Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way the body processes sugar (glucose). With type 2 diabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin or does not use insulin well, which leads to high levels of sugar in the blood. Over time, high blood sugar can damage the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves.
Type 2 diabetes is the most common type of diabetes, accounting for about 90% of all cases. It typically develops in adults over the age of 40, although it can occur in younger people as well. Risk factors for type 2 diabetes include obesity, physical inactivity, family history of diabetes, and certain ethnicities.
There is no cure for type 2 diabetes, but it can be managed with a healthy lifestyle, including eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight. Medications may also be necessary to help control blood sugar levels.
What are the Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way the body processes sugar (glucose). With type 2 diabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin or does not use insulin well, which leads to high levels of sugar in the blood. Over time, high blood sugar can damage the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves.
- Chronic condition: Type 2 diabetes is a lifelong condition that requires ongoing management.
- Blood sugar: Type 2 diabetes affects the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels.
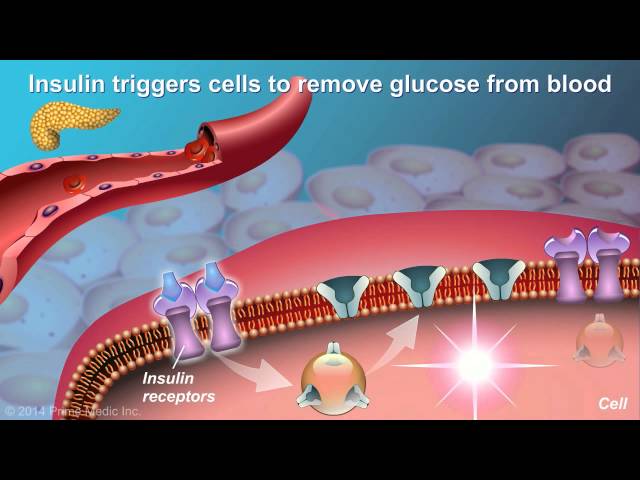
- Insulin: Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose enter cells for energy.
- Risk factors: Obesity, physical inactivity, family history, and certain ethnicities increase the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Complications: High blood sugar can lead to serious complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and blindness.
- Management: Type 2 diabetes can be managed with a healthy lifestyle and medication.
- Prevention: Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise can help prevent type 2 diabetes.
- Prevalence: Type 2 diabetes is the most common type of diabetes, accounting for about 90% of all cases.
Type 2 diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with a healthy lifestyle and medication. By understanding the key aspects of type 2 diabetes, you can take steps to prevent or manage the condition and live a long, healthy life.
Chronic condition
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition, meaning that it is a lifelong condition that requires ongoing management. This is because type 2 diabetes affects the way the body processes sugar (glucose), and there is no cure for this underlying cause. People with type 2 diabetes need to manage their condition through lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet and getting regular exercise, and they may also need to take medication to help control their blood sugar levels.
The chronic nature of type 2 diabetes means that it is important for people with this condition to take steps to manage their condition every day. This can be challenging, but it is important to remember that managing type 2 diabetes can help to prevent serious complications, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and blindness.
There are a number of resources available to help people with type 2 diabetes manage their condition. These resources include diabetes educators, dietitians, and support groups. There are also a number of online resources available, such as the website of the American Diabetes Association.
Managing type 2 diabetes is a lifelong commitment, but it is possible to live a long and healthy life with this condition. By understanding the chronic nature of type 2 diabetes and taking steps to manage the condition, people with type 2 diabetes can reduce their risk of developing serious complications.
Blood sugar
Blood sugar is the amount of glucose in the blood. Glucose is the body’s main source of energy. In people with type 2 diabetes, the body does not produce enough insulin or does not use insulin well. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose enter cells for energy. Without enough insulin, glucose builds up in the blood.
High blood sugar can damage the blood vessels and nerves. This can lead to serious health problems, including heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and blindness.
Managing blood sugar levels is essential for people with type 2 diabetes. This can be done through a healthy lifestyle, including eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight. Medications may also be necessary to help control blood sugar levels.
Understanding the connection between blood sugar and type 2 diabetes is important for managing the condition and preventing serious health problems.
Insulin
Insulin is a key hormone in the body that helps regulate blood sugar levels. It is produced by the pancreas and helps glucose, or sugar, enter cells for energy. In people with type 2 diabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin or does not use insulin well, which leads to high levels of sugar in the blood.
There are a number of factors that can contribute to insulin resistance, including obesity, physical inactivity, and family history. Insulin resistance can lead to a number of health problems, including type 2 diabetes, heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease.
Managing insulin resistance is essential for people with type 2 diabetes. This can be done through a healthy lifestyle, including eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight. Medications may also be necessary to help control blood sugar levels.
Risk factors
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way the body processes sugar (glucose). With type 2 diabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin or does not use insulin well, which leads to high levels of sugar in the blood. Over time, high blood sugar can damage the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves.
There are a number of risk factors that can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, including:
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Family history of diabetes
- Certain ethnicities
Obesity is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes. People who are obese are more likely to have insulin resistance, which is a condition in which the body does not use insulin well. Insulin resistance can lead to high blood sugar levels and type 2 diabetes.
Physical inactivity is another major risk factor for type 2 diabetes. People who are physically inactive are more likely to be overweight or obese, and they are also more likely to have insulin resistance. Physical activity helps to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels.
Family history of diabetes is also a risk factor for type 2 diabetes. People who have a family history of diabetes are more likely to develop the condition themselves. This is because genes play a role in the development of type 2 diabetes.
Certain ethnicities are also at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. For example, African Americans, Hispanic Americans, American Indians, and Asian Americans are all at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. This is due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Understanding the risk factors for type 2 diabetes is important for preventing and managing the condition. By making healthy lifestyle choices, such as eating a healthy diet and getting regular exercise, people can reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Complications
High blood sugar is a major risk factor for a number of serious health complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and blindness. These complications can occur when high blood sugar damages the blood vessels and nerves.
Heart disease is the leading cause of death in people with diabetes. High blood sugar can damage the blood vessels that supply blood to the heart, leading to heart attack and stroke. Stroke occurs when a blood clot blocks an artery in the brain, depriving the brain of oxygen. Kidney failure occurs when the kidneys are damaged and can no longer filter waste products from the blood. Blindness can occur when high blood sugar damages the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye.
The connection between high blood sugar and these serious complications is well-established. A number of studies have shown that people with diabetes are at an increased risk of developing these complications. For example, a study published in the journal Diabetes Care found that people with type 2 diabetes were more than twice as likely to have a heart attack or stroke than people without diabetes. Another study, published in the journal JAMA Internal Medicine, found that people with diabetes were more than three times as likely to develop kidney failure than people without diabetes.
Understanding the connection between high blood sugar and these serious complications is important for people with diabetes. By managing their blood sugar levels, people with diabetes can reduce their risk of developing these complications and living a long and healthy life.
Management
Understanding the connection between management and what type 2 diabetes is essential for effective management of the condition. Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels. Without proper management, high blood sugar levels can lead to serious health complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and blindness.
Management of type 2 diabetes involves two key components: a healthy lifestyle and medication. A healthy lifestyle includes eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight. These lifestyle changes can help to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. In some cases, medication may also be necessary to help control blood sugar levels.
The connection between management and what type 2 diabetes is significant because it highlights the importance of taking steps to manage the condition. By understanding the impact of high blood sugar levels and the role of lifestyle changes and medication in managing blood sugar levels, people with type 2 diabetes can take control of their condition and reduce their risk of developing serious health complications.
Prevention
The connection between prevention and understanding “what type 2 diabetes is” lies in the fact that type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that can be prevented or delayed with lifestyle modifications. Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise are crucial components of preventing type 2 diabetes. These lifestyle choices help maintain healthy blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of developing insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes.
Prevention is a vital aspect of managing type 2 diabetes because it empowers individuals to take proactive steps towards their health. By understanding the preventable nature of type 2 diabetes and the significance of healthy lifestyle choices, people can make informed decisions to reduce their risk of developing the condition.
The practical significance of this understanding lies in the potential to reduce the prevalence of type 2 diabetes and its associated health complications. Implementing preventive measures can lead to better health outcomes, improved quality of life, and reduced healthcare costs associated with managing type 2 diabetes.
Prevalence
The high prevalence of type 2 diabetes highlights its significance as the most prevalent form of diabetes, affecting a vast majority of individuals with the condition. Understanding this prevalence is crucial because it underscores the widespread nature of type 2 diabetes and its impact on global health.
The prevalence of type 2 diabetes serves as a critical component in defining “what type 2 diabetes is.” It signifies the magnitude and scope of the condition, emphasizing its common occurrence among the diabetic population. This understanding aids in recognizing type 2 diabetes as a prevalent health concern, requiring targeted strategies for prevention, management, and treatment.
In practical terms, the prevalence of type 2 diabetes informs healthcare systems, policymakers, and researchers about the substantial burden of the condition. This knowledge assists in allocating resources, developing effective public health interventions, and prioritizing research efforts to address the widespread impact of type 2 diabetes.
FAQs about Type 2 Diabetes
This section addresses frequently asked questions about type 2 diabetes. Understanding these questions and their answers can provide valuable insights into the condition and its management.
Question 1: What causes type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is caused by a combination of factors, including genetics, lifestyle choices, and environmental influences. It is characterized by insulin resistance, where the body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin, and impaired insulin production.
Question 2: What are the symptoms of type 2 diabetes?
Common symptoms include frequent urination, excessive thirst, increased hunger, unexplained weight loss, blurred vision, fatigue, and slow-healing sores.
Question 3: How is type 2 diabetes diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a physical exam, medical history review, and blood tests, including fasting blood glucose, oral glucose tolerance test, or HbA1c test.
Question 4: Is type 2 diabetes curable?
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management. There is currently no cure, but lifestyle changes, medication, and proper care can help control blood sugar levels and prevent complications.
Question 5: What are the risks of uncontrolled type 2 diabetes?
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to serious health complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage, vision problems, and amputation.
Question 6: How can I prevent or manage type 2 diabetes?
Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, following a balanced diet, and quitting smoking can help prevent or manage type 2 diabetes. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and adherence to prescribed treatment plans are also essential.
Summary: Type 2 diabetes is a serious but manageable condition. By understanding its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, risks, and preventive measures, individuals can take proactive steps to optimize their health outcomes and live well with type 2 diabetes.
Transition to the next article section: For more in-depth information and support, consult reputable medical resources, connect with healthcare professionals, and join diabetes support groups.
Tips for Type 2 Diabetes Management
Effectively managing type 2 diabetes requires a multifaceted approach. Here are several crucial tips to help individuals optimize their health outcomes:
Tip 1: Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can worsen insulin resistance. Aim for a healthy Body Mass Index (BMI) through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
Tip 2: Engage in Regular Physical Activity: Physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control. Incorporate at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week.
Tip 3: Follow a Balanced Diet: Focus on consuming nutrient-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats.
Tip 4: Monitor Blood Sugar Levels: Regular blood sugar monitoring is essential for effective diabetes management. Consult a healthcare professional to determine an appropriate monitoring schedule.
Tip 5: Take Medications as Prescribed: If prescribed diabetes medications, adhere strictly to the dosage and schedule. Medications can help lower blood sugar levels and prevent complications.
Tip 6: Quit Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and worsens insulin resistance. Quitting smoking is crucial for overall health and diabetes management.
Tip 7: Manage Stress: Stress can raise blood sugar levels. Engage in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature.
Tip 8: Get Regular Check-Ups: Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional are essential for monitoring diabetes and assessing overall health. These check-ups may include blood tests, eye exams, and foot exams.
Summary: By implementing these tips, individuals with type 2 diabetes can effectively manage their condition, prevent complications, and live healthier, more fulfilling lives.
Transition to the article’s conclusion: Remember, managing type 2 diabetes is an ongoing journey that requires commitment and collaboration between individuals and their healthcare team.
Conclusion
In summary, type 2 diabetes is a prevalent chronic condition characterized by impaired insulin production and insulin resistance. It poses significant health risks, including heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and blindness. However, with proper management, individuals with type 2 diabetes can effectively control their blood sugar levels and prevent complications.
Understanding type 2 diabetes empowers individuals to take proactive steps towards prevention and management. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, following a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and adhering to prescribed medications are crucial aspects of diabetes management. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and collaborating closely with healthcare professionals are essential for optimizing health outcomes.
By raising awareness about type 2 diabetes, we can encourage early detection, promote healthy behaviors, and foster a supportive environment for individuals living with this condition. Together, we can work towards a future where type 2 diabetes is effectively managed, and its impact on individuals and society is minimized.
Youtube Video: