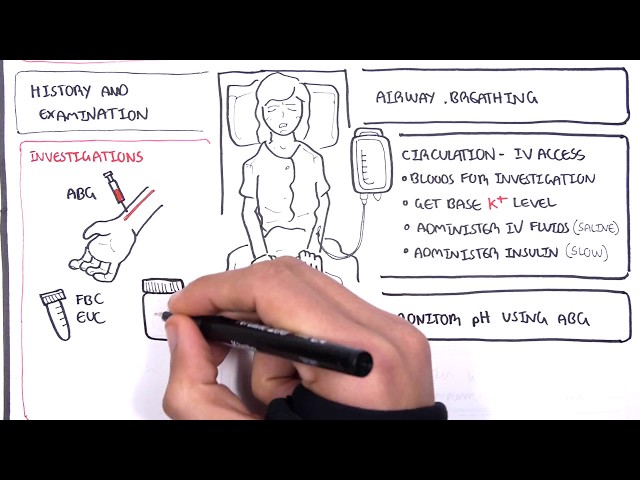
Diabetes ketoacidosis, also known as DKA, is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a build-up of ketones in the blood, which can be dangerous.
DKA is a medical emergency and can be fatal if not treated promptly. Symptoms of DKA include:
- High blood sugar levels
- Ketones in the blood or urine
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Rapid breathing
- Confusion
- Loss of consciousness
DKA is treated with fluids, insulin, and electrolytes. Treatment is usually given in a hospital setting.
DKA can be prevented by managing blood sugar levels and taking insulin as prescribed. People with diabetes should also be aware of the symptoms of DKA and seek medical attention immediately if they experience any of these symptoms.
Diabetes Ketoacidosis
Diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a build-up of ketones in the blood, which can be dangerous.
- Symptoms: High blood sugar levels, ketones in the blood or urine, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, rapid breathing, confusion, loss of consciousness
- Causes: Uncontrolled blood sugar levels, infection, injury, surgery
- Treatment: Fluids, insulin, and electrolytes
- Prevention: Managing blood sugar levels and taking insulin as prescribed
- Complications: Diabetic coma, death
- Risk factors: Type 1 diabetes, poor diabetes management, history of DKA
DKA is a medical emergency and can be fatal if not treated promptly. It is important for people with diabetes to be aware of the symptoms of DKA and to seek medical attention immediately if they experience any of these symptoms.
Symptoms
The symptoms listed above are all indicative of diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA), a serious complication of diabetes that can be fatal if not treated promptly. DKA occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones, which are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a build-up of ketones in the blood, which can be dangerous.
The symptoms of DKA are caused by the high levels of ketones in the blood. These ketones can cause the blood to become acidic, which can lead to a number of health problems, including dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and coma. DKA is a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment.
It is important for people with diabetes to be aware of the symptoms of DKA and to seek medical attention immediately if they experience any of these symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment of DKA can help to prevent serious complications and even death.
Causes
Diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can be caused by a number of factors, including uncontrolled blood sugar levels, infection, injury, and surgery.
-
Uncontrolled blood sugar levels
When blood sugar levels are too high, the body cannot use glucose for energy. This can lead to a build-up of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA. -
Infection
Infection can raise blood sugar levels and lead to DKA. This is because the body releases hormones during infection that can cause blood sugar levels to rise. -
Injury
Injury can also raise blood sugar levels and lead to DKA. This is because the body releases hormones during injury that can cause blood sugar levels to rise. -
Surgery
Surgery can also raise blood sugar levels and lead to DKA. This is because the body releases hormones during surgery that can cause blood sugar levels to rise.
It is important for people with diabetes to be aware of the causes of DKA and to take steps to prevent it. This includes managing blood sugar levels, getting vaccinated against infection, and avoiding injury and surgery if possible.
Treatment
Diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that requires prompt and aggressive treatment. The primary goals of treatment are to correct the fluid and electrolyte imbalances, lower blood sugar levels, and stop the production of ketones. This is achieved through the administration of fluids, insulin, and electrolytes.
-
Fluids
People with DKA are often dehydrated due to the loss of fluids through vomiting and urination. Intravenous fluids are given to replace these lost fluids and restore hydration. -
Insulin
Insulin is a hormone that helps the body use glucose for energy. In people with DKA, insulin levels are often low or ineffective. Intravenous insulin is given to lower blood sugar levels and stop the production of ketones. -
Electrolytes
Electrolytes are minerals that are essential for many bodily functions, such as regulating blood pressure and muscle function. People with DKA often have electrolyte imbalances, which can be corrected with intravenous fluids and electrolyte supplements.
Treatment for DKA is typically given in a hospital setting. The length of treatment will vary depending on the severity of the DKA. With prompt and appropriate treatment, most people with DKA will recover fully.
Prevention
Managing blood sugar levels and taking insulin as prescribed are essential for preventing diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA). DKA is a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when blood sugar levels are too high. When blood sugar levels are high, the body cannot use glucose for energy and breaks down fat instead. This process produces ketones, which can build up in the blood and cause DKA.
-
Regular blood sugar monitoring
People with diabetes should monitor their blood sugar levels regularly to make sure they are within a healthy range. This will help to prevent blood sugar levels from getting too high and triggering DKA. -
Taking insulin as prescribed
People with diabetes who take insulin need to take it exactly as prescribed by their doctor. Skipping or delaying insulin doses can lead to high blood sugar levels and DKA. -
Eating a healthy diet
Eating a healthy diet is important for managing blood sugar levels and preventing DKA. A healthy diet includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It also limits processed foods, sugary drinks, and saturated and unhealthy fats. -
Getting regular exercise
Regular exercise helps to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. This can help to prevent DKA.
Managing blood sugar levels and taking insulin as prescribed are essential for preventing DKA. By following these tips, people with diabetes can help to reduce their risk of developing this serious complication.
Complications
Diabetic coma and death are two of the most serious complications of diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA). DKA is a condition that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones, which are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a build-up of ketones in the blood, which can be dangerous.
Diabetic coma occurs when the blood sugar level drops too low. This can happen if a person with diabetes takes too much insulin or if they do not eat enough food. Diabetic coma is a medical emergency and can be fatal if not treated promptly.
Death can occur from DKA if it is not treated promptly. DKA can lead to dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and coma. If left untreated, DKA can be fatal.
It is important for people with diabetes to be aware of the symptoms of DKA and to seek medical attention immediately if they experience any of these symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment of DKA can help to prevent serious complications and even death.
Risk factors
Diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when blood sugar levels are too high. There are a number of risk factors for DKA, including type 1 diabetes, poor diabetes management, and a history of DKA.
-
Type 1 diabetes
People with type 1 diabetes are at an increased risk of DKA because their bodies do not produce insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps the body use glucose for energy. Without insulin, the body breaks down fat for energy, which produces ketones. High levels of ketones can lead to DKA.
-
Poor diabetes management
People who do not manage their diabetes well are at an increased risk of DKA. This includes people who do not take their insulin as prescribed, do not monitor their blood sugar levels regularly, or do not eat a healthy diet.
-
History of DKA
People who have had DKA in the past are at an increased risk of developing it again. This is because DKA can damage the pancreas, which is the organ that produces insulin.
It is important for people with diabetes to be aware of the risk factors for DKA and to take steps to reduce their risk. This includes taking insulin as prescribed, monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise.
Diabetes Ketoacidosis FAQs
Diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when blood sugar levels are too high. DKA is a medical emergency and can be fatal if not treated promptly. Here are some frequently asked questions about DKA:
Question 1: What are the symptoms of DKA?
Answer: Symptoms of DKA include high blood sugar levels, ketones in the blood or urine, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, rapid breathing, confusion, and loss of consciousness.
Question 2: What causes DKA?
Answer: DKA is caused by uncontrolled blood sugar levels, infection, injury, or surgery.
Question 3: How is DKA treated?
Answer: DKA is treated with fluids, insulin, and electrolytes.
Question 4: How can DKA be prevented?
Answer: DKA can be prevented by managing blood sugar levels, taking insulin as prescribed, and avoiding infection, injury, and surgery.
Question 5: What are the risk factors for DKA?
Answer: Risk factors for DKA include type 1 diabetes, poor diabetes management, and a history of DKA.
Question 6: What are the complications of DKA?
Answer: Complications of DKA include diabetic coma and death.
Summary: DKA is a serious complication of diabetes that can be fatal if not treated promptly. It is important for people with diabetes to be aware of the symptoms of DKA and to seek medical attention immediately if they experience any of these symptoms.
Transition to the next article section: For more information on DKA, please see the following resources:
- American Diabetes Association: Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
- Mayo Clinic: Diabetic Ketoacidosis
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
Tips for Managing Diabetes Ketoacidosis (DKA)
Diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when blood sugar levels are too high. DKA can be a life-threatening condition, so it is important to be aware of the symptoms and to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of them.
Here are some tips for managing DKA:
Tip 1: Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly.
Regular blood sugar monitoring is essential for managing diabetes and preventing DKA. You should test your blood sugar levels several times a day, especially if you are sick or under stress.
Tip 2: Take your insulin as prescribed.
If you take insulin, it is important to take it exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Skipping or delaying insulin doses can lead to high blood sugar levels and DKA.
Tip 3: Eat a healthy diet.
Eating a healthy diet is important for managing diabetes and preventing DKA. A healthy diet includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It also limits processed foods, sugary drinks, and saturated and unhealthy fats.
Tip 4: Get regular exercise.
Regular exercise helps to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. This can help to prevent DKA.
Tip 5: Avoid infection.
Infection can raise blood sugar levels and lead to DKA. It is important to take steps to avoid infection, such as washing your hands frequently, covering your mouth and nose when you cough or sneeze, and getting vaccinated against common infections.
Tip 6: Manage stress.
Stress can raise blood sugar levels and lead to DKA. It is important to find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, yoga, or meditation.
Summary: DKA is a serious complication of diabetes that can be prevented and managed with proper care. By following these tips, you can help to reduce your risk of developing DKA and improve your overall health.
Transition to the article’s conclusion: If you have any questions or concerns about DKA, please talk to your doctor or diabetes educator.
Conclusion
Diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when blood sugar levels are too high. DKA is a medical emergency and can be fatal if not treated promptly. It is important for people with diabetes to be aware of the symptoms of DKA and to seek medical attention immediately if they experience any of these symptoms.
DKA can be prevented by managing blood sugar levels, taking insulin as prescribed, and avoiding infection, injury, and surgery. People with diabetes should also be aware of the risk factors for DKA and take steps to reduce their risk.
If you have any questions or concerns about DKA, please talk to your doctor or diabetes educator.
Youtube Video: