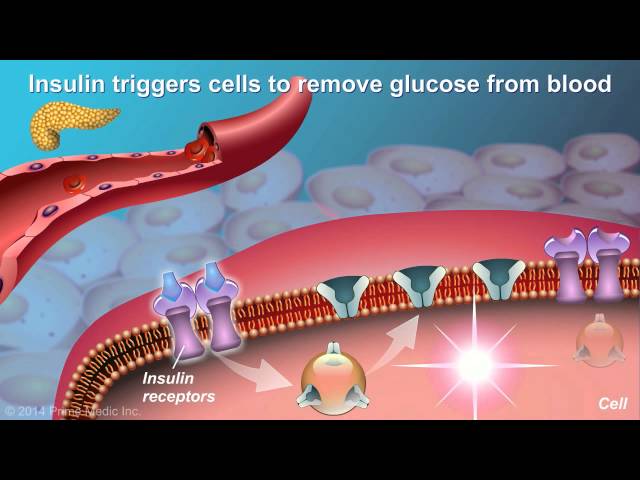
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way the body uses sugar (glucose). With type 2 diabetes, the body either resists the effects of insulin or does not produce enough insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get from the blood into the cells. Without enough insulin, glucose builds up in the blood. Over time, high blood glucose levels can damage the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves.
The exact cause of type 2 diabetes is unknown, but it is thought to be caused by a combination of factors, including genetics, lifestyle, and environmental factors. Risk factors for type 2 diabetes include:
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Family history of diabetes
- Age (over 45)
- Race/ethnicity (African Americans, Hispanic Americans, American Indians, and Asian Americans are at increased risk)
- Certain medical conditions, such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol
- Certain medications, such as steroids
There is no cure for type 2 diabetes, but it can be managed with medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring of blood sugar levels.
Type 2 diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed. By following a healthy lifestyle and taking medication as prescribed, people with type 2 diabetes can live long, healthy lives.
Type 2 Diabetes Cause
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way the body uses sugar (glucose). The exact cause of type 2 diabetes is unknown, but it is thought to be caused by a combination of factors, including genetics, lifestyle, and environmental factors.
- Genetics: Family history of diabetes is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes.
- Lifestyle: Obesity and physical inactivity are major risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
- Age: The risk of type 2 diabetes increases with age.
- Race/ethnicity: African Americans, Hispanic Americans, American Indians, and Asian Americans are at increased risk for type 2 diabetes.
- Certain medical conditions: High blood pressure and high cholesterol are risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
- Certain medications: Steroids and other medications can increase the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to certain chemicals and pollutants may increase the risk of type 2 diabetes.
These are just some of the key factors that are thought to contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes. More research is needed to fully understand the causes of this condition.
Genetics
Family history is a significant risk factor for type 2 diabetes. If you have a parent or sibling with type 2 diabetes, you are more likely to develop the condition yourself. This is because you inherit certain genes from your parents that make you more susceptible to developing type 2 diabetes.
-
Facet 1: Genes and Type 2 Diabetes
Certain genes play a role in the development of type 2 diabetes. These genes affect the way your body produces and uses insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get from the blood into the cells. Without enough insulin, glucose builds up in the blood and can lead to type 2 diabetes.
-
Facet 2: Family History and Risk
If you have a family history of type 2 diabetes, you are more likely to develop the condition yourself. This is because you inherit certain genes from your parents that make you more susceptible to developing type 2 diabetes. The more relatives you have with type 2 diabetes, the greater your risk.
-
Facet 3: Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, such as diet and exercise, can also play a role in the development of type 2 diabetes. However, family history is a major risk factor, regardless of your lifestyle.
-
Facet 4: Prevention and Management
If you have a family history of type 2 diabetes, there are things you can do to reduce your risk of developing the condition. These include eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight. If you are diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, there are medications and lifestyle changes that can help you manage the condition and prevent complications.
Family history is a significant risk factor for type 2 diabetes. However, it is important to remember that not everyone with a family history of the condition will develop it. There are things you can do to reduce your risk, such as eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight. If you are concerned about your risk of type 2 diabetes, talk to your doctor.
Lifestyle
Obesity and physical inactivity are two of the most important modifiable risk factors for type 2 diabetes. Obesity is a condition in which a person has excess body fat. Physical inactivity is a lack of regular physical activity. Both obesity and physical inactivity can lead to insulin resistance, a condition in which the body’s cells do not respond to insulin as well as they should. Insulin resistance can lead to high blood sugar levels, which can eventually lead to type 2 diabetes.
-
Facet 1: Obesity and Insulin Resistance
Obesity is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes because it can lead to insulin resistance. Insulin resistance occurs when the body’s cells do not respond to insulin as well as they should. This can lead to high blood sugar levels, which can eventually lead to type 2 diabetes.
-
Facet 2: Physical Inactivity and Insulin Resistance
Physical inactivity is another major risk factor for type 2 diabetes because it can also lead to insulin resistance. When a person is physically inactive, their muscles do not use glucose as well as they should. This can lead to high blood sugar levels, which can eventually lead to type 2 diabetes.
-
Facet 3: Obesity and Physical Inactivity Together
The combination of obesity and physical inactivity is particularly harmful when it comes to the risk of type 2 diabetes. This is because obesity can make it more difficult for the body to use insulin, and physical inactivity can further worsen insulin resistance.
-
Facet 4: Prevention and Management
Fortunately, both obesity and physical inactivity are modifiable risk factors for type 2 diabetes. This means that people can reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes by maintaining a healthy weight and getting regular physical activity.
Lifestyle factors, such as obesity and physical inactivity, play a major role in the development of type 2 diabetes. By understanding the connection between these risk factors and type 2 diabetes, people can take steps to reduce their risk of developing this serious condition.
Age
As we age, our bodies undergo a number of changes that can increase our risk of developing type 2 diabetes. These changes include:
- Decreased insulin production: The pancreas produces insulin, a hormone that helps glucose get from the blood into the cells. As we age, our pancreas produces less insulin.
- Decreased insulin sensitivity: As we age, our cells become less sensitive to insulin. This means that the insulin that is produced is less effective at lowering blood sugar levels.
- Increased inflammation: Inflammation is a natural process that helps the body heal from injury and infection. However, chronic inflammation can damage the cells and tissues in the body, including the pancreas and the cells that are responsible for using insulin.
- Weight gain: Many people gain weight as they age. Weight gain can increase the risk of type 2 diabetes, as it can lead to insulin resistance.
These age-related changes can all contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes. It is important to be aware of these changes and to take steps to reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes, such as eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Race/ethnicity
Race and ethnicity are important factors in the development of type 2 diabetes. African Americans, Hispanic Americans, American Indians, and Asian Americans are all at increased risk for developing this condition. There are a number of factors that contribute to this increased risk, including genetics, lifestyle, and socioeconomic status.
-
Title of Facet 1: Genetics
Race and ethnicity can influence a person’s genetic predisposition to type 2 diabetes. For example, African Americans have a higher risk of developing certain genetic variations that are linked to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
-
Title of Facet 2: Lifestyle
Lifestyle factors, such as diet and exercise, also play a role in the development of type 2 diabetes. African Americans, Hispanic Americans, American Indians, and Asian Americans are more likely to live in poverty and to have less access to healthy food and safe places to exercise. These factors can contribute to the development of obesity and physical inactivity, which are both major risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
-
Title of Facet 3: Socioeconomic status
Socioeconomic status is another important factor that contributes to the increased risk of type 2 diabetes among African Americans, Hispanic Americans, American Indians, and Asian Americans. These populations are more likely to experience discrimination and racism, which can lead to chronic stress. Chronic stress can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
The increased risk of type 2 diabetes among African Americans, Hispanic Americans, American Indians, and Asian Americans is a serious public health concern. It is important to understand the factors that contribute to this increased risk so that we can develop effective strategies to prevent and treat type 2 diabetes in these populations.
Certain medical conditions
High blood pressure and high cholesterol are two medical conditions that can increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a condition in which the force of blood against the walls of your arteries is too high. High cholesterol is a condition in which you have too much cholesterol in your blood. Both high blood pressure and high cholesterol can damage the cells in your body, including the cells that are responsible for producing and using insulin.
-
Title of Facet 1: How high blood pressure can lead to type 2 diabetes
High blood pressure can damage the cells in your pancreas, which is the organ responsible for producing insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get from your blood into your cells. When your pancreas is damaged, it cannot produce enough insulin, which can lead to high blood sugar levels and eventually to type 2 diabetes.
-
Title of Facet 2: How high cholesterol can lead to type 2 diabetes
High cholesterol can damage the cells in your arteries, which can make it difficult for blood to flow to your pancreas. When your pancreas does not get enough blood, it cannot produce enough insulin, which can lead to high blood sugar levels and eventually to type 2 diabetes.
-
Title of Facet 3: The link between high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and type 2 diabetes
High blood pressure and high cholesterol often occur together, and they can both increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. This is because high blood pressure can damage the cells in your arteries, which can make it difficult for blood to flow to your pancreas. When your pancreas does not get enough blood, it cannot produce enough insulin, which can lead to high blood sugar levels and eventually to type 2 diabetes.
-
Title of Facet 4: Preventing and managing high blood pressure and high cholesterol
There are a number of things you can do to prevent and manage high blood pressure and high cholesterol, including eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight. If you have high blood pressure or high cholesterol, your doctor may prescribe medication to help you manage your condition.
High blood pressure and high cholesterol are two serious medical conditions that can increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. By understanding the link between these conditions and type 2 diabetes, you can take steps to reduce your risk of developing this serious condition.
Certain medications
Steroids and other medications can increase the risk of type 2 diabetes by causing insulin resistance. Insulin resistance is a condition in which the body’s cells do not respond to insulin as well as they should. This can lead to high blood sugar levels, which can eventually lead to type 2 diabetes.
There are a number of different types of medications that can cause insulin resistance, including:
- Steroids
- Antipsychotics
- Antidepressants
- Beta-blockers
- Diuretics
If you are taking any of these medications, it is important to be aware of the potential risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Your doctor may recommend monitoring your blood sugar levels more closely and making lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet and getting regular exercise, to reduce your risk.
Understanding the connection between certain medications and the increased risk of type 2 diabetes is important for healthcare professionals and individuals alike. By being aware of this potential side effect, individuals can make informed decisions about their medication use and take steps to reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Healthcare professionals can play a vital role in educating patients about the risks and benefits of different medications. They can also work with patients to develop strategies to manage their blood sugar levels and reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Environmental factors
Environmental factors, such as exposure to certain chemicals and pollutants, may increase the risk of type 2 diabetes. This is because these substances can damage the cells in the pancreas, which is the organ responsible for producing insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get from the blood into the cells. When the pancreas is damaged, it cannot produce enough insulin, which can lead to high blood sugar levels and eventually to type 2 diabetes.
-
Title of Facet 1: Air pollution
Air pollution is a major environmental risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Air pollution can damage the cells in the pancreas, which can lead to insulin resistance and eventually to type 2 diabetes. Air pollution can also increase inflammation in the body, which is another risk factor for type 2 diabetes.
-
Title of Facet 2: Water pollution
Water pollution is another environmental risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Water pollution can contaminate drinking water with chemicals and pollutants that can damage the pancreas and lead to insulin resistance. Water pollution can also increase the risk of other health problems, such as gastrointestinal problems and cancer.
-
Title of Facet 3: Soil pollution
Soil pollution is another environmental risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Soil pollution can contaminate food with chemicals and pollutants that can damage the pancreas and lead to insulin resistance. Soil pollution can also increase the risk of other health problems, such as gastrointestinal problems and cancer.
-
Title of Facet 4: Occupational exposure to chemicals
Occupational exposure to chemicals is another environmental risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Certain chemicals, such as pesticides and solvents, can damage the pancreas and lead to insulin resistance. Occupational exposure to chemicals can also increase the risk of other health problems, such as cancer and respiratory problems.
Exposure to certain chemicals and pollutants is a serious environmental risk factor for type 2 diabetes. It is important to be aware of these risks and to take steps to reduce your exposure to these substances. You can reduce your exposure to air pollution by avoiding areas with high levels of air pollution, such as busy roads and industrial areas. You can reduce your exposure to water pollution by drinking filtered water and avoiding swimming in polluted water. You can reduce your exposure to soil pollution by growing your own food in a clean environment and avoiding eating food that has been grown in polluted soil. You can reduce your exposure to occupational exposure to chemicals by wearing protective clothing and equipment and by following safe work practices.
FAQs
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way the body uses sugar (glucose). The exact cause of type 2 diabetes is unknown, but it is thought to be caused by a combination of factors, including genetics, lifestyle, and environmental factors.
Question 1: What are the risk factors for type 2 diabetes?
Answer: There are a number of risk factors for type 2 diabetes, including obesity, physical inactivity, family history of diabetes, age (over 45), race/ethnicity (African Americans, Hispanic Americans, American Indians, and Asian Americans are at increased risk), certain medical conditions (such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol), and certain medications (such as steroids).
Question 2: What are the symptoms of type 2 diabetes?
Answer: The symptoms of type 2 diabetes can include increased thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, increased hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow-healing sores.
Question 3: How is type 2 diabetes diagnosed?
Answer: Type 2 diabetes is diagnosed with a blood test that measures your blood sugar levels. A fasting blood sugar level of 126 mg/dL or higher on two separate tests indicates diabetes.
Question 4: How is type 2 diabetes treated?
Answer: Type 2 diabetes is treated with a combination of lifestyle changes and medication. Lifestyle changes include eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight. Medications for type 2 diabetes include insulin, metformin, and sulfonylureas.
Question 5: What are the complications of type 2 diabetes?
Answer: The complications of type 2 diabetes can include heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, blindness, and nerve damage.
Question 6: How can I prevent type 2 diabetes?
Answer: You can reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes by eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight. If you have a family history of diabetes, talk to your doctor about other steps you can take to reduce your risk.
Summary of key takeaways or final thought:
Type 2 diabetes is a serious condition, but it can be managed with lifestyle changes and medication. By understanding the risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and complications of type 2 diabetes, you can take steps to prevent or manage this condition.
Transition to the next article section:
For more information on type 2 diabetes, please visit the following resources:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
- American Diabetes Association
Tips for Preventing Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a serious condition that can lead to heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, blindness, and nerve damage. However, there are a number of things you can do to prevent or manage type 2 diabetes, including:
Tip 1: Eat a healthy diet.
A healthy diet for type 2 diabetes includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It also includes lean protein and low-fat dairy products. Limit your intake of saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium.Tip 2: Get regular exercise.
Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. Exercise helps to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.Tip 3: Maintain a healthy weight.
If you are overweight or obese, losing even a small amount of weight can help to reduce your risk of type 2 diabetes.Tip 4: Quit smoking.
Smoking damages the blood vessels and can lead to insulin resistance.Tip 5: Manage your blood pressure and cholesterol.
High blood pressure and high cholesterol are both risk factors for type 2 diabetes. Talk to your doctor about ways to lower your blood pressure and cholesterol.Tip 6: Get enough sleep.
When you don’t get enough sleep, your body produces more of the stress hormone cortisol, which can lead to insulin resistance.Tip 7: Reduce stress.
Chronic stress can lead to insulin resistance and increase your risk of type 2 diabetes. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, yoga, or meditation.Tip 8: Get regular checkups.
If you are at risk for type 2 diabetes, your doctor may recommend regular blood sugar screenings. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent or delay the complications of type 2 diabetes.
Type 2 Diabetes Cause
Type 2 diabetes is a complex condition with a multifaceted etiology. While the exact cause remains elusive, it is widely accepted that both genetic and environmental factors play significant roles in its development. Obesity, physical inactivity, and family history are well-established risk factors. Additionally, certain medical conditions, medications, and exposure to environmental toxins can contribute to the onset of type 2 diabetes.
Understanding the intricate interplay of factors that contribute to type 2 diabetes is crucial for devising effective preventive strategies. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, managing, and addressing modifiable risk factors, individuals can significantly reduce their likelihood of developing this prevalent condition. Ongoing research endeavors continue to shed light on the complex mechanisms underlying type 2 diabetes, offering hope for improved treatments and personalized approaches to prevention.
Youtube Video: