Insulin for diabetes is a treatment option for individuals with diabetes, a condition characterized by the body’s inability to produce or effectively utilize insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels.
Insulin therapy involves administering insulin to the body via injection or an insulin pump to help control blood sugar levels. It is a crucial treatment for people with type 1 diabetes, who cannot produce insulin naturally, and can be beneficial for those with type 2 diabetes who are unable to manage their blood sugar levels effectively through lifestyle modifications or oral medications.
Insulin therapy has revolutionized the management of diabetes, enabling individuals to live longer, healthier lives. It helps prevent or delay the onset of serious diabetes-related complications, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness.
Insulin for Diabetes
Insulin for diabetes plays a vital role in managing blood sugar levels and preventing complications. Here are seven key aspects to consider:
- Treatment: Insulin is a crucial treatment for individuals with diabetes, helping control blood sugar levels.
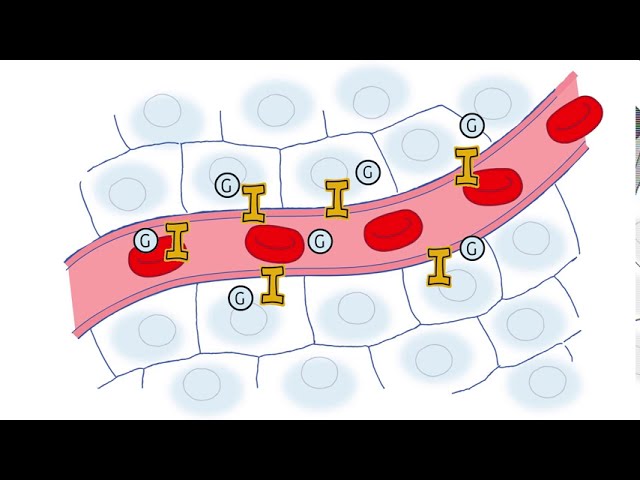
- Hormone: Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels.
- Injections: Insulin is typically administered via injections or an insulin pump.
- Type 1 Diabetes: Insulin therapy is essential for people with type 1 diabetes, who cannot produce insulin naturally.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Insulin may be beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes who cannot manage blood sugar levels effectively through other means.
- Complications: Insulin therapy helps prevent or delay serious diabetes-related complications, such as heart disease and kidney disease.
- Lifelong Management: Insulin therapy is typically a lifelong treatment for individuals with diabetes.
These aspects underscore the importance of insulin for diabetes management. Insulin therapy has transformed the lives of countless individuals with diabetes, enabling them to live longer, healthier, and more fulfilling lives.
Treatment
Insulin for diabetes is a crucial treatment option for individuals who cannot produce or effectively utilize insulin. Insulin is a hormone that plays a vital role in regulating blood sugar levels. Insulin therapy helps control blood sugar levels, preventing serious complications and improving the quality of life for people with diabetes.
- Management of Blood Sugar Levels: Insulin helps manage blood sugar levels by allowing glucose to enter cells for energy production.
- Prevention of Complications: Insulin therapy can help prevent or delay the onset of diabetes-related complications, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness.
- Improved Quality of Life: Insulin enables individuals with diabetes to live longer, healthier, and more active lives by managing their blood sugar levels effectively.
- Lifelong Treatment: Insulin therapy is typically a lifelong treatment for individuals with diabetes, as it helps maintain blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
In conclusion, insulin for diabetes is a crucial treatment that helps manage blood sugar levels, prevents complications, and improves the quality of life for individuals with diabetes. Its role in diabetes management is essential and underscores the importance of effective insulin therapy for overall health and well-being.
Hormone
Insulin is a critical hormone produced by the pancreas that plays a vital role in regulating blood sugar levels. It acts as a key component of “insulin for diabetes,” a treatment option for individuals with diabetes, a condition characterized by the body’s inability to produce or effectively utilize insulin.
The connection between “Hormone: Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels.” and “insulin for diabetes” is fundamental. In individuals with diabetes, the pancreas either does not produce enough insulin or cannot utilize insulin effectively, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Insulin therapy, which involves administering insulin to the body, helps regulate blood sugar levels.
Understanding the role of insulin as a hormone in diabetes management is crucial. It enables healthcare professionals to tailor insulin therapy to individual needs, ensuring optimal blood sugar control and preventing complications. Moreover, ongoing research on insulin and its role in diabetes helps improve treatment strategies and outcomes for individuals with this condition.
Injections
In the context of “insulin for diabetes”, injections play a crucial role in administering insulin to individuals with diabetes. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps regulate blood sugar levels. When the body cannot produce or effectively utilize insulin, insulin therapy becomes necessary to manage blood sugar levels and prevent complications.
-
Subcutaneous Injections:
Subcutaneous injections involve injecting insulin into the fatty tissue beneath the skin. This method is commonly used for insulin therapy, allowing for flexible injection sites and convenient administration.
-
Intravenous Injections:
Intravenous injections, while less common, involve administering insulin directly into a vein. This method is typically used in emergency situations or when rapid insulin delivery is required.
-
Insulin Pumps:
Insulin pumps are small, computerized devices that deliver insulin continuously throughout the day. Pumps offer precise insulin delivery and allow for adjustments based on individual needs and varying blood sugar levels.
-
Injection Devices:
Various injection devices, such as pens and syringes, are available to facilitate insulin administration. These devices make injections more convenient and less painful, improving adherence to insulin therapy.
The choice of insulin administration method depends on individual preferences, lifestyle factors, and medical recommendations. Injections and insulin pumps are effective methods for delivering insulin, enabling individuals with diabetes to manage their blood sugar levels effectively.
Type 1 Diabetes
In the context of “insulin for diabetes,” understanding the connection between type 1 diabetes and insulin therapy is crucial. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, rendering the body incapable of producing insulin.
Insulin, as a critical hormone in blood sugar regulation, is essential for people with type 1 diabetes. Without insulin, glucose cannot enter cells for energy production, leading to dangerously high blood sugar levels. Insulin therapy becomes the only way for individuals with type 1 diabetes to manage their blood sugar and maintain overall health.
The practical significance of this understanding lies in the life-saving implications of insulin therapy for people with type 1 diabetes. Insulin injections or an insulin pump provide the necessary insulin, allowing individuals to regulate their blood sugar levels and prevent life-threatening complications such as diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state.
Type 2 Diabetes
In the context of “insulin for diabetes,” understanding the role of insulin in type 2 diabetes is essential. Type 2 diabetes is characterized by the body’s inability to effectively utilize insulin, a condition known as insulin resistance. This can lead to elevated blood sugar levels, requiring additional support to manage blood sugar effectively.
Insulin therapy may become necessary when lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise, and oral medications are not sufficient to control blood sugar levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Insulin can help improve insulin sensitivity, allowing glucose to enter cells more effectively and reducing blood sugar levels.
The connection between “Type 2 Diabetes: Insulin may be beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes who cannot manage blood sugar levels effectively through other means.” and “insulin for diabetes” lies in the recognition that insulin therapy can be a valuable tool for managing blood sugar levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes who are unable to do so through other means. Insulin therapy can help prevent or delay the onset of serious diabetes-related complications, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness, improving the overall health and well-being of individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Complications
Insulin therapy plays a crucial role in preventing or delaying the onset of serious diabetes-related complications, such as heart disease and kidney disease. Understanding this connection is essential in recognizing the importance of insulin therapy as a component of “insulin for diabetes.”
High blood sugar levels, if left uncontrolled, can damage blood vessels and organs, leading to various complications. Insulin therapy helps maintain blood sugar levels within a healthy range, reducing the risk of these complications.
For instance, uncontrolled blood sugar levels can contribute to the development of heart disease by damaging blood vessels and increasing the risk of blood clots. Insulin therapy helps prevent this damage by regulating blood sugar levels, thus reducing the risk of heart disease.
Similarly, high blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys, leading to kidney disease. Insulin therapy helps protect the kidneys by maintaining blood sugar levels within a healthy range, preventing or delaying the onset of kidney disease.
In conclusion, the connection between “Complications: Insulin therapy helps prevent or delay serious diabetes-related complications, such as heart disease and kidney disease.” and “insulin for diabetes” underscores the critical role of insulin therapy in managing blood sugar levels and preventing serious health complications.
Lifelong Management
The connection between “Lifelong Management: Insulin therapy is typically a lifelong treatment for individuals with diabetes.” and “insulin for diabetes” lies in the chronic nature of diabetes and the ongoing need for insulin therapy to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
- Continuous Insulin Requirement: Individuals with diabetes, particularly those with type 1 diabetes, require lifelong insulin therapy because their bodies either do not produce insulin (type 1 diabetes) or do not produce enough insulin to meet their needs (type 2 diabetes).
- Prevention of Complications: Insulin therapy is crucial for preventing or delaying the onset of serious diabetes-related complications, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness. Maintaining stable blood sugar levels through lifelong insulin therapy helps reduce the risk of these complications.
- Improved Quality of Life: Lifelong insulin therapy enables individuals with diabetes to live longer, healthier, and more fulfilling lives by effectively managing their blood sugar levels. It allows them to participate in daily activities, maintain social connections, and pursue their goals without the debilitating effects of uncontrolled blood sugar.
- Advancements in Insulin Therapy: Ongoing research and advancements in insulin therapy have led to the development of various insulin formulations and delivery methods, providing individuals with diabetes with greater flexibility and convenience in managing their condition.
In conclusion, the connection between “Lifelong Management: Insulin therapy is typically a lifelong treatment for individuals with diabetes.” and “insulin for diabetes” underscores the importance of ongoing insulin therapy for effective diabetes management. It not only helps prevent serious complications but also improves the overall quality of life for individuals with diabetes.
Frequently Asked Questions about Insulin for Diabetes
This section aims to address some of the common concerns or misconceptions surrounding insulin for diabetes, providing concise and informative answers to frequently asked questions.
Question 1: Is insulin therapy necessary for all people with diabetes?
Answer: Insulin therapy is essential for individuals with type 1 diabetes, as their bodies do not produce insulin. For individuals with type 2 diabetes, insulin therapy may be recommended if lifestyle modifications and oral medications are not sufficient to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
Question 2: Is insulin therapy a lifelong treatment?
Answer: For individuals with type 1 diabetes, insulin therapy is typically a lifelong treatment, as their bodies cannot produce insulin on their own. For individuals with type 2 diabetes, insulin therapy may be used long-term or discontinued if blood sugar levels can be managed through other means.
Question 3: Can insulin therapy cause weight gain?
Answer: Insulin can cause weight gain as it promotes glucose uptake into cells, which can lead to increased fat storage. However, weight gain can be managed through careful monitoring of food intake, regular exercise, and working with healthcare professionals to adjust insulin dosage if necessary.
Question 4: Is it possible to develop an allergy to insulin?
Answer: Insulin allergies are rare but can occur. Symptoms of an insulin allergy may include hives, swelling, redness, or itching at the injection site. If an allergic reaction is suspected, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately.
Question 5: How often should blood sugar levels be checked when using insulin?
Answer: The frequency of blood sugar monitoring when using insulin varies depending on individual needs and the type of insulin being used. Healthcare professionals will provide personalized recommendations based on factors such as blood sugar control, insulin dosage, and lifestyle.
Question 6: What are the potential risks and side effects of insulin therapy?
Answer: Insulin therapy can cause side effects such as hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), injection site reactions, and weight gain. It is important to be aware of these potential risks and to work closely with healthcare professionals to manage them effectively.
These questions and answers provide a general overview of insulin for diabetes. It is essential to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance on diabetes management.
Transition to the next article section: Understanding the Role of Insulin in Diabetes Management
Tips for Managing Diabetes with Insulin Therapy
Insulin therapy is a crucial aspect of diabetes management, helping individuals regulate blood sugar levels and prevent complications. Here are five essential tips to optimize insulin therapy and improve overall diabetes management:
1. Monitor Blood Sugar Regularly:
Regular blood sugar monitoring is vital for adjusting insulin dosage and ensuring effective blood sugar control. Use a blood glucose meter as directed by your healthcare provider to track blood sugar levels throughout the day.
2. Follow a Balanced Diet:
A healthy diet is fundamental for diabetes management. Focus on consuming nutrient-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
3. Exercise Regularly:
Regular physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control. Engage in moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling.
4. Take Insulin as Prescribed:
Adherence to the prescribed insulin regimen is crucial. Take insulin at the correct times and in the correct doses to maintain optimal blood sugar control. Do not alter your insulin dosage without consulting your healthcare provider.
5. Manage Stress:
Stress can affect blood sugar levels. Engage in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature to cope with stress and improve overall diabetes management.
These tips can empower individuals with diabetes to effectively manage their condition through insulin therapy. By following these recommendations, you can improve blood sugar control, prevent complications, and live a healthier, more fulfilling life with diabetes.
Transition to the article’s conclusion: Insulin therapy is an essential tool for diabetes management, and these tips provide practical guidance for optimizing its effectiveness. By incorporating these strategies into your diabetes management plan, you can achieve better blood sugar control and improve your overall health and well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, insulin for diabetes plays a pivotal role in managing blood sugar levels and preventing diabetes-related complications. Insulin therapy has revolutionized the lives of individuals with diabetes, enabling them to live longer, healthier lives.
The effective use of insulin therapy requires regular blood sugar monitoring, adherence to prescribed insulin regimens, and lifestyle modifications such as a balanced diet and regular exercise. By incorporating these practices into their daily routines, individuals with diabetes can optimize the benefits of insulin therapy and achieve better blood sugar control.
Ongoing research and advancements in insulin therapy continue to improve its efficacy and convenience. The development of new insulin formulations, delivery systems, and glucose monitoring technologies empower individuals with diabetes to manage their condition more effectively and seamlessly.
Insulin for diabetes is an essential tool that, when used appropriately, can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with diabetes. By understanding the principles of insulin therapy and adopting recommended management strategies, individuals can harness its benefits to achieve optimal health outcomes and live full and active lives.
Youtube Video: