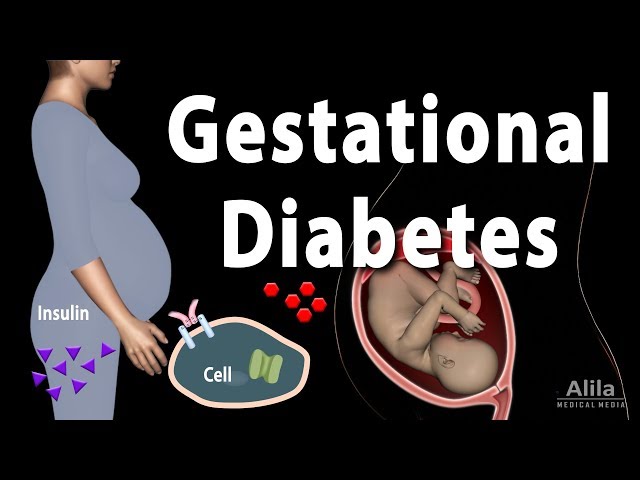
Diabetes during pregnancy, also known as gestational diabetes, is a type of diabetes mellitus that develops during pregnancy. It is characterized by hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) that begins or is first recognized during pregnancy. Normally, the body’s pancreas makes the hormone insulin, which helps glucose get from the blood into the body’s cells to be used for energy. During pregnancy, hormonal changes can make the body less sensitive to insulin, which can lead to high blood sugar levels.
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can affect both the mother and the baby. It increases the risk of premature birth, macrosomia (large birth weight), and other complications. If left untreated, gestational diabetes can also lead to type 2 diabetes in both the mother and the child later in life.
Fortunately, with proper management, most women with gestational diabetes can have a healthy pregnancy and deliver a healthy baby. Treatment typically involves diet, exercise, and blood sugar monitoring. In some cases, medication may also be necessary.
diabetes during pregnancy
Diabetes during pregnancy, also known as gestational diabetes, is a serious condition that can affect both the mother and the baby. It is important to understand the key aspects of this condition in order to ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
- Definition: Diabetes during pregnancy is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy.
- Causes: It is caused by hormonal changes that make the body less sensitive to insulin.
- Risks: Gestational diabetes increases the risk of premature birth, macrosomia (large birth weight), and other complications.
- Treatment: Treatment typically involves diet, exercise, and blood sugar monitoring.
- Prevention: There is no sure way to prevent gestational diabetes, but maintaining a healthy weight before and during pregnancy can help to reduce the risk.
- Management: With proper management, most women with gestational diabetes can have a healthy pregnancy and deliver a healthy baby.
These are just some of the key aspects of diabetes during pregnancy. By understanding these aspects, you can help to ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
Definition
The definition of diabetes during pregnancy is crucial for understanding this condition and its implications. Diabetes during pregnancy, also known as gestational diabetes, is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is characterized by hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) that begins or is first recognized during pregnancy. Normally, the body’s pancreas makes the hormone insulin, which helps glucose get from the blood into the body’s cells to be used for energy. During pregnancy, hormonal changes can make the body less sensitive to insulin, which can lead to high blood sugar levels.
Understanding the definition of diabetes during pregnancy is important for several reasons. First, it helps to identify women who are at risk for developing this condition. Second, it allows for early diagnosis and treatment, which can help to prevent or minimize complications. Third, it provides a framework for understanding the causes and effects of diabetes during pregnancy, which can lead to better prevention and management strategies.
In conclusion, the definition of diabetes during pregnancy is a critical component of understanding this condition. By understanding the definition, we can better identify, diagnose, treat, and prevent diabetes during pregnancy, ultimately leading to improved outcomes for both mothers and babies.
Causes
During pregnancy, the placenta produces hormones that help the baby grow and develop. These hormones can also make the mother’s body less sensitive to insulin, which is a hormone that helps glucose get from the blood into the body’s cells to be used for energy. When the body is less sensitive to insulin, glucose can build up in the blood, leading to high blood sugar levels.
High blood sugar levels can cause a number of problems for both the mother and the baby. For the mother, high blood sugar levels can increase the risk of developing preeclampsia, a serious condition that can lead to high blood pressure and other complications. For the baby, high blood sugar levels can increase the risk of macrosomia (large birth weight), which can lead to a difficult delivery and other problems.
Understanding the cause of diabetes during pregnancy is important for several reasons. First, it helps to identify women who are at risk for developing this condition. Second, it allows for early diagnosis and treatment, which can help to prevent or minimize complications. Third, it provides a framework for understanding the causes and effects of diabetes during pregnancy, which can lead to better prevention and management strategies.
In conclusion, the cause of diabetes during pregnancy is a critical component of understanding this condition. By understanding the cause, we can better identify, diagnose, treat, and prevent diabetes during pregnancy, ultimately leading to improved outcomes for both mothers and babies.
Risks
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can affect both the mother and the baby. One of the main risks associated with gestational diabetes is the increased risk of premature birth. Premature babies are born before 37 weeks of gestation and are at risk for a number of health problems, including respiratory problems, feeding difficulties, and developmental delays. Gestational diabetes also increases the risk of macrosomia, or large birth weight. Macrosomia can make delivery difficult and can also lead to health problems for the baby, such as shoulder dystocia and birth injuries.
In addition to premature birth and macrosomia, gestational diabetes can increase the risk of other complications, such as preeclampsia, a serious condition that can lead to high blood pressure and other complications. Gestational diabetes can also increase the risk of cesarean delivery and postpartum hemorrhage.
Understanding the risks associated with gestational diabetes is important for both mothers and healthcare providers. By understanding the risks, mothers can take steps to manage their diabetes and reduce the risk of complications. Healthcare providers can also screen for and diagnose gestational diabetes and provide appropriate treatment and monitoring to help reduce the risk of complications.
In conclusion, gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can increase the risk of a number of complications, including premature birth, macrosomia, preeclampsia, cesarean delivery, and postpartum hemorrhage. Understanding the risks associated with gestational diabetes is important for both mothers and healthcare providers. By understanding the risks, mothers can take steps to manage their diabetes and reduce the risk of complications. Healthcare providers can also screen for and diagnose gestational diabetes and provide appropriate treatment and monitoring to help reduce the risk of complications.
Treatment
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can affect both the mother and the baby. Treatment for gestational diabetes typically involves diet, exercise, and blood sugar monitoring.
-
Diet
A healthy diet is essential for managing gestational diabetes. The diet should be low in sugar and carbohydrates and high in fiber. Eating regular meals and snacks throughout the day can help to keep blood sugar levels stable.
-
Exercise
Exercise can help to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Exercise should be done regularly, but it is important to start slowly and gradually increase the amount of exercise over time.
-
Blood sugar monitoring
Blood sugar monitoring is essential for managing gestational diabetes. Blood sugar levels should be checked several times a day, and more often if blood sugar levels are high.
By following these treatment recommendations, most women with gestational diabetes can have a healthy pregnancy and deliver a healthy baby.
Prevention
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can affect both the mother and the baby. While there is no sure way to prevent gestational diabetes, maintaining a healthy weight before and during pregnancy can help to reduce the risk.
Being overweight or obese before pregnancy increases the risk of developing gestational diabetes. This is because excess weight can make the body less sensitive to insulin, which can lead to high blood sugar levels. During pregnancy, the body produces hormones that can also make the body less sensitive to insulin. This can lead to high blood sugar levels, even in women who were not overweight or obese before pregnancy.
Maintaining a healthy weight before and during pregnancy can help to reduce the risk of gestational diabetes by improving insulin sensitivity. This can help to keep blood sugar levels within a healthy range and reduce the risk of developing gestational diabetes.
In addition to maintaining a healthy weight, there are other things that women can do to reduce their risk of developing gestational diabetes, such as eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and getting enough sleep. However, maintaining a healthy weight is one of the most important things that women can do to reduce their risk of developing this condition.
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with proper treatment. If you are diagnosed with gestational diabetes, your doctor will work with you to develop a treatment plan that is right for you. This plan may include diet, exercise, and blood sugar monitoring. By following your doctor’s recommendations, you can help to manage your gestational diabetes and have a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
Management
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can affect both the mother and the baby. However, with proper management, most women with gestational diabetes can have a healthy pregnancy and deliver a healthy baby.
-
Regular monitoring
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential for managing gestational diabetes. This can be done with a blood glucose meter at home. Monitoring blood sugar levels helps to ensure that they are within a healthy range and allows for adjustments to be made to the treatment plan as needed.
-
Healthy diet
Eating a healthy diet is also essential for managing gestational diabetes. This includes eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It is also important to limit sugar and processed foods.
-
Exercise
Exercise can help to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Exercise should be done regularly, but it is important to start slowly and gradually increase the amount of exercise over time.
-
Medication
In some cases, medication may be necessary to manage gestational diabetes. This may include insulin or other medications that help to lower blood sugar levels.
By following these management recommendations, most women with gestational diabetes can have a healthy pregnancy and deliver a healthy baby. It is important to remember that gestational diabetes is a temporary condition that will go away after pregnancy. However, it is important to follow the doctor’s recommendations during pregnancy to ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
FAQs on Diabetes During Pregnancy
Diabetes during pregnancy, also known as gestational diabetes, is a serious condition that can affect both the mother and the baby. It is important to understand the key aspects of this condition in order to ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
Question 1: What is diabetes during pregnancy?
Diabetes during pregnancy is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is characterized by hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) that begins or is first recognized during pregnancy.
Question 2: What causes diabetes during pregnancy?
Diabetes during pregnancy is caused by hormonal changes that make the body less sensitive to insulin, a hormone that helps glucose get from the blood into the body’s cells to be used for energy.
Question 3: What are the risks of diabetes during pregnancy?
Diabetes during pregnancy can increase the risk of premature birth, macrosomia (large birth weight), and other complications for both the mother and the baby.
Question 4: How is diabetes during pregnancy treated?
Treatment for diabetes during pregnancy typically involves diet, exercise, and blood sugar monitoring. In some cases, medication may also be necessary.
Question 5: Can diabetes during pregnancy be prevented?
There is no sure way to prevent diabetes during pregnancy, but maintaining a healthy weight before and during pregnancy can help to reduce the risk.
Question 6: How can I manage diabetes during pregnancy?
With proper management, most women with diabetes during pregnancy can have a healthy pregnancy and deliver a healthy baby. Management typically involves regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and taking medication if necessary.
These are just a few of the frequently asked questions about diabetes during pregnancy. By understanding the answers to these questions, you can help to ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery for yourself and your baby.
Transition to the next article section: Understanding the key aspects of diabetes during pregnancy is crucial for ensuring a healthy pregnancy and delivery. This article provides a comprehensive overview of this condition, including its definition, causes, risks, treatment, and management. By understanding the information provided in this article, you can empower yourself to make informed decisions about your health and the health of your baby.
Tips for Managing Diabetes During Pregnancy
Diabetes during pregnancy, also known as gestational diabetes, is a serious condition that can affect both the mother and the baby. By following these tips, you can help to manage your diabetes during pregnancy and reduce the risk of complications.
Tip 1: Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly.
Monitoring your blood sugar levels is essential for managing diabetes during pregnancy. This can be done with a blood glucose meter at home. Monitoring blood sugar levels helps to ensure that they are within a healthy range and allows for adjustments to be made to the treatment plan as needed.Tip 2: Eat a healthy diet.
Eating a healthy diet is also essential for managing diabetes during pregnancy. This includes eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It is also important to limit sugar and processed foods.Tip 3: Exercise regularly.
Exercise can help to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Exercise should be done regularly, but it is important to start slowly and gradually increase the amount of exercise over time.Tip 4: Take your medication as prescribed.
In some cases, medication may be necessary to manage diabetes during pregnancy. This may include insulin or other medications that help to lower blood sugar levels. It is important to take your medication as prescribed by your doctor.Tip 5: Get enough sleep.
Getting enough sleep is important for overall health, including managing diabetes. When you are sleep-deprived, your body is less able to regulate blood sugar levels. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep each night.Tip 6: Manage stress.
Stress can raise blood sugar levels. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, yoga, or meditation.Tip 7: Quit smoking.
Smoking can damage blood vessels and make it more difficult to control blood sugar levels. Quitting smoking is one of the best things you can do for your health and the health of your baby.Tip 8: See your doctor regularly.
It is important to see your doctor regularly for prenatal care and to monitor your diabetes. Your doctor will check your blood sugar levels, weight, and other health factors. Seeing your doctor regularly will help to ensure that you are receiving the best possible care and that your diabetes is being managed effectively.By following these tips, you can help to manage your diabetes during pregnancy and reduce the risk of complications for both you and your baby.
Summary of key takeaways or benefits:
- Managing diabetes during pregnancy can help to reduce the risk of complications for both the mother and the baby.
- Following these tips can help to manage blood sugar levels, eat a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and take medication as prescribed.
- It is important to see your doctor regularly for prenatal care and to monitor your diabetes.
Transition to the article’s conclusion:
By understanding the information provided in this article and following the tips above, you can empower yourself to make informed decisions about your health and the health of your baby.
Conclusion on Diabetes During Pregnancy
Diabetes during pregnancy, also known as gestational diabetes, is a serious condition that can affect both the mother and the baby. By understanding the key aspects of this condition, including its definition, causes, risks, treatment, and management, you can help to ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
This article has provided a comprehensive overview of diabetes during pregnancy, including information on its causes, risks, and management. By understanding the information provided in this article, you can empower yourself to make informed decisions about your health and the health of your baby. Following the tips provided in this article can help you to manage your blood sugar levels, eat a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and take medication as prescribed. It is also important to see your doctor regularly for prenatal care and to monitor your diabetes. By following these recommendations, you can help to reduce the risk of complications for both you and your baby.
Youtube Video: