
- Dehydration: DKA can cause dehydration because the body loses fluids through urination.
- Nausea and vomiting: DKA can cause nausea and vomiting.
- Abdominal pain: DKA can cause abdominal pain.
- Confusion: DKA can cause confusion.
- Loss of consciousness: DKA can cause loss of consciousness.
Treatment for DKA involves giving fluids, insulin, and electrolytes. Treatment is usually given in a hospital setting.
Emergency condition
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This process produces ketones, which can build up in the blood and cause DKA.
- Rapid onset: DKA can develop rapidly, over a period of hours or days. It is important to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of the symptoms of DKA.
- Life-threatening: DKA is a life-threatening condition if not treated promptly. It can lead to coma or death.
- Treatment: Treatment for DKA involves giving fluids, insulin, and electrolytes. Treatment is usually given in a hospital setting.
DKA is a serious complication of diabetes, but it can be prevented. By managing your blood sugar levels and following your doctor’s recommendations, you can help reduce your risk of developing DKA.
High blood sugar
High blood sugar is the main cause of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). When blood sugar levels are high, the body cannot use glucose for energy. Instead, the body breaks down fat for energy, which produces ketones. Ketones are acidic and can build up in the blood, leading to DKA.
DKA is a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to coma or death if not treated promptly. It is important to manage blood sugar levels to prevent DKA.
There are a number of things that can cause high blood sugar levels, including:
- Not taking enough insulin
- Eating too many carbohydrates
- Getting sick
- Exercising less than usual
If you have diabetes, it is important to monitor your blood sugar levels regularly and to follow your doctor’s recommendations for managing your diabetes.
Ketones in the blood
Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This process produces ketones, which can build up in the blood and cause diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA).
- Ketone levels: The level of ketones in the blood is measured in millimoles per liter (mmol/L). A ketone level of 0.5 mmol/L or higher is considered elevated.
- DKA risk: The risk of DKA increases as the level of ketones in the blood increases. A ketone level of 3 mmol/L or higher is considered a medical emergency.
- Symptoms of DKA: Symptoms of DKA include high blood sugar levels, dehydration, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, confusion, and loss of consciousness.
- Treatment for DKA: Treatment for DKA involves giving fluids, insulin, and electrolytes. Treatment is usually given in a hospital setting.
Ketones in the blood are a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to DKA. It is important to manage blood sugar levels to prevent ketones from building up in the blood.
Dehydration
Dehydration is a serious complication of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). When the body cannot use glucose for energy, it breaks down fat instead. This process produces ketones, which can build up in the blood and cause DKA. DKA can also cause dehydration because the body loses fluids through urination.
- Increased urination: When blood sugar levels are high, the kidneys try to get rid of the excess glucose by filtering it out of the blood and into the urine. This can lead to increased urination, which can cause dehydration.
- Vomiting and diarrhea: DKA can also cause vomiting and diarrhea, which can further contribute to dehydration.
- Electrolyte imbalance: DKA can also cause an electrolyte imbalance, which can lead to dehydration. Electrolytes are minerals that are essential for the body’s function. When electrolyte levels are imbalanced, the body cannot retain fluids properly.
Dehydration is a serious complication of DKA that can lead to coma or death. It is important to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of the symptoms of DKA, including dehydration.
Nausea and vomiting
Nausea and vomiting are common symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). DKA is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This process produces ketones, which can build up in the blood and cause DKA.
- Dehydration: DKA can cause dehydration, which can lead to nausea and vomiting.
- Ketones: Ketones can irritate the stomach and intestines, which can cause nausea and vomiting.
- Electrolyte imbalance: DKA can also cause an electrolyte imbalance, which can lead to nausea and vomiting. Electrolytes are minerals that are essential for the body’s function. When electrolyte levels are imbalanced, the body cannot function properly, which can lead to nausea and vomiting.
Nausea and vomiting are serious symptoms of DKA. If you experience nausea and vomiting, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain is a common symptom of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). DKA is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This process produces ketones, which can build up in the blood and cause DKA.
Abdominal pain is caused by the ketones that build up in the blood during DKA. Ketones can irritate the stomach and intestines, which can lead to pain. Abdominal pain can also be caused by the dehydration that often occurs with DKA. Dehydration can cause the muscles in the abdomen to cramp, which can also lead to pain.
Abdominal pain is a serious symptom of DKA. If you experience abdominal pain, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. DKA is a medical emergency that can lead to coma or death if not treated promptly.
Confusion
Confusion is a common symptom of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). DKA is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This process produces ketones, which can build up in the blood and cause DKA.
- Dehydration: DKA can cause dehydration, which can lead to confusion. Dehydration occurs when the body does not have enough fluids. This can happen when a person is not drinking enough fluids or when they are losing fluids through vomiting or diarrhea. Dehydration can cause the brain to shrink, which can lead to confusion.
- Ketones: Ketones can also directly affect the brain and cause confusion. Ketones are acidic and can build up in the blood during DKA. This can lead to a condition called ketoacidosis, which can cause confusion and other neurological problems.
- Electrolyte imbalance: DKA can also cause an electrolyte imbalance, which can lead to confusion. Electrolytes are minerals that are essential for the body’s function. When electrolyte levels are imbalanced, the body cannot function properly, which can lead to confusion.
- Other factors: Other factors that can contribute to confusion in people with DKA include high blood sugar levels, low blood pressure, and infection.
Confusion is a serious symptom of DKA. If you experience confusion, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. DKA is a medical emergency that can lead to coma or death if not treated promptly.
Loss of consciousness
Loss of consciousness (LOC) is a serious complication of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). DKA is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This process produces ketones, which can build up in the blood and cause DKA.
LOC can occur in DKA for a number of reasons. First, DKA can cause dehydration, which can lead to a decrease in blood pressure and a loss of consciousness. Second, ketones can directly affect the brain and cause LOC. Third, DKA can cause an electrolyte imbalance, which can also lead to LOC.
LOC is a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment. Treatment for LOC in DKA involves giving fluids, insulin, and electrolytes. Treatment is usually given in a hospital setting.
Preventing LOC in DKA is important. People with diabetes should manage their blood sugar levels to prevent DKA from developing. If you have diabetes, it is important to follow your doctor’s recommendations for managing your diabetes and to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any symptoms of DKA, including LOC.
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) FAQs
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This process produces ketones, which can build up in the blood and cause DKA.
Question 1: What are the symptoms of DKA?
Answer: Symptoms of DKA include high blood sugar levels, dehydration, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, confusion, and loss of consciousness.
Question 2: What causes DKA?
Answer: DKA is caused by high blood sugar levels. When blood sugar levels are high, the body cannot use glucose for energy and breaks down fat instead. This process produces ketones, which can build up in the blood and cause DKA.
Question 3: How is DKA treated?
Answer: Treatment for DKA involves giving fluids, insulin, and electrolytes. Treatment is usually given in a hospital setting.
Question 4: Can DKA be prevented?
Answer: DKA can be prevented by managing blood sugar levels. People with diabetes should follow their doctor’s recommendations for managing their diabetes and seek medical attention immediately if they experience any symptoms of DKA.
Question 5: What are the long-term effects of DKA?
Answer: DKA can cause serious long-term health problems, including kidney damage, heart disease, and stroke. It is important to manage blood sugar levels to prevent DKA from developing.
Question 6: Is DKA a medical emergency?
Answer: Yes, DKA is a medical emergency. If you experience any symptoms of DKA, seek medical attention immediately.
Summary: DKA is a serious complication of diabetes that can be prevented by managing blood sugar levels. If you have diabetes, it is important to follow your doctor’s recommendations for managing your diabetes and to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any symptoms of DKA.
Transition to the next article section: For more information on DKA, please visit the following resources:
Tips to Prevent and Manage Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This process produces ketones, which can build up in the blood and cause DKA.
DKA can be a life-threatening condition, but it can be prevented and managed with proper care. Here are five tips to help prevent and manage DKA:
Tip 1: Manage Your Blood Sugar Levels
The most important thing you can do to prevent DKA is to manage your blood sugar levels. This means taking your insulin as prescribed, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise. Your doctor can help you create a personalized plan to manage your blood sugar levels.
Tip 2: Recognize the Signs and Symptoms of DKA
It is important to be able to recognize the signs and symptoms of DKA so that you can seek medical help immediately. Symptoms of DKA include high blood sugar levels, dehydration, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, confusion, and loss of consciousness.
Tip 3: Seek Medical Attention Immediately if You Experience Symptoms of DKA
If you experience any symptoms of DKA, seek medical attention immediately. DKA is a medical emergency that can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
Tip 4: Follow Your Doctor’s Recommendations for Managing DKA
If you are diagnosed with DKA, it is important to follow your doctor’s recommendations for managing the condition. This may include taking insulin, fluids, and electrolytes. You may also need to be hospitalized for treatment.
Tip 5: Make Lifestyle Changes to Prevent DKA
In addition to managing your blood sugar levels, there are other lifestyle changes you can make to help prevent DKA. These include eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and losing weight if you are overweight or obese.
Summary: DKA is a serious complication of diabetes, but it can be prevented and managed with proper care. By following these tips, you can help reduce your risk of developing DKA and improve your overall health.
Transition to the article’s conclusion: If you have any questions or concerns about DKA, please talk to your doctor.
Conclusion
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This process produces ketones, which can build up in the blood and cause DKA.
DKA can be a life-threatening condition, but it can be prevented and managed with proper care. By following the tips outlined in this article, you can help reduce your risk of developing DKA and improve your overall health.
Youtube Video: