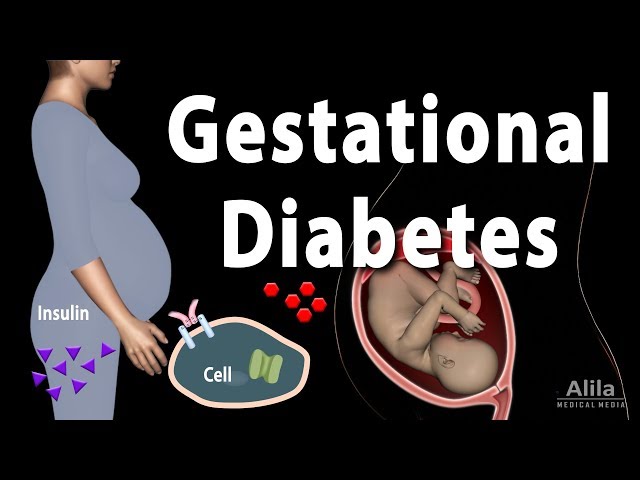
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy and usually goes away after the baby is born. It affects about 2-10% of pregnant women and is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin to meet the increased demands of pregnancy.
Gestational diabetes can cause high blood sugar levels, which can lead to problems for both the mother and the baby. For the mother, it can increase the risk of pre-eclampsia, premature birth, and cesarean section. For the baby, it can increase the risk of macrosomia (large birth weight), hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), and respiratory distress syndrome.
Gestational diabetes is usually diagnosed with a glucose tolerance test between the 24th and 28th weeks of pregnancy. If you are diagnosed with gestational diabetes, you will need to monitor your blood sugar levels and make changes to your diet and lifestyle. Treatment may also include medication.
Pregnancy diabetes
Pregnancy diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin to meet the increased demands of pregnancy. Pregnancy diabetes can cause high blood sugar levels, which can lead to problems for both the mother and the baby.
- Gestational: Pregnancy diabetes is also known as gestational diabetes because it develops during gestation, or pregnancy.
- Temporary: Pregnancy diabetes usually goes away after the baby is born.
- Risks: Pregnancy diabetes can increase the risk of pre-eclampsia, premature birth, and cesarean section for the mother. For the baby, it can increase the risk of macrosomia (large birth weight), hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), and respiratory distress syndrome.
- Diagnosis: Pregnancy diabetes is usually diagnosed with a glucose tolerance test between the 24th and 28th weeks of pregnancy.
- Treatment: Treatment for pregnancy diabetes may include diet changes, lifestyle changes, and medication.
- Prevention: There is no sure way to prevent pregnancy diabetes, but there are some things you can do to reduce your risk, such as eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight.
- Management: Pregnancy diabetes can be managed with diet, exercise, and medication. It is important to follow your doctor’s instructions to help keep your blood sugar levels under control.
Pregnancy diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with proper care. If you are diagnosed with pregnancy diabetes, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions and make healthy lifestyle changes to help keep your blood sugar levels under control. This will help to reduce the risk of complications for both you and your baby.
Gestational
The term “gestational” is used to describe pregnancy diabetes because it develops during gestation, or pregnancy. This is in contrast to other types of diabetes, such as type 1 and type 2 diabetes, which can develop at any time in a person’s life.
Gestational diabetes is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin to meet the increased demands of pregnancy. Insulin is a hormone that helps the body to use glucose for energy. During pregnancy, the body needs more insulin to support the growth of the baby. If the body cannot produce enough insulin, blood sugar levels can rise, leading to gestational diabetes.
Gestational diabetes is a serious condition that can lead to complications for both the mother and the baby. For the mother, gestational diabetes can increase the risk of pre-eclampsia, premature birth, and cesarean section. For the baby, gestational diabetes can increase the risk of macrosomia (large birth weight), hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), and respiratory distress syndrome.
However, gestational diabetes can be managed with diet, exercise, and medication. It is important for women with gestational diabetes to follow their doctor’s instructions to help keep their blood sugar levels under control. This will help to reduce the risk of complications for both the mother and the baby.
Temporary
Pregnancy diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin to meet the increased demands of pregnancy. Pregnancy diabetes usually goes away after the baby is born because the body’s insulin production returns to normal.
However, some women who have had gestational diabetes are at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. This is because gestational diabetes can damage the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. As a result, these women may need to take medication or make lifestyle changes to prevent or manage type 2 diabetes.
It is important for women who have had gestational diabetes to be tested for type 2 diabetes every few years. This will help to ensure that they are diagnosed and treated early if they do develop type 2 diabetes.
Risks
Pregnancy diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin to meet the increased demands of pregnancy. Pregnancy diabetes can cause high blood sugar levels, which can lead to problems for both the mother and the baby.
For the mother, pregnancy diabetes can increase the risk of pre-eclampsia, premature birth, and cesarean section. Pre-eclampsia is a serious condition that can lead to high blood pressure and kidney problems. Premature birth is the birth of a baby before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Cesarean section is a surgical procedure to deliver a baby through an incision in the abdomen.
For the baby, pregnancy diabetes can increase the risk of macrosomia (large birth weight), hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), and respiratory distress syndrome. Macrosomia is a condition in which a baby is born with a birth weight of more than 4,000 grams. Hypoglycemia is a condition in which a baby has low blood sugar levels. Respiratory distress syndrome is a condition in which a baby has difficulty breathing.
It is important for women with pregnancy diabetes to follow their doctor’s instructions to help keep their blood sugar levels under control. This will help to reduce the risk of complications for both the mother and the baby.
Here are some real-life examples of how pregnancy diabetes can affect the mother and the baby:
- A woman with pregnancy diabetes may develop pre-eclampsia, which can lead to high blood pressure and kidney problems. This can be dangerous for both the mother and the baby.
- A woman with pregnancy diabetes may have a premature birth. Premature babies are at an increased risk of health problems, such as respiratory distress syndrome and cerebral palsy.
- A woman with pregnancy diabetes may need to have a cesarean section. Cesarean section is a major surgery, and it can increase the risk of infection and other complications for the mother.
- A baby born to a mother with pregnancy diabetes may have macrosomia. Macrosomia can make it difficult for the baby to be born vaginally, and it can also increase the risk of birth injuries.
- A baby born to a mother with pregnancy diabetes may have hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemia can cause seizures and other serious health problems in babies.
- A baby born to a mother with pregnancy diabetes may have respiratory distress syndrome. Respiratory distress syndrome can make it difficult for the baby to breathe, and it can be fatal.
These are just a few examples of how pregnancy diabetes can affect the mother and the baby. It is important for women with pregnancy diabetes to be aware of these risks and to follow their doctor’s instructions to help keep their blood sugar levels under control.
Pregnancy diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with proper care. If you are diagnosed with pregnancy diabetes, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions and make healthy lifestyle changes to help keep your blood sugar levels under control. This will help to reduce the risk of complications for both you and your baby.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of pregnancy diabetes is usually made with a glucose tolerance test between the 24th and 28th weeks of pregnancy. This test involves drinking a sugary drink and then having your blood sugar levels checked at regular intervals over the next few hours. If your blood sugar levels are too high, you may be diagnosed with pregnancy diabetes.
It is important to diagnose pregnancy diabetes early so that it can be managed and treated. This will help to reduce the risk of complications for both the mother and the baby.
Here are some real-life examples of how the diagnosis of pregnancy diabetes can affect the mother and the baby:
- A woman who is diagnosed with pregnancy diabetes may be able to manage her condition with diet and exercise. This will help to keep her blood sugar levels under control and reduce the risk of complications.
- A woman who is diagnosed with pregnancy diabetes may need to take medication to help control her blood sugar levels. This will help to reduce the risk of complications for both the mother and the baby.
- A woman who is diagnosed with pregnancy diabetes may need to have a cesarean section if her blood sugar levels cannot be controlled. This is because a vaginal delivery can be dangerous for both the mother and the baby if the mother’s blood sugar levels are too high.
These are just a few examples of how the diagnosis of pregnancy diabetes can affect the mother and the baby. It is important for women who are pregnant to be aware of the risks of pregnancy diabetes and to get tested for the condition if they are at risk.
If you are diagnosed with pregnancy diabetes, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions to help keep your blood sugar levels under control. This will help to reduce the risk of complications for both you and your baby.
Treatment
The treatment for pregnancy diabetes is crucial in managing blood sugar levels and ensuring a healthy pregnancy. It involves a combination of dietary modifications, lifestyle adjustments, and potentially medication to maintain optimal blood sugar control.
-
Dietary Changes
Dietary changes are a cornerstone of pregnancy diabetes management. This includes consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats. Maintaining a healthy weight and following specific dietary guidelines recommended by a healthcare professional can help regulate blood sugar levels.
-
Lifestyle Changes
Regular physical activity, such as brisk walking or swimming, is encouraged during pregnancy to promote overall well-being and improve insulin sensitivity. Quitting smoking and managing stress levels are also crucial lifestyle changes that can positively impact blood sugar control.
-
Medication
In some cases, medication may be necessary to manage blood sugar levels effectively. Insulin injections or oral medications may be prescribed to regulate blood sugar and prevent complications. Healthcare professionals will closely monitor blood sugar levels and adjust medication as needed throughout the pregnancy.
Adhering to the recommended treatment plan, including dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, and medication when necessary, is essential for managing pregnancy diabetes successfully. By maintaining optimal blood sugar control, the risks of complications for both the mother and the baby can be significantly reduced.
Prevention
Pregnancy diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin to meet the increased demands of pregnancy. Pregnancy diabetes can cause high blood sugar levels, which can lead to problems for both the mother and the baby.
There is no sure way to prevent pregnancy diabetes, but there are some things you can do to reduce your risk. These include:
- Eating a healthy diet: Eating a healthy diet that is low in sugar and processed foods can help to keep your blood sugar levels under control.
- Getting regular exercise: Getting regular exercise can help to improve your insulin sensitivity and lower your blood sugar levels.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Maintaining a healthy weight can help to reduce your risk of developing pregnancy diabetes.
If you are at risk for pregnancy diabetes, your doctor may recommend that you have a glucose tolerance test. This test can help to diagnose pregnancy diabetes early so that it can be managed and treated.
Managing pregnancy diabetes is important for the health of both the mother and the baby. By following your doctor’s instructions and making healthy lifestyle changes, you can help to keep your blood sugar levels under control and reduce your risk of complications.
Management
Pregnancy diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin to meet the increased demands of pregnancy. Pregnancy diabetes can cause high blood sugar levels, which can lead to problems for both the mother and the baby.
There is no cure for pregnancy diabetes, but it can be managed with diet, exercise, and medication. It is important for women with pregnancy diabetes to follow their doctor’s instructions to help keep their blood sugar levels under control. This will help to reduce the risk of complications for both the mother and the baby.
-
Diet
Eating a healthy diet is an important part of managing pregnancy diabetes. A healthy diet for pregnancy diabetes includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It also includes lean protein and low-fat dairy products. Women with pregnancy diabetes should limit their intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats.
-
Exercise
Getting regular exercise is another important part of managing pregnancy diabetes. Exercise helps to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. Women with pregnancy diabetes should get at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
-
Medication
Some women with pregnancy diabetes may need to take medication to help control their blood sugar levels. Medication for pregnancy diabetes includes insulin injections or oral medications. Women with pregnancy diabetes should take their medication as prescribed by their doctor.
Managing pregnancy diabetes is important for the health of both the mother and the baby. By following their doctor’s instructions and making healthy lifestyle changes, women with pregnancy diabetes can help to keep their blood sugar levels under control and reduce the risk of complications.
Frequently Asked Questions about Pregnancy Diabetes
Pregnancy diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin to meet the increased demands of pregnancy. Pregnancy diabetes can cause high blood sugar levels, which can lead to problems for both the mother and the baby.
Question 1: What are the symptoms of pregnancy diabetes?
Answer: Pregnancy diabetes often has no symptoms. However, some women may experience increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision.
Question 2: What causes pregnancy diabetes?
Answer: Pregnancy diabetes is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin to meet the increased demands of pregnancy.
Question 3: Who is at risk for pregnancy diabetes?
Answer: Women who are overweight or obese, have a family history of diabetes, or are over the age of 35 are at increased risk for pregnancy diabetes.
Question 4: How is pregnancy diabetes diagnosed?
Answer: Pregnancy diabetes is usually diagnosed with a glucose tolerance test between the 24th and 28th weeks of pregnancy.
Question 5: How is pregnancy diabetes treated?
Answer: Pregnancy diabetes is treated with diet, exercise, and medication. It is important for women with pregnancy diabetes to follow their doctor’s instructions to help keep their blood sugar levels under control.
Question 6: What are the risks of pregnancy diabetes?
Answer: Pregnancy diabetes can increase the risk of pre-eclampsia, premature birth, and cesarean section for the mother. For the baby, it can increase the risk of macrosomia (large birth weight), hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), and respiratory distress syndrome.
Summary of key takeaways or final thought: Pregnancy diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with proper care. If you are diagnosed with pregnancy diabetes, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions and make healthy lifestyle changes to help keep your blood sugar levels under control. This will help to reduce the risk of complications for both you and your baby.
Transition to the next article section: For more information on pregnancy diabetes, please visit the following resources:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- National Institute of Child Health and Human Development
- March of Dimes
Tips to Manage Pregnancy Diabetes
Pregnancy diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is caused by the body’s inability to produce enough insulin to meet the increased demands of pregnancy. Pregnancy diabetes can cause high blood sugar levels, which can lead to problems for both the mother and the baby.
There is no cure for pregnancy diabetes, but it can be managed with diet, exercise, and medication. It is important for women with pregnancy diabetes to follow their doctor’s instructions to help keep their blood sugar levels under control. This will help to reduce the risk of complications for both the mother and the baby.
Here are some tips to help manage pregnancy diabetes:
Tip 1: Eat a healthy diet
Eating a healthy diet is an important part of managing pregnancy diabetes. A healthy diet for pregnancy diabetes includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It also includes lean protein and low-fat dairy products. Women with pregnancy diabetes should limit their intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats.
Tip 2: Get regular exercise
Getting regular exercise is another important part of managing pregnancy diabetes. Exercise helps to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. Women with pregnancy diabetes should get at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
Tip 3: Monitor your blood sugar levels
Monitoring your blood sugar levels is important for managing pregnancy diabetes. This will help you to make sure that your blood sugar levels are under control and that you are taking the appropriate steps to manage your condition.
Tip 4: Take your medication as prescribed
Some women with pregnancy diabetes may need to take medication to help control their blood sugar levels. Medication for pregnancy diabetes includes insulin injections or oral medications. Women with pregnancy diabetes should take their medication as prescribed by their doctor.
Tip 5: Follow your doctor’s instructions
It is important for women with pregnancy diabetes to follow their doctor’s instructions. This includes following a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, monitoring your blood sugar levels, and taking your medication as prescribed. Following your doctor’s instructions will help you to manage your pregnancy diabetes and reduce the risk of complications for both you and your baby.
Summary of key takeaways or benefits: Pregnancy diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with proper care. By following the tips above, women with pregnancy diabetes can help to keep their blood sugar levels under control and reduce the risk of complications.
Transition to the article’s conclusion: For more information on pregnancy diabetes, please visit the following resources:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- National Institute of Child Health and Human Development
- March of Dimes
Conclusion
Pregnancy diabetes is a serious condition that can lead to complications for both the mother and the baby. However, it can be managed with proper care. By following the tips above, women with pregnancy diabetes can help to keep their blood sugar levels under control and reduce the risk of complications.
If you are diagnosed with pregnancy diabetes, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions and make healthy lifestyle changes. This will help you to manage your pregnancy diabetes and reduce the risk of complications for both you and your baby.
Youtube Video: