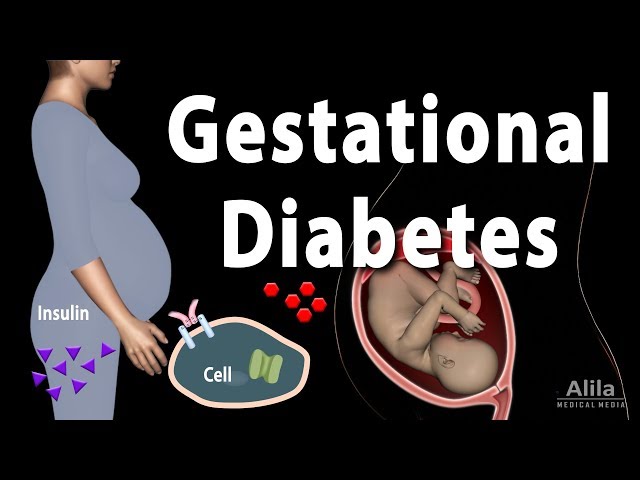
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It usually goes away after the baby is born, but it can increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. If you have gestational diabetes, your body does not make enough insulin or does not use insulin well. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, get from your blood into your cells. Without enough insulin, glucose builds up in your blood. High blood sugar levels can harm your baby and increase your risk of pregnancy complications.
There are no specific symptoms of gestational diabetes. However, some women may experience increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue. If you have any of these symptoms, it is important to see your doctor to be tested for gestational diabetes.
Gestational diabetes is usually treated with diet and exercise. Your doctor may also recommend insulin therapy if diet and exercise are not enough to control your blood sugar levels. Treatment for gestational diabetes is important to help prevent complications for both you and your baby.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can develop during pregnancy. It is important to be aware of the key aspects of gestational diabetes in order to understand the risks and complications associated with it.
- Definition: Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy.
- Causes: Gestational diabetes is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin or use insulin effectively.
- Symptoms: There are often no symptoms of gestational diabetes, but some women may experience increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue.
- Risks: Gestational diabetes can increase the risk of pregnancy complications, such as pre-eclampsia, premature birth, and cesarean section.
- Treatment: Gestational diabetes is usually treated with diet and exercise. Insulin therapy may also be necessary to control blood sugar levels.
- Prevention: There is no sure way to prevent gestational diabetes, but eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight can help to reduce the risk.
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with proper treatment. By understanding the key aspects of gestational diabetes, women can take steps to reduce their risk and improve their health and the health of their baby.
Definition
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin or use insulin effectively. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, get from your blood into your cells. Without enough insulin, glucose builds up in your blood. High blood sugar levels can harm your baby and increase your risk of pregnancy complications.
There are no specific symptoms of gestational diabetes. However, some women may experience increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue. If you have any of these symptoms, it is important to see your doctor to be tested for gestational diabetes.
Gestational diabetes is usually treated with diet and exercise. Your doctor may also recommend insulin therapy if diet and exercise are not enough to control your blood sugar levels. Treatment for gestational diabetes is important to help prevent complications for both you and your baby.
Causes
Gestational diabetes is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin or use insulin effectively. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, get from your blood into your cells. Without enough insulin, glucose builds up in your blood. High blood sugar levels can harm your baby and increase your risk of pregnancy complications.
There are many factors that can contribute to gestational diabetes, including:
- Obesity
- Family history of diabetes
- Age (over 25)
- Certain ethnicities (African American, Hispanic, American Indian, Asian)
- Previous history of gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes usually goes away after the baby is born, but it can increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. If you have gestational diabetes, it is important to follow your doctor’s recommendations for diet, exercise, and blood sugar monitoring. Treatment for gestational diabetes can help prevent complications for both you and your baby.
Understanding the causes of gestational diabetes is important for preventing and managing the condition. By making healthy lifestyle choices and working with your doctor, you can reduce your risk of developing gestational diabetes and improve your chances of having a healthy pregnancy.
Symptoms
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin or use insulin effectively. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, get from your blood into your cells. Without enough insulin, glucose builds up in your blood. High blood sugar levels can harm your baby and increase your risk of pregnancy complications.
There are often no symptoms of gestational diabetes. However, some women may experience increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue. These symptoms are often mild and may not be noticeable at first. However, it is important to be aware of these symptoms and to see your doctor if you experience any of them during pregnancy.
If you have gestational diabetes, it is important to follow your doctor’s recommendations for diet, exercise, and blood sugar monitoring. Treatment for gestational diabetes can help prevent complications for both you and your baby.
Risks
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin or use insulin effectively. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, get from your blood into your cells. Without enough insulin, glucose builds up in your blood. High blood sugar levels can harm your baby and increase your risk of pregnancy complications.
- Pre-eclampsia: Pre-eclampsia is a serious condition that can develop during pregnancy. It is characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine. Pre-eclampsia can lead to serious health problems for both the mother and the baby, including stroke, seizures, and premature birth.
- Premature birth: Premature birth is the birth of a baby before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Babies who are born prematurely are at increased risk for a number of health problems, including respiratory problems, feeding difficulties, and developmental delays.
- Cesarean section: A cesarean section is a surgical procedure to deliver a baby through an incision in the abdomen. Cesarean sections are sometimes necessary when vaginal delivery is not possible or safe. However, cesarean sections can increase the risk of infection and other complications for both the mother and the baby.
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with proper treatment. By following your doctor’s recommendations for diet, exercise, and blood sugar monitoring, you can help reduce your risk of pregnancy complications and improve the health of your baby.
Treatment
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin or use insulin effectively. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, get from your blood into your cells. Without enough insulin, glucose builds up in your blood. High blood sugar levels can harm your baby and increase your risk of pregnancy complications.
Gestational diabetes is usually treated with diet and exercise. Your doctor may also recommend insulin therapy if diet and exercise are not enough to control your blood sugar levels. Treatment for gestational diabetes is important to help prevent complications for both you and your baby.
- Diet: A healthy diet for gestational diabetes includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It is also important to limit your intake of sugary foods and drinks. Eating a healthy diet can help to control your blood sugar levels and reduce your risk of pregnancy complications.
- Exercise: Regular exercise can help to control blood sugar levels and improve your overall health. It is important to talk to your doctor before starting an exercise program during pregnancy.
- Insulin therapy: Insulin therapy may be necessary if diet and exercise are not enough to control your blood sugar levels. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get from your blood into your cells. Insulin therapy can help to lower your blood sugar levels and reduce your risk of pregnancy complications.
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with proper treatment. By following your doctor’s recommendations for diet, exercise, and blood sugar monitoring, you can help reduce your risk of pregnancy complications and improve the health of your baby.
Prevention
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin or use insulin effectively. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, get from your blood into your cells. Without enough insulin, glucose builds up in your blood. High blood sugar levels can harm your baby and increase your risk of pregnancy complications.
There is no sure way to prevent gestational diabetes, but eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight can help to reduce the risk. Eating a healthy diet includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It is also important to limit your intake of sugary foods and drinks. Regular exercise can help to control blood sugar levels and improve your overall health. Maintaining a healthy weight can also help to reduce your risk of gestational diabetes.
If you have gestational diabetes, it is important to follow your doctor’s recommendations for diet, exercise, and blood sugar monitoring. Treatment for gestational diabetes can help prevent complications for both you and your baby.
Preventing gestational diabetes is important for the health of both the mother and the baby. By eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight, women can reduce their risk of developing gestational diabetes and improve their chances of having a healthy pregnancy.
FAQs on Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin or use insulin effectively. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, get from your blood into your cells. Without enough insulin, glucose builds up in your blood. High blood sugar levels can harm your baby and increase your risk of pregnancy complications.
Question 1: What are the symptoms of gestational diabetes?
Answer: There are often no symptoms of gestational diabetes. However, some women may experience increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue.
Question 2: What causes gestational diabetes?
Answer: Gestational diabetes is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin or use insulin effectively. Many factors can contribute to gestational diabetes, including obesity, family history of diabetes, age (over 25), certain ethnicities, and previous history of gestational diabetes.
Question 3: How is gestational diabetes treated?
Answer: Gestational diabetes is usually treated with diet and exercise. Your doctor may also recommend insulin therapy if diet and exercise are not enough to control your blood sugar levels.
Question 4: What are the risks of gestational diabetes?
Answer: Gestational diabetes can increase the risk of pregnancy complications, such as pre-eclampsia, premature birth, and cesarean section.
Question 5: Can gestational diabetes be prevented?
Answer: There is no sure way to prevent gestational diabetes, but eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight can help to reduce the risk.
Question 6: What happens if gestational diabetes is not treated?
Answer: Untreated gestational diabetes can lead to serious health problems for both the mother and the baby. It can increase the risk of birth defects, premature birth, and cesarean section. It can also lead to health problems for the baby later in life, such as obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Summary of key takeaways or final thought: Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can develop during pregnancy. It is important to be aware of the symptoms, causes, and risks of gestational diabetes. If you have gestational diabetes, it is important to follow your doctor’s recommendations for diet, exercise, and blood sugar monitoring. Treatment for gestational diabetes can help prevent complications for both you and your baby.
Transition to the next article section: If you have any questions or concerns about gestational diabetes, please talk to your doctor.
Tips for Managing Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin or use insulin effectively. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, or sugar, get from your blood into your cells. Without enough insulin, glucose builds up in your blood. High blood sugar levels can harm your baby and increase your risk of pregnancy complications.
There is no cure for gestational diabetes, but it can be managed with diet, exercise, and medication. By following these tips, you can help control your blood sugar levels and reduce your risk of complications.
Tip 1: Eat a healthy diet.
A healthy diet for gestational diabetes includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It is also important to limit your intake of sugary foods and drinks. Eating a healthy diet can help to control your blood sugar levels and reduce your risk of pregnancy complications.
Tip 2: Exercise regularly.
Regular exercise can help to control blood sugar levels and improve your overall health. It is important to talk to your doctor before starting an exercise program during pregnancy.
Tip 3: Monitor your blood sugar levels.
Monitoring your blood sugar levels is an important part of managing gestational diabetes. Your doctor will tell you how often to check your blood sugar levels and what your target blood sugar levels are.
Tip 4: Take medication if needed.
If diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes are not enough to control your blood sugar levels, your doctor may prescribe medication. Medication can help to lower your blood sugar levels and reduce your risk of pregnancy complications.
Tip 5: Follow your doctor’s recommendations.
It is important to follow your doctor’s recommendations for diet, exercise, and blood sugar monitoring. Your doctor can help you create a treatment plan that is right for you and your baby.
Summary of key takeaways or benefits:
By following these tips, you can help control your blood sugar levels and reduce your risk of pregnancy complications. Gestational diabetes can be managed with proper treatment, and you can have a healthy pregnancy and a healthy baby.
Transition to the article’s conclusion:
If you have any questions or concerns about gestational diabetes, please talk to your doctor.
Conclusion
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can develop during pregnancy. It is important to be aware of the risks and complications associated with gestational diabetes so that you can take steps to prevent or manage the condition.
If you have gestational diabetes, it is important to follow your doctor’s recommendations for diet, exercise, and blood sugar monitoring. Treatment for gestational diabetes can help prevent complications for both you and your baby. By working with your doctor, you can manage gestational diabetes and have a healthy pregnancy and a healthy baby.
Youtube Video: