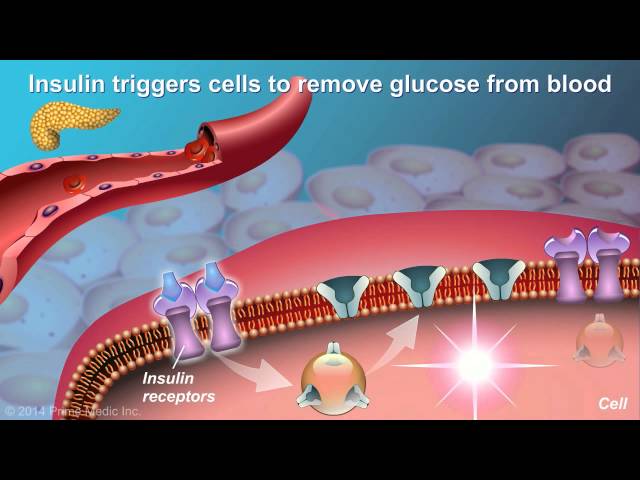
Type 2 diabetes is a condition in which the body does not properly process sugar (glucose). Glucose is a type of sugar that the body uses for energy. With type 2 diabetes, the body either does not make enough insulin or does not use insulin well. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get from the blood into the cells.
There are many risk factors for type 2 diabetes, including:
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Family history of diabetes
- Age (over 45)
- Race/ethnicity (African Americans, Hispanic Americans, American Indians, and Asian Americans are at increased risk)
- Certain medical conditions, such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol
- Certain medications, such as steroids
Type 2 diabetes can lead to a number of serious health problems, including:
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Kidney disease
- Blindness
- Amputation
Causes of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a condition in which the body does not properly process sugar (glucose). Glucose is a type of sugar that the body uses for energy. With type 2 diabetes, the body either does not make enough insulin or does not use insulin well. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get from the blood into the cells.
There are many risk factors for type 2 diabetes, including:
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Family history of diabetes
- Age (over 45)
- Race/ethnicity (African Americans, Hispanic Americans, American Indians, and Asian Americans are at increased risk)
- Certain medical conditions, such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol
- Certain medications, such as steroids
These risk factors can be divided into two main categories: modifiable and non-modifiable. Modifiable risk factors are those that can be changed, such as obesity, physical inactivity, and diet. Non-modifiable risk factors are those that cannot be changed, such as age, family history, and race/ethnicity.
It is important to understand the causes of type 2 diabetes in order to develop strategies for prevention and treatment. By understanding the modifiable risk factors, we can take steps to reduce our risk of developing type 2 diabetes. For example, we can lose weight, get regular exercise, and eat a healthy diet.
Obesity
Obesity is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes. In fact, it is estimated that 80-85% of people with type 2 diabetes are overweight or obese. There are several reasons why obesity increases the risk of type 2 diabetes:
- Obesity can lead to insulin resistance, which is a condition in which the cells of the body do not respond to insulin as well as they should. This can lead to high blood sugar levels.
- Obesity can also lead to inflammation, which is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes.
- Obesity can also increase the risk of other health problems that can contribute to type 2 diabetes, such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol.
Losing weight can help to reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes. Even a small amount of weight loss can make a difference. For example, a study published in the journal JAMA Internal Medicine found that people who lost just 5% of their body weight were able to reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes by 58%.If you are overweight or obese, talk to your doctor about ways to lose weight. Losing weight can help to improve your overall health and reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes and other health problems.
Physical inactivity
Physical inactivity is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes. In fact, it is estimated that people who are physically inactive are twice as likely to develop type 2 diabetes than people who are physically active. There are several reasons why physical inactivity increases the risk of type 2 diabetes:
- Reduced insulin sensitivity: Physical inactivity can lead to insulin resistance, which is a condition in which the cells of the body do not respond to insulin as well as they should. This can lead to high blood sugar levels.
- Increased inflammation: Physical inactivity can also lead to inflammation, which is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes.
- Weight gain: Physical inactivity can also lead to weight gain, which is another major risk factor for type 2 diabetes.
- Other health problems: Physical inactivity can also increase the risk of other health problems that can contribute to type 2 diabetes, such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol.
Getting regular exercise can help to reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes. Even a small amount of exercise can make a difference. For example, a study published in the journal JAMA Internal Medicine found that people who walked for just 30 minutes a day were able to reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes by 12%.If you are physically inactive, talk to your doctor about ways to get more exercise. Getting regular exercise can help to improve your overall health and reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes and other health problems.
Family history of diabetes
A family history of diabetes is a major risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes. In fact, people who have a parent or sibling with type 2 diabetes are two to three times more likely to develop the condition than people who do not have a family history of diabetes.
There are several reasons why a family history of diabetes increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. First, people who have a family history of diabetes are more likely to inherit genes that increase their risk of developing the condition. Second, people who have a family history of diabetes are more likely to be exposed to environmental factors that increase their risk of developing the condition, such as unhealthy eating habits and physical inactivity.
While a family history of diabetes does increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, it is important to remember that it is not a guarantee. Many people with a family history of diabetes never develop the condition. There are several things that people with a family history of diabetes can do to reduce their risk of developing the condition, such as eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight.
If you have a family history of diabetes, it is important to talk to your doctor about your risk of developing the condition. Your doctor can recommend lifestyle changes that you can make to reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Age (over 45)
Age is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes. The risk of developing type 2 diabetes increases with age, and people over the age of 45 are at a significantly higher risk than younger people. There are several reasons why age is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes:
- Decreased insulin sensitivity: As we age, our cells become less sensitive to insulin, which can lead to high blood sugar levels.
- Reduced physical activity: As we age, we tend to become less physically active, which can also lead to insulin resistance and high blood sugar levels.
- Weight gain: Many people gain weight as they age, which can also increase the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Other health problems: As we age, we are more likely to develop other health problems, such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol, which can all increase the risk of type 2 diabetes.
While age is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes, it is important to remember that it is not a guarantee. Many people over the age of 45 never develop type 2 diabetes. There are several things that people over the age of 45 can do to reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes, such as eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Race/ethnicity (African Americans, Hispanic Americans, American Indians, and Asian Americans are at increased risk)
Certain racial and ethnic groups are at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. These groups include African Americans, Hispanic Americans, American Indians, and Asian Americans. There are several reasons why these groups are at an increased risk, including:
- Genetic factors: Some racial and ethnic groups are more likely to have certain genes that increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Environmental factors: Certain racial and ethnic groups are more likely to be exposed to environmental factors that increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, such as unhealthy eating habits and physical inactivity.
- Socioeconomic factors: Certain racial and ethnic groups are more likely to live in poverty, which can limit access to healthy food and safe places to exercise.
- Cultural factors: Certain racial and ethnic groups have cultural beliefs and practices that can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, such as eating a diet high in processed foods and sugary drinks.
It is important to understand the reasons why certain racial and ethnic groups are at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes in order to develop targeted prevention and treatment strategies. By understanding the unique risk factors faced by these groups, we can work to address these risk factors and reduce the disparities in diabetes rates.
For example, one study found that African Americans are more likely to have a variant of the gene PPARG that increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. This gene is involved in regulating blood sugar levels. Another study found that Hispanic Americans are more likely to be exposed to air pollution, which is a risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes.
Understanding the connection between race/ethnicity and type 2 diabetes can help us to develop more effective prevention and treatment strategies. By targeting the specific risk factors faced by different racial and ethnic groups, we can help to reduce the disparities in diabetes rates and improve the health of all Americans.
Certain medical conditions, such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol
High blood pressure and high cholesterol are two medical conditions that are closely linked to type 2 diabetes. In fact, people with high blood pressure or high cholesterol are at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. There are several reasons for this connection.
First, high blood pressure and high cholesterol can damage the blood vessels, which can lead to insulin resistance. Insulin resistance is a condition in which the cells of the body do not respond to insulin as well as they should. This can lead to high blood sugar levels, which can eventually lead to type 2 diabetes.
Second, high blood pressure and high cholesterol can also increase the risk of developing other health problems, such as heart disease and stroke. These health problems can also increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
It is important to manage high blood pressure and high cholesterol to reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. There are several things that people can do to manage these conditions, such as eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and taking medication if necessary.
Here are some real-life examples of how high blood pressure and high cholesterol can lead to type 2 diabetes:
- A study published in the journal JAMA Internal Medicine found that people with high blood pressure were twice as likely to develop type 2 diabetes than people with normal blood pressure.
- A study published in the journal The Lancet found that people with high cholesterol were three times more likely to develop type 2 diabetes than people with normal cholesterol levels.
These studies show that high blood pressure and high cholesterol are significant risk factors for type 2 diabetes. It is important to manage these conditions to reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and other health problems.
Certain medications, such as steroids
Certain medications, such as steroids, can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Steroids are a type of medication that is used to treat a variety of conditions, including asthma, arthritis, and lupus. Steroids work by reducing inflammation in the body.
- Increased blood sugar levels: Steroids can cause the liver to release more glucose into the bloodstream, which can lead to high blood sugar levels.
- Insulin resistance: Steroids can also make the cells of the body less responsive to insulin, which can lead to insulin resistance. Insulin resistance is a condition in which the body does not use insulin effectively, which can lead to high blood sugar levels.
- Weight gain: Steroids can also cause weight gain, which is another risk factor for type 2 diabetes.
People who take steroids for a long period of time are at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. The risk is even higher for people who take high doses of steroids or who take steroids for a long period of time.
If you are taking steroids, it is important to talk to your doctor about your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Your doctor may recommend that you have your blood sugar levels checked regularly and that you make lifestyle changes to reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
FAQs on Causes of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a serious chronic condition affecting millions of people worldwide. Understanding its causes is vital for prevention and management. Below are frequently asked questions and answers regarding the causes of type 2 diabetes:
Question 1: What is the primary cause of type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels, leading to elevated glucose levels in the bloodstream.
Question 2: What are the modifiable risk factors for type 2 diabetes?
Modifiable risk factors include obesity, physical inactivity, unhealthy diet, and smoking. Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise, adopting a balanced nutrition plan, and quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk.
Question 3: Are there non-modifiable risk factors for type 2 diabetes?
Yes, non-modifiable risk factors include age (over 45), family history of the condition, certain ethnicities, and certain medical conditions like high blood pressure or high cholesterol.
Question 4: How does obesity contribute to type 2 diabetes?
Obesity increases the risk of insulin resistance, promotes inflammation, and can lead to weight-related health issues that further contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes.
Question 5: Why is physical inactivity a risk factor for type 2 diabetes?
Physical inactivity leads to reduced insulin sensitivity, increased inflammation, and weight gain, all of which are associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
Question 6: What is the role of genetics in type 2 diabetes?
While family history is a non-modifiable risk factor, it’s important to note that genetics alone do not determine whether an individual will develop type 2 diabetes. Adopting a healthy lifestyle can help mitigate the genetic predisposition.
Remember, understanding the causes of type 2 diabetes empowers individuals to take proactive steps towards prevention and management. Consulting with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and support is highly recommended.
Proceed to the next section for further insights on type 2 diabetes.
Tips on Reducing the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a serious chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While there is no cure, it can be managed through lifestyle changes, including adopting healthy habits and managing risk factors.
Tip 1: Maintain a Healthy Weight
Obesity is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Losing weight and maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce your risk of developing the condition. Aim for a gradual weight loss of 1-2 pounds per week through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
Tip 2: Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week. Choose activities you enjoy and incorporate them into your daily routine.
Tip 3: Adopt a Healthy Diet
A balanced diet is crucial for managing blood sugar levels. Focus on consuming whole, unprocessed foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. Limit your intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats.
Tip 4: Quit Smoking
Smoking increases inflammation and insulin resistance, contributing to the development of type 2 diabetes. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce your risk and improve your overall health.
Tip 5: Manage Blood Pressure and Cholesterol
High blood pressure and high cholesterol are risk factors for type 2 diabetes. Follow your doctor’s recommendations for managing these conditions, including lifestyle changes or medication if necessary.
Tip 6: Get Regular Checkups
Regular checkups with your healthcare provider allow for early detection and monitoring of blood sugar levels. This enables prompt intervention and lifestyle modifications to prevent or manage type 2 diabetes effectively.
Tip 7: Be Aware of Your Family History
If you have a family history of type 2 diabetes, you are at an increased risk. Talk to your doctor about additional preventive measures and lifestyle changes you can adopt.
Tip 8: Manage Stress
Chronic stress can elevate blood sugar levels and increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Engage in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature.
Remember, adopting these tips can significantly reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes or improve its management if you already have the condition. Consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and support.
Proceed to the next section for more information on type 2 diabetes.
Conclusion on Causes of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions worldwide, and understanding its causes is crucial for prevention and management. This article explored various factors contributing to the development of type 2 diabetes, emphasizing the importance of modifiable risk factors such as obesity, physical inactivity, and unhealthy diet.
Recognizing these causes empowers individuals to take proactive steps towards reducing their risk. Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise, and adopting a balanced nutrition plan can significantly lower the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes. Additionally, managing non-modifiable risk factors like family history and certain medical conditions is essential.
By raising awareness and promoting healthy lifestyle choices, we can work towards reducing the prevalence of type 2 diabetes and its associated complications. Ongoing research and advancements in diabetes management continue to provide hope for improved outcomes and a better quality of life for those affected by this condition.
Youtube Video: