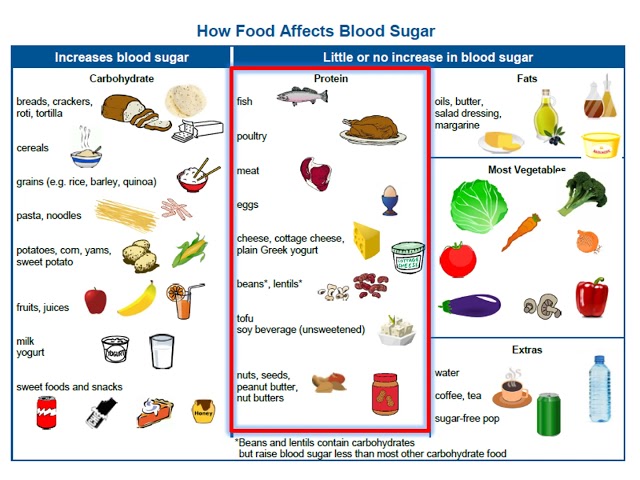
A “diabetic diet” refers to a specialized eating plan designed for individuals with diabetes, a condition characterized by the body’s inability to properly process sugar. This diet aims to manage blood sugar levels, promote overall well-being, and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Adhering to a diabetic diet is crucial for maintaining optimal health. It involves consuming foods that are low in carbohydrates and sugar, while emphasizing fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. This approach helps regulate blood sugar levels, preventing spikes and crashes that can be harmful to the body. Additionally, a diabetic diet can aid in weight management, reducing the risk of obesity, a common comorbidity associated with diabetes.
The history of diabetic diets dates back to the early 20th century, with the introduction of the “Joslin Diet” developed by Dr. Elliott Joslin. Since then, advancements in medical research have led to a better understanding of diabetes and its dietary management. Today, registered dietitians and healthcare professionals work closely with individuals with diabetes to create personalized diabetic diets that meet their specific needs and preferences.
Diabetic Diet
A diabetic diet is a specialized eating plan designed for individuals with diabetes, a condition characterized by the body’s inability to properly process sugar. This diet aims to manage blood sugar levels, promote overall well-being, and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
- Blood sugar management: The primary goal of a diabetic diet is to regulate blood sugar levels, preventing spikes and crashes that can be harmful to the body.
- Nutritional adequacy: A diabetic diet should provide all the essential nutrients that the body needs, including carbohydrates, protein, fat, vitamins, and minerals.
- Individualization: Diabetic diets are tailored to the specific needs and preferences of each individual, taking into account factors such as age, weight, activity level, and diabetes management goals.
- Variety: A diabetic diet should include a wide variety of foods from all food groups, ensuring that the individual enjoys their meals and does not feel deprived.
- Lifestyle integration: A diabetic diet should be integrated into the individual’s lifestyle, taking into account their daily routine, social activities, and cultural background.
- Long-term sustainability: A diabetic diet should be sustainable over the long term, helping the individual manage their diabetes effectively throughout their life.
In summary, a diabetic diet is an essential component of diabetes management. It involves consuming foods that are low in carbohydrates and sugar, while emphasizing fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. This approach helps regulate blood sugar levels, prevent diabetes-related complications, and promote overall well-being.
Blood sugar management
Individuals with diabetes have impaired insulin production or function, which leads to elevated blood sugar levels. A diabetic diet plays a crucial role in managing blood sugar by emphasizing foods that are low in carbohydrates and sugar, while promoting fiber intake.
- Carbohydrate counting: Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for the body and have the greatest impact on blood sugar levels. A diabetic diet involves counting carbohydrates to ensure that the individual consumes a consistent amount throughout the day, preventing blood sugar spikes after meals.
- Fiber intake: Fiber is an indigestible carbohydrate that helps slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream. By incorporating soluble fiber into their diet, individuals with diabetes can manage blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Glycemic index: The glycemic index (GI) measures how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. A diabetic diet should include foods with a low to moderate GI to avoid blood sugar spikes.
- Portion control: Consuming appropriate portion sizes is crucial for blood sugar management. Individuals with diabetes should use measuring cups and spoons to ensure that they are not consuming excessive amounts of carbohydrates or calories, which can lead to blood sugar spikes.
By following these principles, a diabetic diet can effectively regulate blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness.
Nutritional adequacy
Nutritional adequacy is a cornerstone of a diabetic diet. Individuals with diabetes have unique nutritional needs due to the impact of the condition on their metabolism and overall health. A well-balanced diabetic diet must provide all the essential nutrients that the body needs, including carbohydrates, protein, fat, vitamins, and minerals, to ensure optimal health and well-being.
Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for the body and play a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels. Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues, and fat provides energy and supports hormone production. Vitamins and minerals are vital for various bodily functions, including metabolism, immune system function, and bone health.
A diabetic diet that is nutritionally adequate can help individuals with diabetes manage their blood sugar levels effectively, reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications, and improve their overall health and well-being. Conversely, a diet that is deficient in essential nutrients can lead to malnutrition, fatigue, impaired immune function, and increased susceptibility to infections.
In conclusion, nutritional adequacy is a critical component of a diabetic diet. By ensuring that their diet provides all the essential nutrients that the body needs, individuals with diabetes can optimize their health outcomes and live full and active lives.
Individualization
Individualization is a crucial aspect of diabetic diets. Unlike a one-size-fits-all approach, a tailored diet considers the unique characteristics and circumstances of each individual, ensuring that their nutritional needs are met and their diabetes management goals are supported.
- Age: Nutritional needs vary with age, and a diabetic diet should be adjusted accordingly. For example, older adults may require fewer calories and a greater emphasis on certain nutrients, such as calcium and vitamin D, to support bone health.
- Weight: Weight management is an important consideration for individuals with diabetes. A diabetic diet should be tailored to help individuals maintain a healthy weight or lose weight if necessary. This may involve adjusting calorie intake and choosing nutrient-rich foods that promote satiety.
- Activity level: Physical activity level significantly impacts nutritional needs. Individuals with diabetes who engage in regular exercise may require a higher intake of carbohydrates to fuel their workouts. A diabetic diet should be adjusted to support their activity level and prevent hypoglycemia during or after exercise.
- Diabetes management goals: Individual diabetes management goals also influence the design of a diabetic diet. For example, individuals seeking to improve their blood sugar control may need to limit their intake of certain carbohydrates or follow a specific meal plan, such as the Mediterranean diet or the DASH diet.
By considering these individual factors, healthcare professionals and registered dietitians can create personalized diabetic diets that meet the unique needs of each person. This individualized approach is essential for effective diabetes management and improved health outcomes.
Variety
Variety is an essential aspect of a diabetic diet as it helps individuals manage their blood sugar levels, prevent nutrient deficiencies, and maintain a balanced and enjoyable eating plan.
- Nutritional Adequacy: Eating a variety of foods from all food groups ensures that individuals with diabetes receive all the essential nutrients they need, including carbohydrates, protein, fat, vitamins, and minerals. This helps prevent nutrient deficiencies and supports overall health and well-being.
- Blood Sugar Management: Consuming a variety of low-glycemic index foods can help individuals with diabetes manage their blood sugar levels more effectively. By choosing foods with a low to moderate GI, individuals can avoid blood sugar spikes and maintain steadier blood sugar levels throughout the day.
- Weight Management: A varied diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help individuals with diabetes manage their weight. These foods are nutrient-rich and filling, which can help reduce calorie intake and promote satiety.
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases: Eating a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains has been linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, stroke, and some types of cancer. These foods are rich in antioxidants, fiber, and other protective compounds that can help protect against cellular damage and inflammation.
In conclusion, variety is a crucial component of a diabetic diet as it supports nutritional adequacy, blood sugar management, weight management, and reduces the risk of chronic diseases. By incorporating a wide range of foods from all food groups, individuals with diabetes can enjoy a balanced and satisfying eating plan that promotes their overall health and well-being.
Lifestyle Integration
Integrating a diabetic diet into one’s lifestyle is crucial for successful diabetes management and improved health outcomes. This involves aligning dietary choices with daily routines, social activities, and cultural traditions to ensure sustainability and adherence.
- Daily Routine: A diabetic diet should fit seamlessly into an individual’s daily schedule and eating patterns. Meal planning and food preparation should align with work, school, or family commitments to avoid disruptions and promote consistency.
- Social Activities: Social events and gatherings often revolve around food, making it challenging for individuals with diabetes to manage their blood sugar levels. Learning to navigate social situations with food choices that align with a diabetic diet is essential for maintaining social connections while managing diabetes effectively.
- Cultural Background: Cultural traditions and food preferences play a significant role in dietary habits. A diabetic diet should incorporate culturally appropriate foods and flavors to enhance acceptance and adherence. Collaborating with registered dietitians or cultural health workers can help individuals find creative ways to adapt traditional dishes to meet their dietary needs.
- Flexibility and Empowerment: A sustainable diabetic diet empowers individuals to make informed choices and adjust their eating plan based on their unique circumstances. Providing education and support on meal planning, carbohydrate counting, and blood sugar monitoring can enhance self-management skills and promote long-term success.
Integrating a diabetic diet into one’s lifestyle is not merely about following a set of rules but rather about creating a balanced and enjoyable approach to eating that supports diabetes management goals. By considering daily routines, social activities, and cultural backgrounds, healthcare professionals and individuals with diabetes can work together to develop a personalized plan that fosters adherence, improves health outcomes, and enhances quality of life.
Long-term sustainability
Long-term sustainability is a cornerstone of a successful diabetic diet plan. It’s about creating a balanced and manageable approach to eating that can be maintained over a lifetime. When a diabetic diet is sustainable, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of complications, and improve their overall health and well-being.
One key aspect of sustainability is flexibility. No two people are exactly alike, and neither are their dietary needs. A sustainable diabetic diet should be adaptable to individual preferences, lifestyles, and circumstances. It should allow for occasional indulgences without causing feelings of guilt or derailment. By working with a registered dietitian or other qualified healthcare professional, individuals with diabetes can develop a personalized meal plan that meets their specific needs and goals.
Another important factor is variety. A sustainable diabetic diet should include a wide range of nutrient-rich foods from all food groups. This ensures that individuals with diabetes are getting all the essential nutrients they need without feeling restricted or deprived. By incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein into their meals, individuals with diabetes can create a satisfying and balanced eating plan that supports their long-term health.
Finally, a sustainable diabetic diet should be enjoyable. Food is one of life’s great pleasures, and it should be savored, not feared. Individuals with diabetes can find joy in eating by experimenting with new recipes, exploring different cuisines, and cooking meals with family and friends. By focusing on the positive aspects of eating, individuals with diabetes can create a sustainable and enjoyable diet that supports their long-term health and well-being.
In conclusion, long-term sustainability is an essential component of a diabetic diet. By creating a flexible, varied, and enjoyable eating plan, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of complications, and live long, healthy, and fulfilling lives.
Frequently Asked Questions about Diabetic Diets
Diabetic diets are a crucial aspect of diabetes management, helping individuals regulate blood sugar levels, prevent complications, and improve overall health. Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about diabetic diets:
Question 1: What is a diabetic diet?
A diabetic diet is a specialized eating plan designed for individuals with diabetes, a condition characterized by the body’s inability to properly process sugar. This diet focuses on managing blood sugar levels by emphasizing low-carbohydrate, low-sugar foods while promoting nutrient-rich choices like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
Question 2: Why is a diabetic diet important?
A diabetic diet is essential for managing diabetes effectively. It helps regulate blood sugar levels, preventing spikes and crashes that can damage blood vessels and organs. Additionally, a diabetic diet can aid in weight management, reduce the risk of heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness, and improve overall well-being.
Question 3: What foods should I include in a diabetic diet?
A diabetic diet should include a variety of nutrient-rich foods from all food groups, with an emphasis on:
- Fruits and vegetables (non-starchy)
- Whole grains
- Lean protein
- Healthy fats
- Low-fat dairy
Question 4: What foods should I limit or avoid in a diabetic diet?
Foods to limit or avoid in a diabetic diet include:
- Sugary drinks and foods
- Processed carbohydrates (white bread, pasta, rice)
- High-fat meats
- Full-fat dairy
- Alcohol
Question 5: How can I make a diabetic diet enjoyable?
Making a diabetic diet enjoyable involves finding healthy and satisfying alternatives to favorite foods. Experiment with different recipes, explore new cuisines, and incorporate herbs and spices to enhance flavors. Focus on the positive aspects of eating and find ways to make meals social and enjoyable.
Question 6: Should I consult a healthcare professional before starting a diabetic diet?
Yes, it is highly recommended to consult a registered dietitian, doctor, or other qualified healthcare professional before starting a diabetic diet. They can provide personalized guidance, help create a tailored meal plan, and monitor progress to ensure optimal outcomes.
In summary, diabetic diets are essential for managing diabetes effectively and improving overall health. By understanding the basics of a diabetic diet and addressing common concerns, individuals can make informed choices and create a sustainable eating plan that supports their well-being.
Transition to the next article section:
Additional Resources:
- American Diabetes Association: Recipes and Meal Plans
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Diet, Eating, and Physical Activity
Tips for a Successful Diabetic Diet
Managing diabetes through diet requires careful planning and mindful eating habits. Here are some tips to help you create and maintain a successful diabetic diet:
Tip 1: Focus on Nutrient-Rich Foods
Prioritize whole, unprocessed foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. These foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants that support overall health and blood sugar control.
Tip 2: Limit Processed Carbohydrates
White bread, pasta, rice, and sugary drinks contain refined carbohydrates that can rapidly raise blood sugar levels. Instead, opt for complex carbohydrates from whole grains, legumes, and non-starchy vegetables, which provide sustained energy and promote satiety.
Tip 3: Choose Lean Protein Sources
Incorporate lean protein sources such as fish, poultry, beans, and tofu into your meals. Protein helps stabilize blood sugar levels, promote muscle mass, and increase satiety, reducing the risk of overeating.
Tip 4: Emphasize Healthy Fats
Include healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil in moderation. These fats promote satiety, support hormone production, and may improve insulin sensitivity.
Tip 5: Limit Sugar and Sweetened Beverages
Sugary foods and drinks can cause blood sugar spikes and contribute to weight gain. Replace sugary drinks with water, unsweetened tea, or coffee, and limit the consumption of desserts and processed snacks.
Tip 6: Pay Attention to Portion Sizes
Controlling portion sizes helps manage carbohydrate intake and prevent overeating. Use measuring cups and spoons, and be mindful of serving sizes when dining out or preparing meals at home.
Tip 7: Read Food Labels Carefully
Pay attention to food labels to make informed choices. Check the carbohydrate content, sugar content, and serving size to ensure your meals align with your dietary goals.
Tip 8: Consult a Healthcare Professional
Seek guidance from a registered dietitian or other qualified healthcare professional to create a personalized diabetic diet plan that meets your individual needs and health goals. They can provide tailored advice, support, and monitoring to enhance your success.
Summary of key takeaways or benefits:
By following these tips, you can create a balanced and sustainable diabetic diet that supports blood sugar control, promotes overall health, and reduces the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Transition to the article’s conclusion:
Remember, managing diabetes through diet is an ongoing process that requires commitment and consistency. By adopting these tips and working closely with your healthcare team, you can effectively manage your diabetes and live a healthy and fulfilling life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a diabetic diet is a cornerstone of diabetes management, playing a vital role in regulating blood sugar levels, preventing complications, and promoting overall health. By adopting a balanced and individualized approach that emphasizes nutrient-rich foods, limits processed carbohydrates, and includes lean protein and healthy fats, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their condition.
Remember, creating a successful diabetic diet is an ongoing process that requires collaboration with healthcare professionals, careful planning, and mindful eating habits. Through commitment and consistency, individuals can harness the power of nutrition to optimize their health, prevent complications, and live fulfilling lives with diabetes.
Youtube Video: