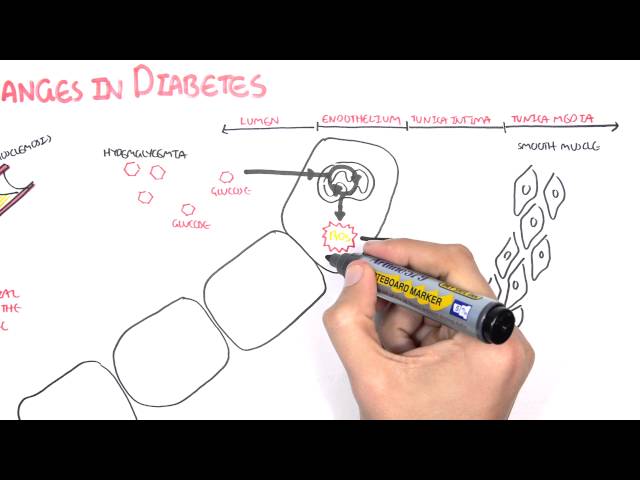
Complications of diabetes refer to any of the various health problems that can occur in people with diabetes. These complications can affect many different parts of the body, including the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves.
Some of the most common complications of diabetes include:
- Cardiovascular disease, including heart attack, stroke, and heart failure
- Retinopathy, a condition that damages the blood vessels in the retina, which can lead to blindness
- Nephropathy, a condition that damages the kidneys
- Neuropathy, a condition that damages the nerves
The risk of developing complications of diabetes increases with the length of time a person has diabetes and the severity of their blood sugar control. Good blood sugar control can help to reduce the risk of developing these complications.
There are a number of treatments available for the complications of diabetes, including medications, surgery, and lifestyle changes. The goal of treatment is to manage the symptoms of the complication and to prevent further damage.
Complications of Diabetes
Complications of diabetes are a serious concern for people with this condition. They can affect many different parts of the body, and can lead to disability and even death. It is important to be aware of the potential complications of diabetes so that you can take steps to prevent them or manage them effectively.
- Cardiovascular disease: Diabetes increases your risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular problems.
- Retinopathy: Diabetes can damage the blood vessels in the retina, leading to vision loss or even blindness.
- Nephropathy: Diabetes can damage the kidneys, leading to kidney failure.
- Neuropathy: Diabetes can damage the nerves, leading to numbness, tingling, and pain.
- Foot problems: Diabetes can cause foot ulcers, infections, and even amputation.
- Other complications: Diabetes can also increase your risk of other health problems, such as depression, anxiety, and erectile dysfunction.
The good news is that many of the complications of diabetes can be prevented or managed with proper care. By keeping your blood sugar under control, eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and taking your medications as prescribed, you can help to reduce your risk of developing these complications.
Cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease is a major complication of diabetes. In fact, people with diabetes are two to four times more likely to die from heart disease than people without diabetes. There are a number of reasons for this increased risk, including:
- High blood sugar: High blood sugar can damage the blood vessels and lead to the formation of plaque, which can narrow the arteries and increase the risk of heart attack and stroke.
- High blood pressure: Diabetes is also a major risk factor for high blood pressure, which is another major risk factor for heart disease and stroke.
- High cholesterol: Diabetes can also lead to high cholesterol, which is another major risk factor for heart disease and stroke.
- Obesity: Obesity is a common problem for people with diabetes, and it is another major risk factor for heart disease and stroke.
The combination of these risk factors makes people with diabetes much more likely to develop cardiovascular disease. It is important to be aware of these risks and to take steps to reduce them, such as controlling your blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol, and losing weight if you are overweight or obese.
Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to blindness. It is caused by damage to the blood vessels in the retina, which is the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye.
- Symptoms: In the early stages, diabetic retinopathy often has no symptoms. However, as the condition progresses, you may experience blurred vision, difficulty seeing colors, and floaters. In severe cases, diabetic retinopathy can lead to blindness.
- Risk factors: The longer you have diabetes, the greater your risk of developing diabetic retinopathy. Other risk factors include high blood sugar, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol.
- Treatment: There is no cure for diabetic retinopathy, but treatment can help to slow the progression of the disease and prevent vision loss. Treatment options include laser therapy, eye injections, and surgery.
- Prevention: The best way to prevent diabetic retinopathy is to control your blood sugar levels. You should also have regular eye exams to check for signs of the disease.
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious complication of diabetes, but it can be prevented or managed with proper care. By controlling your blood sugar levels and having regular eye exams, you can help to protect your vision.
Nephropathy
Nephropathy is a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to kidney failure. It is caused by damage to the blood vessels in the kidneys, which can lead to the buildup of waste products in the blood. Kidney failure can be a life-threatening condition, and people with diabetes are at high risk of developing it.
- Symptoms: In the early stages, nephropathy often has no symptoms. However, as the condition progresses, you may experience fatigue, swelling in your hands and feet, and increased urination. In severe cases, nephropathy can lead to kidney failure, which can be fatal.
- Risk factors: The longer you have diabetes, the greater your risk of developing nephropathy. Other risk factors include high blood sugar, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol.
- Treatment: There is no cure for nephropathy, but treatment can help to slow the progression of the disease and prevent kidney failure. Treatment options include medications, diet changes, and dialysis.
- Prevention: The best way to prevent nephropathy is to control your blood sugar levels. You should also have regular kidney checkups to check for signs of the disease.
Nephropathy is a serious complication of diabetes, but it can be prevented or managed with proper care. By controlling your blood sugar levels and having regular kidney checkups, you can help to protect your kidneys and prevent kidney failure.
Neuropathy
Neuropathy is a serious complication of diabetes that can affect the nerves throughout the body. It is caused by damage to the blood vessels that supply the nerves, which can lead to a number of symptoms, including numbness, tingling, pain, and weakness. Neuropathy can affect the nerves in the hands, feet, legs, and arms, and can make it difficult to walk, use your hands, or perform other everyday activities.
Neuropathy is a common complication of diabetes, and it is estimated that up to 50% of people with diabetes will develop some form of neuropathy. The risk of developing neuropathy increases with the length of time a person has diabetes, and with poor blood sugar control.
There is no cure for neuropathy, but there are treatments that can help to manage the symptoms. These treatments include medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. It is important to treat neuropathy early to prevent further damage to the nerves.
Neuropathy can be a serious complication of diabetes, but it can be managed with proper care. By controlling your blood sugar levels and following your doctor’s recommendations, you can help to reduce your risk of developing neuropathy or manage it effectively if you already have it.
Foot problems
Foot problems are a serious complication of diabetes. In fact, people with diabetes are 15 times more likely to have a foot ulcer than people without diabetes. Foot ulcers are open sores that can occur anywhere on the foot, but they are most common on the bottom of the foot.
Foot ulcers are often caused by nerve damage, which can lead to a loss of sensation in the feet. This can make it difficult to feel pain or pressure, which can lead to injuries that go unnoticed. Foot ulcers can also be caused by poor circulation, which can make it difficult for the feet to heal.
Foot ulcers can be very serious, and they can lead to infections, amputation, and even death. It is important for people with diabetes to take steps to prevent foot ulcers, such as checking their feet daily for any injuries, wearing properly fitting shoes, and keeping their blood sugar levels under control.
If you have diabetes, it is important to be aware of the risk of foot problems. By taking steps to prevent foot ulcers, you can help to protect your feet and your overall health.
Other complications
Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects the body’s ability to produce or use insulin, a hormone that helps glucose enter cells for energy. When glucose builds up in the blood, it can damage the blood vessels and nerves, leading to a variety of complications. These complications can include heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, eye problems, and foot problems.
In addition to these physical complications, diabetes can also increase the risk of mental health problems, such as depression, anxiety, and erectile dysfunction. Depression is a common complication of diabetes, affecting up to 30% of people with the disease. Anxiety is also common, affecting up to 20% of people with diabetes. Erectile dysfunction is a common complication of diabetes, affecting up to 50% of men with the disease.
There is a strong link between diabetes and mental health problems. People with diabetes are more likely to experience depression and anxiety than people without diabetes. This is likely due to a number of factors, including the stress of managing a chronic disease, the physical symptoms of diabetes, and the social stigma associated with the disease.
Mental health problems can have a significant impact on the quality of life for people with diabetes. Depression and anxiety can make it difficult to manage diabetes, which can lead to further health problems. Erectile dysfunction can also have a significant impact on quality of life, leading to relationship problems and low self-esteem.
It is important for people with diabetes to be aware of the risk of mental health problems and to seek help if they are experiencing symptoms of depression, anxiety, or erectile dysfunction. Treatment for these conditions can help to improve quality of life and overall health.
FAQs on Complications of Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic disease that can lead to a number of serious complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, eye problems, and foot problems. These complications can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and even lead to death. It is important to be aware of the potential complications of diabetes and to take steps to prevent them.
Question 1: What are the most common complications of diabetes?
The most common complications of diabetes include heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, eye problems, and foot problems.
Question 2: What are the risk factors for developing complications of diabetes?
The risk of developing complications of diabetes increases with the length of time a person has diabetes and the severity of their blood sugar control. Other risk factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and obesity.
Question 3: How can I prevent complications of diabetes?
The best way to prevent complications of diabetes is to control your blood sugar levels. You should also have regular checkups with your doctor to monitor your blood sugar levels and check for signs of complications.
Question 4: What are the symptoms of complications of diabetes?
The symptoms of complications of diabetes can vary depending on the type of complication. Some common symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling in the hands and feet, and vision problems.
Question 5: How are complications of diabetes treated?
The treatment for complications of diabetes depends on the type of complication. Treatment may include medications, surgery, or lifestyle changes.
Question 6: Can complications of diabetes be reversed?
Some complications of diabetes, such as heart disease and stroke, cannot be reversed. However, other complications, such as kidney disease and eye problems, can be slowed or prevented with proper treatment.
It is important to remember that diabetes is a serious disease that can lead to a number of complications. However, by controlling your blood sugar levels and following your doctor’s recommendations, you can help to reduce your risk of developing complications or manage them effectively if you already have them.
Transition to the next article section: For more information on complications of diabetes, please visit the following resources:
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
- American Diabetes Association
Tips to Prevent Complications of Diabetes
Complications of diabetes are serious health conditions that can significantly impact your quality of life. However, there are many things you can do to prevent or delay these complications.
Tip 1: Control your blood sugar levels.
- High blood sugar levels can damage your blood vessels and nerves, leading to complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness.
- To control your blood sugar levels, take your medications as prescribed, follow a healthy diet, and get regular exercise.
Tip 2: Manage your blood pressure.
- High blood pressure is another major risk factor for complications of diabetes.
- To manage your blood pressure, eat a healthy diet, get regular exercise, and take your medications as prescribed.
Tip 3: Quit smoking.
- Smoking damages your blood vessels and increases your risk of heart disease, stroke, and other complications of diabetes.
- If you smoke, quit as soon as possible.
Tip 4: Manage your cholesterol levels.
- High cholesterol levels can increase your risk of heart disease and stroke.
- To manage your cholesterol levels, eat a healthy diet, get regular exercise, and take your medications as prescribed.
Tip 5: Get regular exercise.
- Regular exercise helps to control blood sugar levels, lower blood pressure, and improve cholesterol levels.
- Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
Tip 6: Eat a healthy diet.
- Eating a healthy diet helps to control blood sugar levels, lower blood pressure, and improve cholesterol levels.
- Focus on eating fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
Tip 7: Get regular checkups.
- Regular checkups allow your doctor to monitor your blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels.
- Early detection and treatment of complications can help to prevent or delay serious health problems.
Summary of key takeaways or benefits:
- By following these tips, you can help to prevent or delay complications of diabetes and improve your overall health.
- It is important to work with your doctor to develop a personalized plan for managing your diabetes and reducing your risk of complications.
Transition to the article’s conclusion:
Complications of diabetes are a serious concern, but they can be prevented or delayed with proper care. By following these tips and working with your doctor, you can take control of your diabetes and live a long, healthy life.
Conclusion
Complications of diabetes are a serious concern, but they can be prevented or delayed with proper care. By controlling your blood sugar levels, managing your blood pressure, and following a healthy lifestyle, you can reduce your risk of developing these complications.
If you have diabetes, it is important to work with your doctor to develop a personalized plan for managing your diabetes and reducing your risk of complications. By following your doctor’s recommendations and taking an active role in your care, you can live a long, healthy life with diabetes.
Youtube Video: