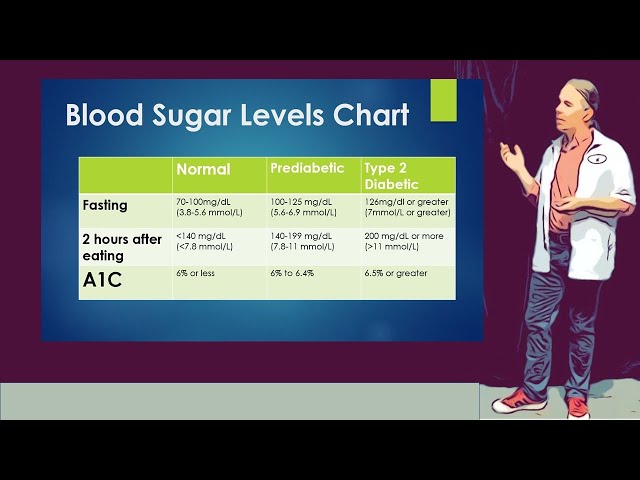
Diabetic levels after eating refer to the levels of glucose in the blood after a person with diabetes has eaten. These levels are important to monitor because they can provide information about how well a person’s diabetes is being managed. If blood glucose levels are too high after eating, it can lead to long-term complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness. However, with careful monitoring and management, people with diabetes can keep their blood glucose levels within a healthy range and reduce their risk of developing these complications.
Importance, benefits, and historical context
Monitoring diabetic levels after eating is an important part of diabetes management. In the past, people with diabetes had to rely on urine tests to check their blood glucose levels. However, urine tests are not as accurate as blood tests, and they can be difficult to interpret. Today, there are a variety of blood glucose monitors available that make it easy for people with diabetes to check their blood glucose levels at home. These monitors are small, portable, and easy to use and can provide accurate results in just a few seconds.
Transition to main article topics
In this article, we will discuss the importance of monitoring diabetic levels after eating, how to check your blood glucose levels, and what to do if your blood glucose levels are too high or too low. We will also provide tips on how to manage your diabetes and reduce your risk of developing complications.
Diabetic levels after eating
Monitoring diabetic levels after eating is an important part of diabetes management. Blood glucose levels that are too high or too low after eating can lead to a number of health problems. It is important to understand the key aspects of diabetic levels after eating in order to manage your diabetes and reduce your risk of developing complications.
- Blood glucose levels: Blood glucose levels are the amount of sugar in your blood. After you eat, your blood glucose levels will rise. The amount that they rise will depend on the type of food you eat and how much you eat.
- Target blood glucose levels: Target blood glucose levels are the levels that you should aim for after eating. These levels will vary depending on your individual diabetes management plan.
- High blood glucose levels: High blood glucose levels after eating can be dangerous. They can lead to a number of health problems, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness.
- Low blood glucose levels: Low blood glucose levels after eating can also be dangerous. They can cause symptoms such as dizziness, confusion, and seizures.
- Monitoring blood glucose levels: It is important to monitor your blood glucose levels regularly after eating. This will help you to identify any problems and make necessary adjustments to your diabetes management plan.
- Managing blood glucose levels: There are a number of things you can do to manage your blood glucose levels after eating, including eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and taking medication as prescribed by your doctor.
By understanding the key aspects of diabetic levels after eating, you can take steps to manage your diabetes and reduce your risk of developing complications. Talk to your doctor or diabetes educator for more information on how to monitor and manage your blood glucose levels.
Blood glucose levels
Blood glucose levels are an important part of diabetic levels after eating. When you eat, your body breaks down the food into glucose, which is then absorbed into your bloodstream. The amount of glucose in your blood will rise after you eat, and the amount that it rises will depend on the type of food you eat and how much you eat. Foods that are high in carbohydrates, such as bread, pasta, and rice, will cause your blood glucose levels to rise more than foods that are low in carbohydrates, such as vegetables and meat. The amount of food that you eat will also affect your blood glucose levels. Eating a large meal will cause your blood glucose levels to rise more than eating a small meal.
It is important to monitor your blood glucose levels after eating to make sure that they do not get too high. High blood glucose levels can damage your blood vessels and organs, and they can lead to a number of health problems, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness. If your blood glucose levels are too high, you may need to take medication or make changes to your diet or exercise routine.
By understanding the connection between blood glucose levels and diabetic levels after eating, you can take steps to manage your diabetes and reduce your risk of developing complications.
Target blood glucose levels
Target blood glucose levels are an important part of diabetic levels after eating. When you eat, your blood glucose levels will rise. The amount that they rise will depend on the type of food you eat and how much you eat. Your target blood glucose levels are the levels that you should aim for after eating to avoid high or low blood glucose levels.
-
Importance of target blood glucose levels
Target blood glucose levels are important because they help to reduce your risk of developing complications from diabetes. High blood glucose levels can damage your blood vessels and organs, and they can lead to a number of health problems, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness. Low blood glucose levels can also be dangerous. They can cause symptoms such as dizziness, confusion, and seizures.
-
Individualized target blood glucose levels
Target blood glucose levels will vary depending on your individual diabetes management plan. Your doctor will work with you to determine what your target blood glucose levels should be. These levels will be based on a number of factors, including your age, activity level, and overall health.
-
Monitoring blood glucose levels
It is important to monitor your blood glucose levels regularly after eating to make sure that they are within your target range. This will help you to identify any problems and make necessary adjustments to your diabetes management plan.
-
Adjusting blood glucose levels
If your blood glucose levels are too high or too low, you may need to make adjustments to your diabetes management plan. This may include changing your diet, increasing your exercise, or taking medication.
By understanding the connection between target blood glucose levels and diabetic levels after eating, you can take steps to manage your diabetes and reduce your risk of developing complications.
High blood glucose levels
High blood glucose levels after eating are a major concern for people with diabetes. When blood glucose levels are too high, they can damage the blood vessels and organs. This damage can lead to a number of health problems, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness.
There are a number of factors that can contribute to high blood glucose levels after eating, including:
- Eating too much food
- Eating foods that are high in carbohydrates
- Not taking enough insulin or diabetes medication
- Being sick or stressed
It is important to monitor blood glucose levels regularly after eating to make sure that they are within a healthy range. If blood glucose levels are too high, steps should be taken to lower them, such as eating a healthy snack, exercising, or taking medication.
By understanding the connection between high blood glucose levels and diabetic levels after eating, people with diabetes can take steps to manage their blood glucose levels and reduce their risk of developing complications.
Here are some real-life examples of how high blood glucose levels after eating can lead to health problems:
- A person with diabetes who eats a large meal may experience a spike in blood glucose levels. This spike can damage the blood vessels in the heart, increasing the risk of heart disease.
- A person with diabetes who eats a sugary snack may experience a spike in blood glucose levels. This spike can damage the blood vessels in the brain, increasing the risk of stroke.
- A person with diabetes who does not take enough insulin or diabetes medication may experience high blood glucose levels after eating. This can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys, increasing the risk of kidney disease.
These are just a few examples of how high blood glucose levels after eating can lead to health problems. It is important to monitor blood glucose levels regularly and take steps to lower them if they are too high.
By understanding the connection between high blood glucose levels and diabetic levels after eating, people with diabetes can take steps to manage their blood glucose levels and reduce their risk of developing complications.
Low blood glucose levels
Low blood glucose levels after eating are a concern for people with diabetes. When blood glucose levels drop too low, it can lead to a condition called hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemia can cause a number of symptoms, including dizziness, confusion, and seizures. In severe cases, hypoglycemia can be fatal.
-
Causes of hypoglycemia
There are a number of things that can cause hypoglycemia, including:
- Taking too much insulin or diabetes medication
- Skipping or delaying meals
- Exercising too much
- Drinking alcohol
-
Symptoms of hypoglycemia
The symptoms of hypoglycemia can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Mild symptoms may include:
- Shaking
- Sweating
- Hunger
- Irritability
- Dizziness
More severe symptoms may include:
- Confusion
- Seizures
- Loss of consciousness
-
Treatment for hypoglycemia
The treatment for hypoglycemia is to raise blood glucose levels. This can be done by eating or drinking something that contains sugar, such as a candy bar, a glass of juice, or a regular soda. If the person is unconscious, glucagon can be given to raise blood glucose levels.
-
Preventing hypoglycemia
There are a number of things that people with diabetes can do to prevent hypoglycemia, including:
- Taking insulin or diabetes medication as prescribed
- Eating regular meals and snacks
- Exercising regularly
- Avoiding alcohol
- Carrying a source of sugar, such as a candy bar or a glucose tablet, at all times
Low blood glucose levels after eating can be dangerous, but they can be prevented and treated. People with diabetes should be aware of the symptoms of hypoglycemia and know what to do if they experience them.
Monitoring blood glucose levels
Monitoring blood glucose levels is an essential part of managing diabetes. By understanding the connection between monitoring blood glucose levels and diabetic levels after eating, you can take steps to manage your diabetes and reduce your risk of developing complications.
-
Identifying problems
Monitoring blood glucose levels after eating can help you to identify any problems with your diabetes management plan. For example, if your blood glucose levels are too high after eating, it may be a sign that you are not taking enough insulin or that you are eating too many carbohydrates. Identifying these problems early on can help you to make necessary adjustments to your diabetes management plan and avoid serious complications.
-
Making adjustments
Monitoring blood glucose levels after eating can also help you to make necessary adjustments to your diabetes management plan. For example, if your blood glucose levels are too high after eating, you may need to increase your insulin dosage or reduce your carbohydrate intake. Making these adjustments can help you to keep your blood glucose levels within a healthy range and reduce your risk of developing complications.
-
Preventing complications
Monitoring blood glucose levels after eating can help you to prevent serious complications from diabetes. High blood glucose levels can damage the blood vessels and organs, leading to heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness. By monitoring your blood glucose levels and making necessary adjustments to your diabetes management plan, you can reduce your risk of developing these complications.
In conclusion, monitoring blood glucose levels after eating is an essential part of managing diabetes. By understanding the connection between monitoring blood glucose levels and diabetic levels after eating, you can take steps to manage your diabetes and reduce your risk of developing complications.
Managing blood glucose levels
Managing blood glucose levels is essential for people with diabetes to avoid diabetic complications. Diabetic levels after eating refer to the blood glucose levels after a person with diabetes has eaten. Managing blood glucose levels after eating is a crucial aspect of diabetic levels after eating as it helps prevent high blood glucose levels, which can cause long-term damage to blood vessels and organs.
Eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and taking prescribed medication are effective ways to manage blood glucose levels after eating. A balanced diet with limited carbohydrate intake helps prevent blood glucose spikes after meals. Regular exercise improves insulin sensitivity, allowing the body to use insulin more effectively and lower blood glucose levels. Furthermore, taking medication as prescribed by a doctor helps regulate blood glucose levels and prevent them from rising too high after eating.
For example, a study published in the journal Diabetes Care found that people with type 2 diabetes who followed a low-carbohydrate diet had significantly lower blood glucose levels after eating compared to those who followed a high-carbohydrate diet. Another study, published in the journal Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, found that people with type 1 diabetes who exercised regularly had better blood glucose control and lower blood glucose levels after eating than those who did not exercise.
Understanding the connection between managing blood glucose levels and diabetic levels after eating is crucial for people with diabetes. By following a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and taking medication as prescribed, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their blood glucose levels after eating, reducing the risk of developing long-term complications.
FAQs on Diabetic Levels After Eating
Diabetic levels after eating refer to the blood glucose levels of individuals with diabetes following a meal. Managing these levels is critical to prevent long-term complications. Here are some frequently asked questions and answers to provide a comprehensive understanding of diabetic levels after eating.
Question 1: Why is monitoring diabetic levels after eating important?
Monitoring diabetic levels after eating is crucial because elevated blood glucose levels after meals can lead to long-term damage to blood vessels and organs, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness.
Question 2: What are the target blood glucose levels after eating for people with diabetes?
Target blood glucose levels vary depending on individual factors and should be discussed with a healthcare professional. Generally, it is recommended to keep blood glucose levels below 180 mg/dL one to two hours after eating.
Question 3: How can I lower my blood glucose levels after eating?
Effective ways to lower blood glucose levels after eating include following a balanced diet with limited carbohydrate intake, engaging in regular physical activity, and taking prescribed diabetes medications.
Question 4: What should I do if my blood glucose levels are too high after eating?
If blood glucose levels are consistently high after eating, consult with a healthcare professional to adjust your diabetes management plan, which may include modifying your diet, increasing exercise, or adjusting medication dosages.
Question 5: What should I do if my blood glucose levels are too low after eating?
If blood glucose levels drop significantly after eating, it could be a sign of hypoglycemia. Immediate action is needed to raise blood glucose levels by consuming a quick-acting source of sugar, such as glucose tablets or fruit juice.
Question 6: How often should I check my blood glucose levels after eating?
The frequency of blood glucose monitoring after eating varies depending on individual needs and diabetes management goals. Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.
Summary of key takeaways or final thought:
Managing diabetic levels after eating is essential for long-term health and well-being. Monitoring blood glucose levels, following a healthy lifestyle, and adhering to prescribed medications are crucial components of effective diabetes management. Regular consultation with healthcare professionals is recommended to optimize treatment plans and prevent complications.
Transition to the next article section:
For further information and support on diabetic levels after eating, refer to the next section of this article or consult with a qualified healthcare professional.
Tips for Managing Diabetic Levels After Eating
Effectively managing diabetic levels after eating is crucial for individuals with diabetes to prevent long-term complications. Here are essential tips to help achieve optimal blood glucose control:
Tip 1: Monitor Blood Glucose Levels Regularly
Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels after eating provides valuable insights into how the body responds to meals. This information enables timely adjustments to diet, exercise, and medication regimens, ensuring effective management.
Tip 2: Follow a Balanced Diet
Consuming a balanced diet with controlled carbohydrate intake helps prevent blood glucose spikes after meals. Prioritizing whole grains, lean proteins, and non-starchy vegetables promotes sustained energy levels and optimal blood sugar control.
Tip 3: Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, allowing the body to utilize insulin more efficiently. Exercise helps lower blood glucose levels and enhances overall well-being.
Tip 4: Take Medications as Prescribed
Adhering to prescribed diabetes medications is essential for managing blood glucose levels. Medications help regulate insulin production or enhance insulin sensitivity, effectively preventing high blood sugar levels after eating.
Tip 5: Stay Hydrated
Maintaining adequate hydration is crucial for overall health, including blood glucose management. Drinking plenty of water helps flush out excess glucose from the body and prevents dehydration, which can worsen blood sugar control.
Tip 6: Avoid Sugary Drinks and Processed Foods
Sugary drinks and processed foods rapidly raise blood glucose levels and contribute to insulin resistance. Limiting their consumption is essential for effective diabetic level management.
Tip 7: Read Food Labels Carefully
Educating oneself about food labels empowers individuals to make informed choices. Paying attention to carbohydrate content and serving sizes helps manage portions and prevent overconsumption, which can lead to elevated blood glucose levels.
Tip 8: Get Enough Sleep
Sufficient sleep is essential for overall health and blood glucose regulation. When sleep is disrupted, the body produces hormones that can interfere with insulin sensitivity, making it harder to control blood sugar levels.
Summary of key takeaways or benefits:
By incorporating these tips into their daily routines, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their diabetic levels after eating, reducing the risk of long-term complications and promoting overall well-being.
Transition to the article’s conclusion:
Managing diabetic levels after eating is an ongoing process that requires commitment and collaboration with healthcare professionals. By following these tips and adhering to personalized treatment plans, individuals with diabetes can maintain optimal blood glucose control and live healthier, more fulfilling lives.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing diabetic levels after eating is crucial for individuals with diabetes to maintain optimal health and prevent long-term complications. This article has explored the significance of monitoring blood glucose levels after meals, emphasizing the importance of adhering to a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and taking prescribed medications as directed.
Effective management of diabetic levels after eating requires ongoing commitment and collaboration with healthcare professionals. By incorporating the tips and strategies outlined in this article, individuals with diabetes can empower themselves to achieve and maintain optimal blood glucose control. This, in turn, reduces the risk of developing severe complications, promotes overall well-being, and allows individuals to lead healthier, more fulfilling lives.
Youtube Video: