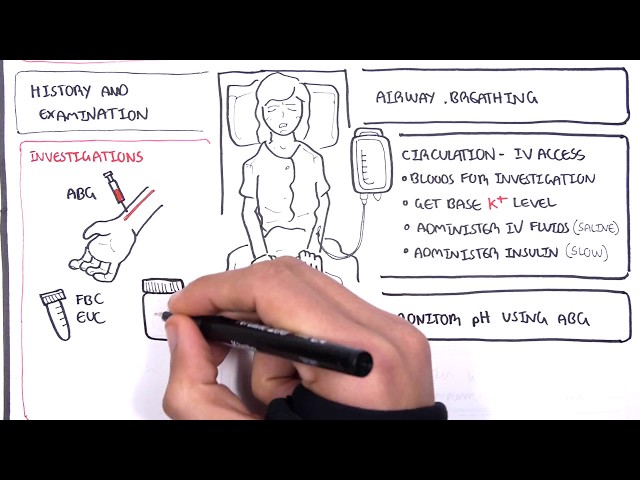
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
The symptoms of DKA can include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Weakness and fatigue
- Confusion
- Loss of consciousness
DKA is a medical emergency and can be fatal if not treated. Treatment for DKA typically involves intravenous fluids and insulin. Early diagnosis and treatment of DKA can help to prevent serious complications.
Symptoms of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. The symptoms of DKA can include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Weakness and fatigue
- Confusion
- Loss of consciousness
- Rapid breathing
- Fruity-smelling breath
DKA is a medical emergency and can be fatal if not treated. Treatment for DKA typically involves intravenous fluids and insulin. Early diagnosis and treatment of DKA can help to prevent serious complications.
The symptoms of DKA can be caused by a number of factors, including: High blood sugar levels: When blood sugar levels are high, the body cannot use glucose for energy. This can lead to the breakdown of fat and the production of ketones. Low insulin levels: Insulin is a hormone that helps the body to use glucose for energy. When insulin levels are low, the body cannot use glucose for energy and this can lead to the production of ketones.* Increased glucagon levels: Glucagon is a hormone that raises blood sugar levels. When glucagon levels are high, the body can break down fat and produce ketones.DKA is a serious condition that can lead to coma and death if not treated. It is important to be aware of the symptoms of DKA and to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of these symptoms.
Nausea and vomiting
Nausea and vomiting are common symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a serious complication of diabetes that can occur when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
- Dehydration: Nausea and vomiting can lead to dehydration, which can worsen DKA. Dehydration can also cause other symptoms, such as dizziness, lightheadedness, and confusion.
- Electrolyte imbalance: Nausea and vomiting can also lead to electrolyte imbalance, which can cause a number of symptoms, such as muscle cramps, weakness, and fatigue. Electrolyte imbalance can also be dangerous if it is severe.
- Acid-base imbalance: Nausea and vomiting can also lead to acid-base imbalance, which can cause a number of symptoms, such as confusion, disorientation, and coma. Acid-base imbalance can also be fatal if it is severe.
- Other symptoms: Nausea and vomiting can also be a symptom of other conditions, such as gastroenteritis, food poisoning, and appendicitis. It is important to see a doctor to rule out other conditions if you are experiencing nausea and vomiting.
Nausea and vomiting are common symptoms of DKA, and they can be a sign of a serious medical condition. It is important to see a doctor if you are experiencing nausea and vomiting, especially if you have diabetes.
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain is a common symptom of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
- Inflammation: Ketones can cause inflammation in the pancreas and other organs in the abdomen. This inflammation can lead to abdominal pain.
- Dehydration: DKA can also lead to dehydration, which can cause abdominal pain. Dehydration can also cause other symptoms, such as dizziness, lightheadedness, and confusion.
- Electrolyte imbalance: DKA can also lead to electrolyte imbalance, which can cause abdominal pain. Electrolyte imbalance can also cause other symptoms, such as muscle cramps, weakness, and fatigue.
- Other causes: Abdominal pain can also be a symptom of other conditions, such as pancreatitis, appendicitis, and gastroenteritis. It is important to see a doctor to rule out other conditions if you are experiencing abdominal pain.
Abdominal pain is a common symptom of DKA, and it can be a sign of a serious medical condition. It is important to see a doctor if you are experiencing abdominal pain, especially if you have diabetes.
Weakness and fatigue
Weakness and fatigue are common symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
Weakness and fatigue can be caused by a number of factors in people with DKA, including:
- Dehydration: DKA can lead to dehydration, which can cause weakness and fatigue. Dehydration can also cause other symptoms, such as dizziness, lightheadedness, and confusion.
- Electrolyte imbalance: DKA can also lead to electrolyte imbalance, which can cause weakness and fatigue. Electrolyte imbalance can also cause other symptoms, such as muscle cramps, nausea, and vomiting.
- Low blood sugar: DKA can also lead to low blood sugar, which can cause weakness and fatigue. Low blood sugar can also cause other symptoms, such as confusion, disorientation, and seizures.
Weakness and fatigue can be a sign of a serious medical condition, and it is important to see a doctor if you are experiencing these symptoms. Treatment for DKA typically involves intravenous fluids and insulin. Early diagnosis and treatment of DKA can help to prevent serious complications.
Confusion
Confusion is a common symptom of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
Confusion can be caused by a number of factors in people with DKA, including:
- Dehydration: DKA can lead to dehydration, which can cause confusion. Dehydration can also cause other symptoms, such as dizziness, lightheadedness, and fatigue.
- Electrolyte imbalance: DKA can also lead to electrolyte imbalance, which can cause confusion. Electrolyte imbalance can also cause other symptoms, such as muscle cramps, nausea, and vomiting.
- Low blood sugar: DKA can also lead to low blood sugar, which can cause confusion. Low blood sugar can also cause other symptoms, such as weakness, fatigue, and seizures.
- Ketones: Ketones themselves can also cause confusion. Ketones are acidic, and they can build up in the blood and cause a condition called ketoacidosis. Ketoacidosis can lead to confusion, disorientation, and coma.
Confusion is a serious symptom of DKA, and it is important to seek medical attention immediately if you are experiencing this symptom. Treatment for DKA typically involves intravenous fluids and insulin. Early diagnosis and treatment of DKA can help to prevent serious complications.
Loss of consciousness
Loss of consciousness is a serious symptom of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a life-threatening complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
- Dehydration: DKA can lead to dehydration, which can cause loss of consciousness. Dehydration can also cause other symptoms, such as dizziness, lightheadedness, and fatigue.
- Electrolyte imbalance: DKA can also lead to electrolyte imbalance, which can cause loss of consciousness. Electrolyte imbalance can also cause other symptoms, such as muscle cramps, nausea, and vomiting.
- Low blood sugar: DKA can also lead to low blood sugar, which can cause loss of consciousness. Low blood sugar can also cause other symptoms, such as weakness, fatigue, and seizures.
- Ketones: Ketones themselves can also cause loss of consciousness. Ketones are acidic, and they can build up in the blood and cause a condition called ketoacidosis. Ketoacidosis can lead to confusion, disorientation, and coma.
Loss of consciousness is a medical emergency, and it is important to seek medical attention immediately if you are experiencing this symptom. Treatment for DKA typically involves intravenous fluids and insulin. Early diagnosis and treatment of DKA can help to prevent serious complications.
Rapid breathing
Rapid breathing, also known as tachypnea, is a common symptom of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
- Dehydration: DKA can lead to dehydration, which can cause rapid breathing. Dehydration can also cause other symptoms, such as dizziness, lightheadedness, and fatigue.
- Electrolyte imbalance: DKA can also lead to electrolyte imbalance, which can cause rapid breathing. Electrolyte imbalance can also cause other symptoms, such as muscle cramps, nausea, and vomiting.
- Metabolic acidosis: DKA is a type of metabolic acidosis, which means that the blood is too acidic. Metabolic acidosis can cause rapid breathing, as the body tries to compensate for the acidosis by blowing off carbon dioxide.
- Other causes: Rapid breathing can also be a symptom of other conditions, such as pneumonia, asthma, and heart failure. It is important to see a doctor to rule out other conditions if you are experiencing rapid breathing.
Rapid breathing is a serious symptom of DKA, and it is important to seek medical attention immediately if you are experiencing this symptom. Treatment for DKA typically involves intravenous fluids and insulin. Early diagnosis and treatment of DKA can help to prevent serious complications.
Fruity-smelling breath
Fruity-smelling breath is a common symptom of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
- Acetone: Acetone is a type of ketone that has a fruity smell. When acetone is present in the breath, it can be a sign of DKA. Acetone is also found in nail polish remover and paint thinner.
- Other ketones: Other types of ketones, such as beta-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate, can also cause fruity-smelling breath. These ketones are not as volatile as acetone, so they are not as likely to be detected in the breath.
- Dehydration: DKA can also lead to dehydration, which can cause fruity-smelling breath. Dehydration can also cause other symptoms, such as dizziness, lightheadedness, and fatigue.
- Other causes: Fruity-smelling breath can also be a symptom of other conditions, such as metabolic acidosis, starvation, and alcohol intoxication. It is important to see a doctor to rule out other conditions if you are experiencing fruity-smelling breath.
Fruity-smelling breath is a serious symptom of DKA, and it is important to seek medical attention immediately if you are experiencing this symptom. Treatment for DKA typically involves intravenous fluids and insulin. Early diagnosis and treatment of DKA can help to prevent serious complications.
Frequently Asked Questions on Symptoms of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones. Ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it breaks down fat instead. This can lead to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can cause DKA.
The symptoms of DKA can include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Weakness and fatigue
- Confusion
- Loss of consciousness
- Rapid breathing
- Fruity-smelling breath
DKA is a medical emergency and can be fatal if not treated. Treatment for DKA typically involves intravenous fluids and insulin. Early diagnosis and treatment of DKA can help to prevent serious complications.
Here are some frequently asked questions about the symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis:
Question 1: What are the most common symptoms of DKA?
The most common symptoms of DKA are nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, weakness and fatigue, confusion, and loss of consciousness.
Question 2: What causes DKA?
DKA is caused by a combination of factors, including high blood sugar levels, low insulin levels, and increased glucagon levels.
Question 3: How is DKA treated?
DKA is treated with intravenous fluids and insulin. Treatment typically takes place in a hospital setting.
Question 4: What are the complications of DKA?
Complications of DKA can include dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and ketoacidosis. These complications can be life-threatening if not treated.
Question 5: How can I prevent DKA?
You can help to prevent DKA by managing your blood sugar levels, taking your insulin as prescribed, and eating a healthy diet.
Summary: DKA is a serious complication of diabetes that can be fatal if not treated. The symptoms of DKA can include nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, weakness and fatigue, confusion, loss of consciousness, rapid breathing, and fruity-smelling breath. Treatment for DKA typically involves intravenous fluids and insulin. Early diagnosis and treatment of DKA can help to prevent serious complications.
Next Article Section: Treatment for Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Tips for Managing Symptoms of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can be fatal if not treated. The symptoms of DKA can include nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, weakness and fatigue, confusion, loss of consciousness, rapid breathing, and fruity-smelling breath.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Treatment for DKA typically involves intravenous fluids and insulin. Early diagnosis and treatment of DKA can help to prevent serious complications.
In addition to medical treatment, there are a number of things you can do to help manage the symptoms of DKA.
Tip 1: Stay hydrated. Dehydration can worsen the symptoms of DKA. Drink plenty of fluids, such as water, broth, or electrolyte-rich drinks.Tip 2: Eat a healthy diet. Eating a healthy diet can help to keep your blood sugar levels under control and prevent DKA. Choose foods that are low in carbohydrates and high in fiber.Tip 3: Get regular exercise. Exercise can help to improve your insulin sensitivity and lower your blood sugar levels.Tip 4: Take your medications as prescribed. If you are taking insulin, it is important to take it as prescribed. Skipping doses of insulin can lead to DKA.Tip 5: Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly. Monitoring your blood sugar levels can help you to identify patterns and trends. This information can help you to make lifestyle changes to prevent DKA.
Summary: DKA is a serious complication of diabetes that can be fatal if not treated. By following these tips, you can help to manage the symptoms of DKA and prevent serious complications.
Next Article Section: Treatment for Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Conclusion
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can be fatal if not treated. The symptoms of DKA can include nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, weakness and fatigue, confusion, loss of consciousness, rapid breathing, and fruity-smelling breath.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Treatment for DKA typically involves intravenous fluids and insulin. Early diagnosis and treatment of DKA can help to prevent serious complications.
In addition to medical treatment, there are a number of things you can do to help manage the symptoms of DKA. These include staying hydrated, eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, taking your medications as prescribed, and monitoring your blood sugar levels regularly.
By following these tips, you can help to prevent DKA and its serious complications.
Youtube Video: